|
Weigeltisauridae
Weigeltisauridae is a family of gliding neodiapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian, between 259.51 and 251.9 million years ago. Fossils of weigeltisaurids have been found in Madagascar, Germany, Great Britain, and Russia. They are characterized by long, hollow rod-shaped bones extending from the torso that probably supported wing-like membranes. Similar membranes are also found in several other extinct reptiles such as kuehneosaurids and '' Mecistotrachelos'', as well as living gliding lizards, although each group evolved these structures independently. Skeleton The skulls and jaws of weigeltisaurids are ornamented with horns and tubercles, including chameleon-like frills. The torso and limbs are slender. The skeletons of weigeltisaurds are lightened by large air spaces (skeletal pneumaticity) within the bones. The phalanges of the hands and feet are elongate contrasting strongly with those of most other primitive diapsids, but are similar to those of modern arbor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelurosauravus
''Coelurosauravus'' (meaning "hollow-tailed lizard grandfather") is an extinct genus of gliding reptile, known from the Late Permian of Madagascar. Like other members of the family Weigeltisauridae, members of this genus possessed long, rod-like ossifications projecting outwards from the body. These bony rods were not extensions of the ribs but were instead a feature unique to weigeltisaurids. It is believed that during life, these structures formed folding wings used for gliding flight, similar to living gliding '' Draco'' lizards. ''Coelurosauravus'' is solely known from the type species, ''C. elivensis'', which was named by Jean Piveteau in 1926 based on fossils from the Lower Sakamena Formation of Madagascar. The species '' Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' from Europe was formerly considered a species of ''Coelurosauravus'', but is now placed in its own genus. History of discovery The only known specimens of ''Coelurosauravus'' were collected in 1907-1908 by J.-M. Colcanap, a cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
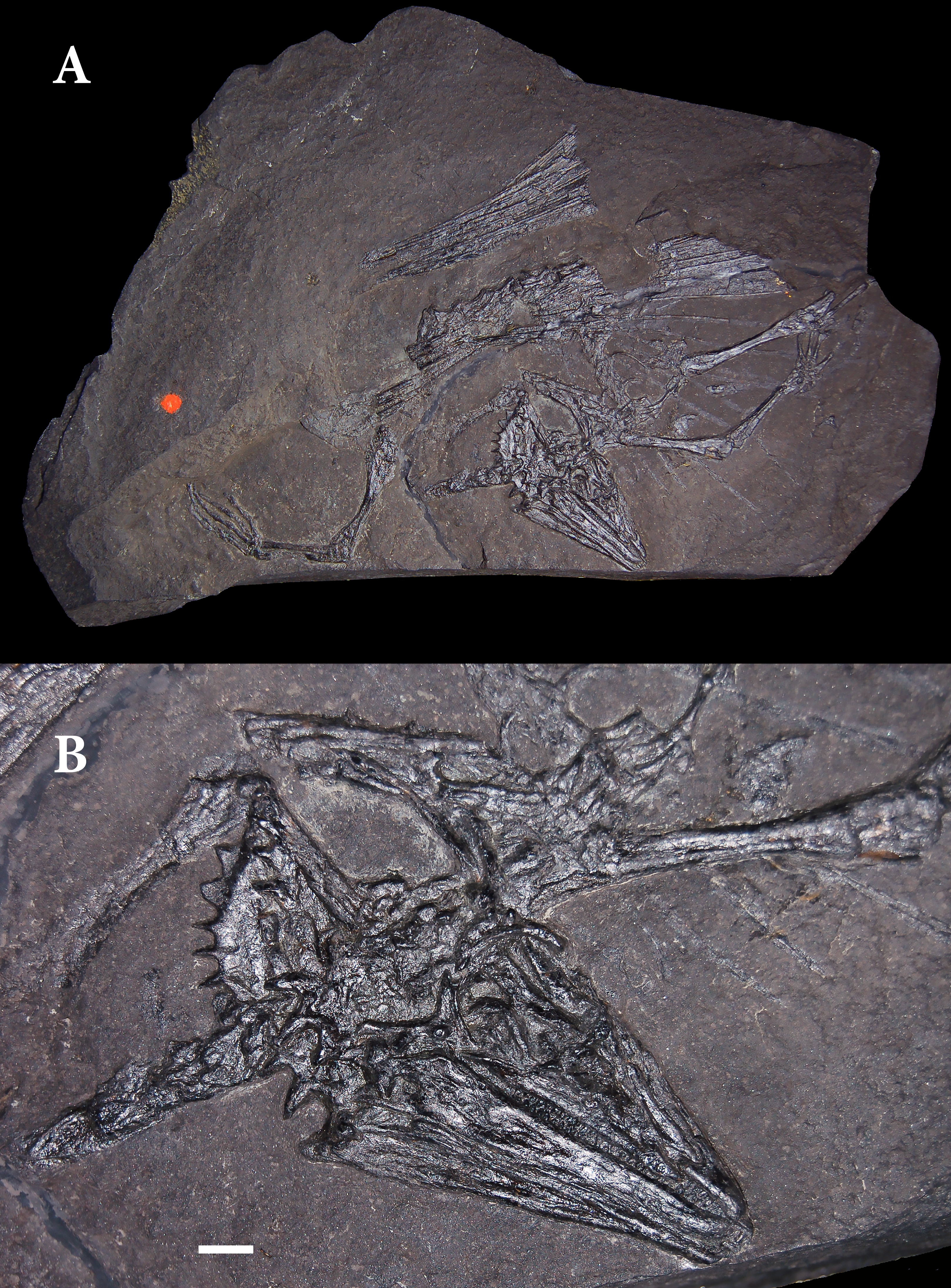
Weigeltisaurus Jaekeli Diagram
''Weigeltisaurus'' is an extinct genus of weigeltisaurid reptile from the Late Permian Kupferschiefer of Germany and Marl Slate of England. It has a single species, originally named as ''Palaechamaeleo jaekeli'' in 1930 and later assigned the name ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' in 1939, when it was revealed that ''Palaeochamaeleo'' was a preoccupied name. A 1987 review by Evans and Haubold later lumped ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' under ''Coelurosauravus'' as a second species of that genus. A 2015 reassessment of skull morphology study substantiated the validity of ''Weigeltisaurus'' and subsequent authors have used this genus. Like other Weigeltisaurids, they possessed long rod-like bones that radiated from the trunk that were likely used to support membranes used for gliding, similar to extant '' Draco'' lizards. History of discovery The first remains of ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' were described by Johannes Weigelt in 1930 from a specimen (SSWG 113/7) found in the Kupferschiefer n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodiapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the Araeoscelidia, araeoscelidians, appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are often placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. All modern reptiles and birds are placed within the neodiapsid subclade Sauria. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still scientific classification, classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weigeltisaurus
''Weigeltisaurus'' is an extinct genus of weigeltisaurid reptile from the Late Permian Kupferschiefer of Germany and Marl Slate of England. It has a single species, originally named as ''Palaechamaeleo jaekeli'' in 1930 and later assigned the name ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' in 1939, when it was revealed that ''Palaeochamaeleo'' was a preoccupied name. A 1987 review by Evans and Haubold later lumped ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' under ''Coelurosauravus'' as a second species of that genus. A 2015 reassessment of skull morphology study substantiated the validity of ''Weigeltisaurus'' and subsequent authors have used this genus. Like other Weigeltisaurids, they possessed long rod-like bones that radiated from the trunk that were likely used to support membranes used for gliding, similar to extant '' Draco'' lizards. History of discovery The first remains of ''Weigeltisaurus jaekeli'' were described by Johannes Weigelt in 1930 from a specimen (SSWG 113/7) found in the Kupferschiefer n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanosaur
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago. The various species of drepanosaurs were characterized by a bird-like skull, a barrell shaped body, and a horizontally narrow tail. A number of drepanosaurs had specialized grasping limbs and often prehensile tails similar to those of chameleons. Drepanosaurs are generally thought to have been arboreal (tree-dwelling), and probably insectivores. Some studies have alternately suggested fossorial (digging) and aquatic lifestyles for some members. Fossils of drepanosaurs have been found in North America (Arizona, New Mexico, New Jersey, Utah) and Europe (England and northern Italy). The name is taken from the family's namesake genus '' Drepanosaurus'', which means "sickle lizard," a reference to their strongly curved claws. Some studies have included Drepanosaurs with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicephala
Avicephala ("bird heads") is a potentially polyphyletic grouping of extinct diapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian and Triassic periods characterised by superficially bird-like skulls and arboreal lifestyles. As a clade, Avicephala is defined as including the gliding weigeltisaurids and the arboreal drepanosaurs to the exclusion of other major diapsid groups. This relationship is not recovered in the majority of phylogenetic analyses of early diapsids and so Avicephala is typically regarded as an artificial or unnatural grouping. However, the clade was recovered again in 2021 following a redescription of '' Weigeltisaurus'', raising the possibility that the clade may be valid after all, although subsequent analyses have not supported this result. Description Avicephalans were named in reference to their pointed, lightly constructed, superficially bird-like skulls. The resemblance is especially striking in some drepanosaurs such as '' Megalancosaurus'' which possess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rautiania
''Rautiania'' is an extinct genus of gliding neodiapsid reptiles belonging to the family Weigeltisauridae. Isolated fossil remains of ''Rautiania'' are known from the Late Permian of Russia. The genus is known from two species, ''Rautiania alexandri'' (the type species) and ''Rautiania minichi'', which differ in aspects of their maxilla and parietal bones. Certain ''Rautiania'' fossils have helped to reveal certain aspects of weigeltisaurid anatomy and lifestyle which had long alluded paleontologists, such as the component bones of the "crest" at the back of the head, and the large amount of adaptations towards life in the canopies of forests. Discovery ''Rautiania'' fossils were first discovered during a 2005 paleontological expedition into the Orenburg Oblast of Russia. Numerous isolated bones from reptiles of the family Weigeltisauridae were found at the Kul'chumovo-A site. Some of these bones (namely, maxillae and parietals) showed two different morphotypes. In 2006, Russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaurung Schneideri
''Glaurung'' is an extinct genus of weigeltisaurid reptile from the Upper Permian of Germany. The only known species is ''Glaurung schneideri''. Originally considered a specimen of ''Coelurosauravus'', a later study named it as a new genus after noting that it had several unique characteristics relative to other weigeltisaurids. These characteristics included a low skull, small eyes, smooth parietal and squamosal bones, and spiny jugal bones. Discovery ''Glaurung schneideri'' is known from a slab and counterslab discovered in 2002 by fossil collector Thomas Schneider. It was found in Late Permian Kupferschiefer sediments near Mansfeld, Germany. Although the original specimen remains in Schneider's private collection, there are several casts in European museums, such as MBR 3610 (stored at the Museum fur Naturkunde in Berlin) and PIN 5392/1 (stored at the Paleontological Institute in Moscow). The specimen consists of a flattened skull as well as material from the pectoral g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauria
Sauria is the clade of diapsids containing the most recent common ancestor of Archosauria (which includes crocodilians and birds) and Lepidosauria (which includes squamates and the tuatara), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely related to archosaurs than to lepidosaurs as part of Archelosauria, Sauria can be considered the crown group of diapsids, or reptiles in general. Depending on the systematics, Sauria includes all modern reptiles or most of them (including birds, a type of archosaur) as well as various extinct groups. Sauria lies within the larger total group Sauropsida, which also contains various stem-reptiles which are more closely related to reptiles than to mammals. Prior to its modern usage, "Sauria" was used as a name for the suborder occupied by lizards, which before 1800 were considered crocodilians. Systematics Sauria was historically used as a partial equivalent for Squamata (which contains lizards and sna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco (lizard)
''Draco'' is a genus of agamid lizards that are also known as flying lizards, flying dragons or gliding lizards. These lizards are capable of gliding flight via membranes that may be extended to create wings (patagia), formed by a support structure from an enlarged set of ribs. They are arboreal insectivores. While not capable of powered flight they often obtain lift in the course of their gliding flights. Glides as long as have been recorded, over which the animal loses only in height which makes for a glide ratio of 6:1. This is done by a lizard of only around in total length, tail included. Piper, Ross (2007). 'Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals'. Santa Barbara, California: Greenwood Press. They are found across Southeast Asia and Southern India and are fairly common in forests, areca gardens, teak plantations and shrub jungle. History of discovery Carl Linnaeus described the genus in 1758, with the type species being '' Draco volans.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |