|
Welfare Trap
The welfare trap (aka the welfare cliff, unemployment trap, or poverty trap in British English) theory asserts that taxation and welfare (financial aid), welfare systems can jointly contribute to keep people on social insurance because the withdrawal of means-tested benefits that comes with entering low-paid work causes there to be no significant increase in total income. According to this theory, an individual sees that the opportunity cost of getting a better paying job is too great for too little a financial return, and this can create a perverse incentive to not pursue a better paying job. Different definitions The term used for this concept varies depending on country. In the United States, where government benefit payments are colloquially referred to as "welfare", the welfare trap often indicates that a person is completely dependent on benefits, with little or no hope of self-sufficiency. The welfare trap is also known as the ''unemployment trap'' or the ''poverty trap'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxation
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal person, legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to Pigouvian tax, regulate and reduce negative Externality, externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behavior aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation occurred in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct tax, direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as labor equivalent. All countries have a tax system in place to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some countries levy a flat tax, flat percentage rate of taxation on personal annual income, but most progressive tax, scale taxes are progressive based on brackets of yearly income amounts. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. List of countries by minimum wage, Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. Because minimum wages increase the cost of labor, companies often try to avoid minimum wage laws by using gig workers, by moving labor to locations with lower or nonexistent minimum wages, or by Automation, automating job functions. Minimum wage policies can vary significantly between countries or even within a country, with different regions, sectors, or age groups having their own minimum wage rates. These variations are often influenced by factors such as the cost of living, regional economic conditions, and industry-specific factors. The movement for minimum wages was first motivated as a way to stop the exploitation of workers in sweatshops, by employers who were thought to have unfair bargaining power o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Lee Crowley
Brian Lee Crowley (born 1955) is a Canadian political economist, author, and public policy commentator. Since 2010 he has been managing director of the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, a think tank in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. From 1995 until about 2009 he was president of the Atlantic Institute for Market Studies in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Books * ''The Self, the Individual and the Community''. Oxford University Press, 1987 * ''The Road to Equity: Impolitic Essays''. Stoddart, 1994 * ''Taking Ownership: Property Rights and Fishery Management on the Atlantic Coast'', editor. Atlantic Institute for Market Studies, 1996. * ''Fearful Symmetry: The Fall and Rise of Canada's Founding Values''. Key Porter Books, 2009. * ''The Canadian Century: Moving Out of America's Shadow'', with Jason Clemens and Neils Veldhuis. Key Porter Books Key Porter Books was a book publishing company based in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Founded in 1979 by Anna Porter, later well known as a writer, the company s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replacement Rates
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were to live from birth until the end of their reproductive life. As of 2023, the total fertility rate varied widely across the world, from 0.7 in South Korea, to 6.1 in Niger. Among sovereign countries that were not city states or had a very small number of inhabitants, in 2024 the following countries had a TFR of 1.0 or lower: South Korea, Taiwan, and Ukraine; the following countries had a TFR of 1.2 or lower: Chile, China, Japan, Malta, Poland, and Spain. Fertility tends to be inversely correlated with levels of economic development. Historically, developed countries have significantly lower fertility rates, generally correlated with greater wealth, education, urbanization, and other factors. Conversely, in least developed countries, fertil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
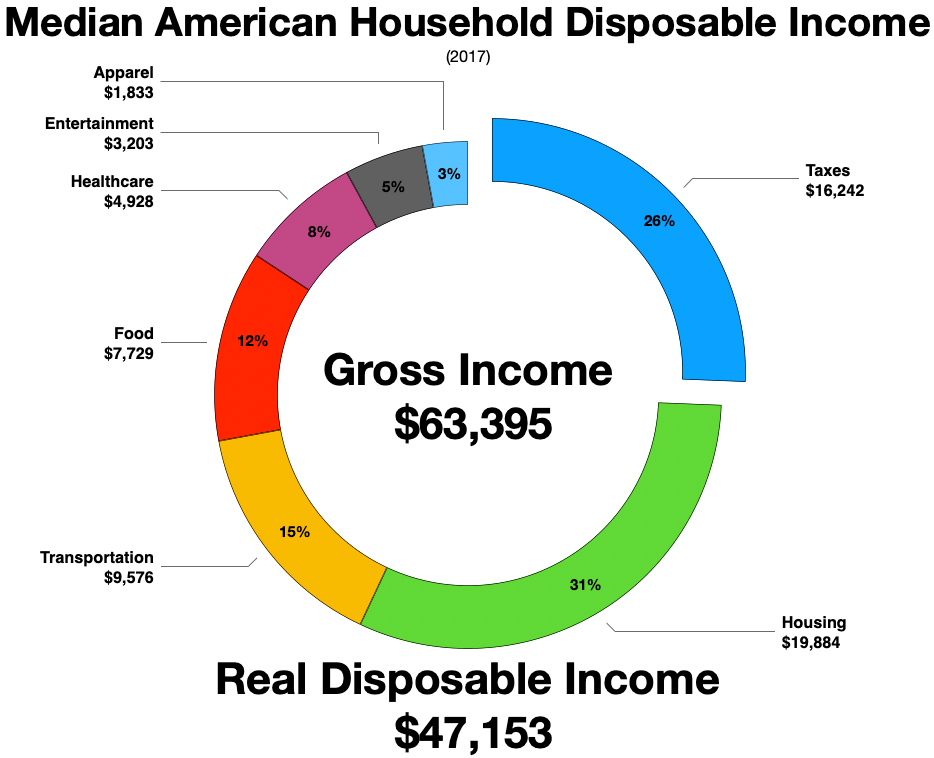
Disposable Income
Disposable income is total personal income minus current taxes on income. In national accounting, personal income minus personal current taxes equals disposable personal income or household disposable income. Subtracting personal outlays (which includes the major category of personal r privateconsumption expenditure) yields personal (or, private) savings, hence the income left after paying away all the taxes is referred to as disposable income. Restated, consumption expenditure plus savings equals disposable income after accounting for transfers such as payments to children in school or elderly parents' living and care arrangements. The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the fraction of a change in disposable income that is consumed. For example, if disposable income rises by $100, and $65 of that $100 is consumed, the MPC is 65%. Restated, the marginal propensity to save is 35%. For the purposes of calculating the amount of income subject to garnishments, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Income
For households and individuals, gross income is the sum of all wages, salaries, profits, interest payments, rents, and other forms of earnings, before any deductions or taxes. It is opposed to net income, defined as the gross income minus taxes and other deductions (e.g., mandatory pension contributions). For a business, gross income (also gross profit, sales profit, or credit sales) is the difference between revenue and the cost of making a product or providing a service, before deducting overheads, payroll, taxation, and interest payments. This is different from operating profit (earnings before interest and taxes). Gross margin is often used interchangeably with gross profit, but the terms are different. When speaking about a monetary amount, it is technically correct to use the term "gross profit", but when referring to a percentage or ratio, it is correct to use "gross margin". Relationship with other accounting terms The various deductions (and their corresponding me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Marginal Tax Rate
The effective marginal tax rate (EMTR) is the percentage of additional income that a taxpayer pays in taxes less any changes in the value of welfare benefits and tax credits received. The benefit reduction rate is the decrease in the value of welfare benefits provided for an additional unit of income. For example, if earning $40,001 results in someone receiving $0.40 less in welfare benefits than they would have received in they earned $40,000, than the benefit reduction rate at $40,000 is 40%. The effective marginal tax rate is the sum of the marginal tax rate and the benefit reduction rate. These definitions can be expressed mathematically as: marginalTaxRate = \frac, benefitReductionRate = \frac, effectiveMarginalTaxRate = \frac where is the total tax liability, is the total value of welfare benefits received, is total income, and ∆ refers to a numerical change. The benefit reduction rate is often zero or positive for means tested benefits as they phase out. However, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Tax Rates
In a tax system, the tax rate is the ratio (usually expressed as a percentage) at which a business or person is taxed. The tax rate that is applied to an individual's or corporation's income is determined by tax laws of the country and can be influenced by many factors such as income level, type of income, and so on. There are several methods used to present a tax rate: statutory, average, marginal, flat, and effective. These rates can also be presented using different definitions applied to a tax base: inclusive and exclusive. Statutory A statutory tax rate is the legally imposed rate. An income tax could have multiple statutory rates for different income levels, where a sales tax may have a flat statutory rate. The statutory tax rate is expressed as a percentage and will always be higher than the effective tax rate. Average An average tax rate is the ratio of the total amount of taxes paid to the total tax base (taxable income or spending), expressed as a percentage. Avera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Safety Net
A social safety net (SSN) consists of non-contributory assistance existing to improve lives of vulnerable families and individuals experiencing poverty and destitution. Examples of SSNs are previously-contributory social pensions, in-kind and food transfers, conditional and unconditional cash transfers, fee waivers, public works, and school feeding programs.World Bank. 2018"The State of Social Safety Nets" 2018. Washington, DC: World Bank. © World Bank. License: CC BY 3.0 IGO. Definitions There is no exact and unified definition of the concept of SSN. The World Bank has one of the widest definitions, but multiple definitions are used by different scholars, institutions, and organizations such as the International Labor Organization (ILO) and ESCAP. This lead some scholars to go so far as to hold that there is no point in using the term SSN as it is rarely used consistently and are instead advocating that the different components of SSN are used for analysis rather than the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Tax Rates Between 10th And 90th Percentiles For Low- And Moderate-Income Taxpayers
Marginal may refer to: * ''Marginal'' (album), the third album of the Belgian rock band Dead Man Ray, released in 2001 * ''Marginal'' (manga) * '' El Marginal'', Argentine TV series * Marginal seat or marginal constituency or marginal, in politics See also Economics * Marginalism *Marginal analysis *Marginal concepts *Marginal cost * Marginal demand *Marginal product *Marginal product of labor *Marginal propensity to consume *Marginal rate of substitution *Marginal use *Marginal utility *Marginal rate Other * Margin (other) * Marginalization * Marginal intra-industry trade, where the change in a country's exports are essentially of the same products as its change in imports * Marginal land, land that is of little value because of its unsuitability for growing crops and other uses * Marginal model, in hierarchical linear modeling * Marginal observables, in physics; see Renormalization group * Marginal person, in sociology; see Marginalization * Marginal plant, see Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both economists and ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally related. Utility function Consider a set of alternatives among which a person has a preference ordering. A utility fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |