|
Weddell Polynya
The Weddell Polynya, or Weddell Sea Polynya, is a polynya or irregular area of open water surrounded by sea ice in the Weddell Sea of the Southern Ocean off Antarctica and near the Maud Rise. The formation of the polynya exposes relatively warmer ocean waters (at surface freezing temperatures of -1.9°C) to a cold atmosphere, leading to a large exchange of heat which drives deep convection in the ocean, often reaching depths of a 1,000 to 2,000 meters! Occurrences The size of New Zealand, it re-occurred each winter between 1974 and 1976. These were the first three austral winters observed by the Nimbus-5 Electrically Scanning Microwave Radiometer (ESMR). From 1976 to 2015 this polynya was rarely observed. The polynya reoccurred in 2016, and has since appeared in 2017. The 2010s occurrence has been smaller than the 1970s occurrence, being about the size of Maine in 2017, or roughly . Since the 1970s, the polar Southern Ocean south of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current has freshened ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynya
A polynya () is an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. It is now used as a geographical term for an area of unfrozen seawater within otherwise contiguous pack ice or fast ice. It is a loanword from the Russian полынья (), which refers to a natural ice hole and was adopted in the 19th century by polar explorers to describe navigable portions of the sea. There are two main types of polynyas: coastal polynyas, which can be found year-round near the Antarctic and Arctic coasts and are mainly created by strong winds pushing the ice away from the coast, and mid-sea or open-ocean polynyas, which may be found more sporadically in the middle of ice pack in certain locations, especially around Antarctica. These locations are generally preconditioned by certain oceanic dynamics. One of the most famous mid-sea polynyas is the Weddell Polynya, also known as the Maud Rise Polynya, which occurs in the Lazarev Sea over the Maud Rise seamount. It was first spotted in September 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Layer
The Ekman layer is the layer in a fluid where there is a force balance between pressure gradient force, Coriolis force and turbulent drag. It was first described by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Ekman layers occur both in the atmosphere and in the ocean. There are two types of Ekman layers. The first type occurs at the surface of the ocean and is forced by surface winds, which act as a drag on the surface of the ocean. The second type occurs at the bottom of the atmosphere and ocean, where frictional forces are associated with flow over rough surfaces. History Ekman developed the theory of the Ekman layer after Fridtjof Nansen observed that ice drifts at an angle of 20°–40° to the right of the prevailing wind direction while on an Arctic expedition aboard the Fram. Nansen asked his colleague, Vilhelm Bjerknes to set one of his students upon study of the problem. Bjerknes tapped Ekman, who presented his results in 1902 as his doctoral thesis. Mathematical formulation The mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagn Walfrid Ekman
Vagn Walfrid Ekman (3 May 1874 – 9 March 1954) was a Swedish oceanographer. Born in Stockholm to Fredrik Laurentz Ekman, himself an oceanographer, he became committed to oceanography while studying physics at the University of Uppsala and, in particular, on hearing Vilhelm Bjerknes lecture on fluid dynamics. During the expedition of the ''Fram'', Fridtjof Nansen had observed that icebergs tend to drift not in the direction of the prevailing wind but at an angle of 20°-40° to the right. Bjerknes invited Ekman, still a student, to investigate the problem. Later, in 1905, Ekman published his theory of the Ekman spiral which explains the phenomenon in terms of the balance between frictional effects in the ocean and the Coriolis force, which arises from moving objects in a rotating environment, like planetary rotation. On completing his doctorate in Uppsala in 1902, Ekman joined the International Laboratory for Oceanographic Research, Oslo where he worked for seven year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nutrient-rich upwelled water stimulates the growth and reproduction of primary producers such as phytoplankton. The biomass of phytoplankton and the presence of cool water in those regions allow upwelling zones to be identified by cool sea surface temperatures (SST) and high concentrations of chlorophyll-a. The increased availability of nutrients in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary production and thus fishery production. Approximately 25% of the total global marine fish catches come from five upwellings, which occupy only 5% of the total ocean area.Jennings, S., Kaiser, M.J., Reynolds, J.D. (2001) "Marine Fisheries Ecology." Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd. Upwellings that are driven by coastal currents or diverging ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nansen's Fram Expedition
Nansen's ''Fram'' expedition of 1893–1896 was an attempt by the Norwegian explorer Fridtjof Nansen to reach the geographical North Pole by harnessing the natural east–west current of the Arctic Ocean. In the face of much discouragement from other polar explorers, Nansen took his ship '' Fram'' to the New Siberian Islands in the eastern Arctic Ocean, froze her into the pack ice, and waited for the drift to carry her towards the pole. Impatient with the slow speed and erratic character of the drift, after 18 months Nansen and a chosen companion, Hjalmar Johansen, left the ship with a team of Samoyed dogs and sledges and made for the pole. They did not reach it, but they achieved a record Farthest North latitude of 86°13.6′N before a long retreat over ice and water to reach safety in Franz Josef Land. Meanwhile, ''Fram'' continued to drift westward, finally emerging in the North Atlantic Ocean. The idea for the expedition had arisen after items from the American vessel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen (; 10 October 186113 May 1930) was a Norwegian polymath and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. He gained prominence at various points in his life as an explorer, scientist, diplomat, and humanitarian. He led the team that made the first crossing of the Greenland interior in 1888, traversing the island on cross-country skis. He won international fame after reaching a record northern latitude of 86°14′ during his ''Fram'' expedition of 1893–1896. Although he retired from exploration after his return to Norway, his techniques of polar travel and his innovations in equipment and clothing influenced a generation of subsequent Arctic and Antarctic expeditions. Nansen studied zoology at the Royal Frederick University in Christiania and later worked as a curator at the University Museum of Bergen where his research on the central nervous system of lower marine creatures earned him a doctorate and helped establish neuron doctrine. Later, neuroscientist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
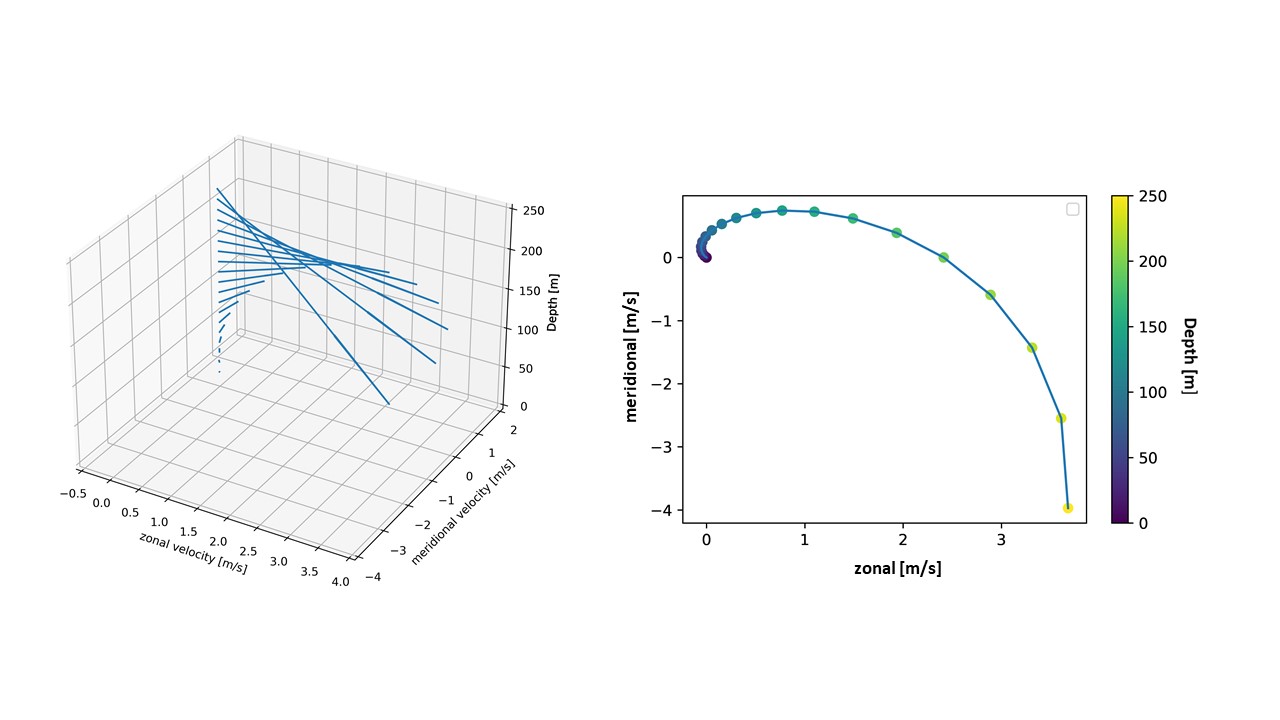
Ekman Velocity
In oceanography, Ekman velocity – also referred as a kind of the residual ageostrophic velocity as it deviates from geostrophy – is part of the total horizontal velocity (''u'') in the upper layer of water of the open ocean. This velocity, caused by winds blowing over the surface of the ocean, is such that the Coriolis force on this layer is balanced by the force of the wind. Typically, it takes about two days for the Ekman velocity to develop before it is directed at right angles to the wind. The Ekman velocity is named after the Swedish oceanographer Vagn Walfrid Ekman (1874–1954). Theory Through vertical eddy viscosity, winds act directly and frictionally on the Ekman layer, which typically is the upper 50–100m in the ocean. The frictional surface flow (''u'') is at an angle to the right of the wind in the northern hemisphere, to the left in the southern hemisphere (45 degrees if viscosity is uniform in the vertical ''z''-direction). This surface flow then modifies th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Transport
Ekman transport is part of Ekman motion theory, first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Winds are the main source of energy for ocean circulation, and Ekman Transport is a component of wind-driven ocean current. Ekman transport occurs when ocean surface waters are influenced by the friction force acting on them via the wind. As the wind blows it casts a friction force on the ocean surface that drags the upper 10-100m of the water column with it. However, due to the influence of the Coriolis effect, the ocean water moves at a 90° angle from the direction of the surface wind. The direction of transport is dependent on the hemisphere: in the northern hemisphere, transport occurs at 90° clockwise from wind direction, while in the southern hemisphere it occurs at 90° anticlockwise.Colling, pp 42-44 This phenomenon was first noted by Fridtjof Nansen, who recorded that ice transport appeared to occur at an angle to the wind direction during his Arctic expedition during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Spiral
The oceanic, wind driven Ekman spiral is the result of a force balance created by a shear stress force, Coriolis force and the water drag. This force balance gives a resulting current of the water different from the winds. In the ocean, there are two places where the Ekman spiral can be observed. At the surface of the ocean, the shear stress force corresponds with the wind stress force. At the bottom of the ocean, the shear stress force is created by friction with the ocean floor. This phenomenon was first observed at the surface by the Norwegian oceanographer Fridtjof Nansen during his Fram expedition. He noticed that icebergs did not drift in the same direction as the wind. His student, the Swedish oceanographer Vagn Walfrid Ekman, was the first person to physically explain this process. Bottom Ekman Spiral In order to derive the properties of an Ekman spiral a look is taken at a uniform, horizontal geostrophic interior flow in a homogeneous fluid. This flow will by denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Number
The Ekman number (Ek) is a dimensionless number used in fluid dynamics to describe the ratio of viscous forces to Coriolis forces. It is frequently used in describing geophysical phenomena in the oceans and atmosphere in order to characterise the ratio of viscous forces to the Coriolis forces arising from planetary rotation. It is named after the Swedish oceanographer Vagn Walfrid Ekman. When the Ekman number is small, disturbances are able to propagate before decaying owing to low frictional effects. The Ekman number also describes the order of magnitude for the thickness of an Ekman layer, a boundary layer in which viscous diffusion is balanced by Coriolis effects, rather than the usual convective inertia. Definitions It is defined as: :\mathrm=\frac - where ''D'' is a characteristic (usually vertical) length scale of a phenomenon; ''ν'', the kinematic eddy viscosity; Ω, the angular velocity of planetary rotation; and φ, the latitude. The term 2 Ω sin φ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coriolis Force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the left of the motion of the object. In one with anticlockwise (or counterclockwise) rotation, the force acts to the right. Deflection of an object due to the Coriolis force is called the Coriolis effect. Though recognized previously by others, the mathematical expression for the Coriolis force appeared in an 1835 paper by French scientist Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis, in connection with the theory of water wheels. Early in the 20th century, the term ''Coriolis force'' began to be used in connection with meteorology. Newton's laws of motion describe the motion of an object in an inertial (non-accelerating) frame of reference. When Newton's laws are transformed to a rotating frame of reference, the Coriolis and centrifugal accelerations app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weddell Sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Martha Coast, Queen Maud Land. To the east of Cape Norvegia is the King Haakon VII Sea. Much of the southern part of the sea is covered by a permanent, massive ice shelf field, the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf. The sea is contained within the two overlapping Antarctic territorial claims of Argentine Antarctica, the British Antarctic Territory, and also resides partially within the Antarctic Chilean Territory. At its widest the sea is around across, and its area is around . Various ice shelves, including the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf, fringe the Weddell sea. Some of the ice shelves on the east side of the Antarctic Peninsula, which formerly covered roughly of the Weddell Sea, had completely disappeared by 2002. The Weddell Sea has been d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |