|
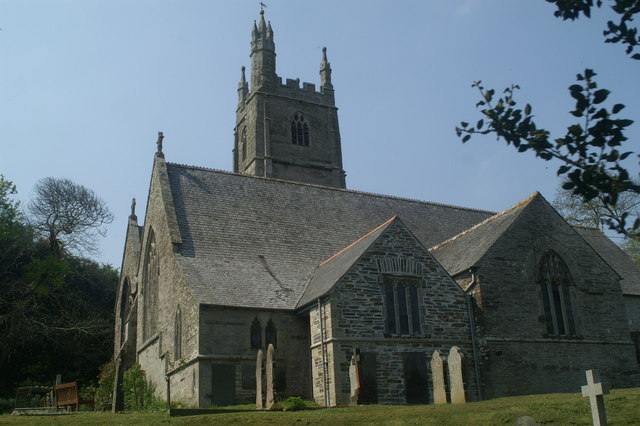
Weare Giffard
Weare Giffard is a small village, civil parish and former manor in the Torridge district, in north Devon. The church and manor house are situated 2 1/2 miles NW of Great Torrington in Devon. Most of the houses within the parish are situated some 1/2-mile east of the church. The church is situated on a hillside to the north and slightly above the wide and flat valley floor of the River Torridge. The Church of the Holy Trinity and the adjacent Weare Giffard Hall are designated members of the Grade I listed buildings in Devon. History The historian of Devon Tristram Risdon (d.1640) supposed the name Weare to be derived from a fish weir which was historically situated in the river to catch fish. The construction of a fish-weir generally required a licence from the feudal overlord, as naturally these affected the catches of other inhabitants further along the river. Many disputes are recorded in the medieval records over disputes concerning fish-weirs. Descent of the manor Giff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weare Giffard - Geograph
*
{{disambiguation ...
Weare may refer to: *Weare (surname) * Weare, New Hampshire, USA * Weare, Somerset, England * Weare Giffard, Devon, England * Weare Township, Michigan, USA See also * Wearing (other) Wearing may refer to: * Wearing (surname), a surname * Wearing clothes, a feature of all modern human societies * Wearing ship, a sailing maneuver See also * Wear (other) Wear is the erosion of material from a solid surface by the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
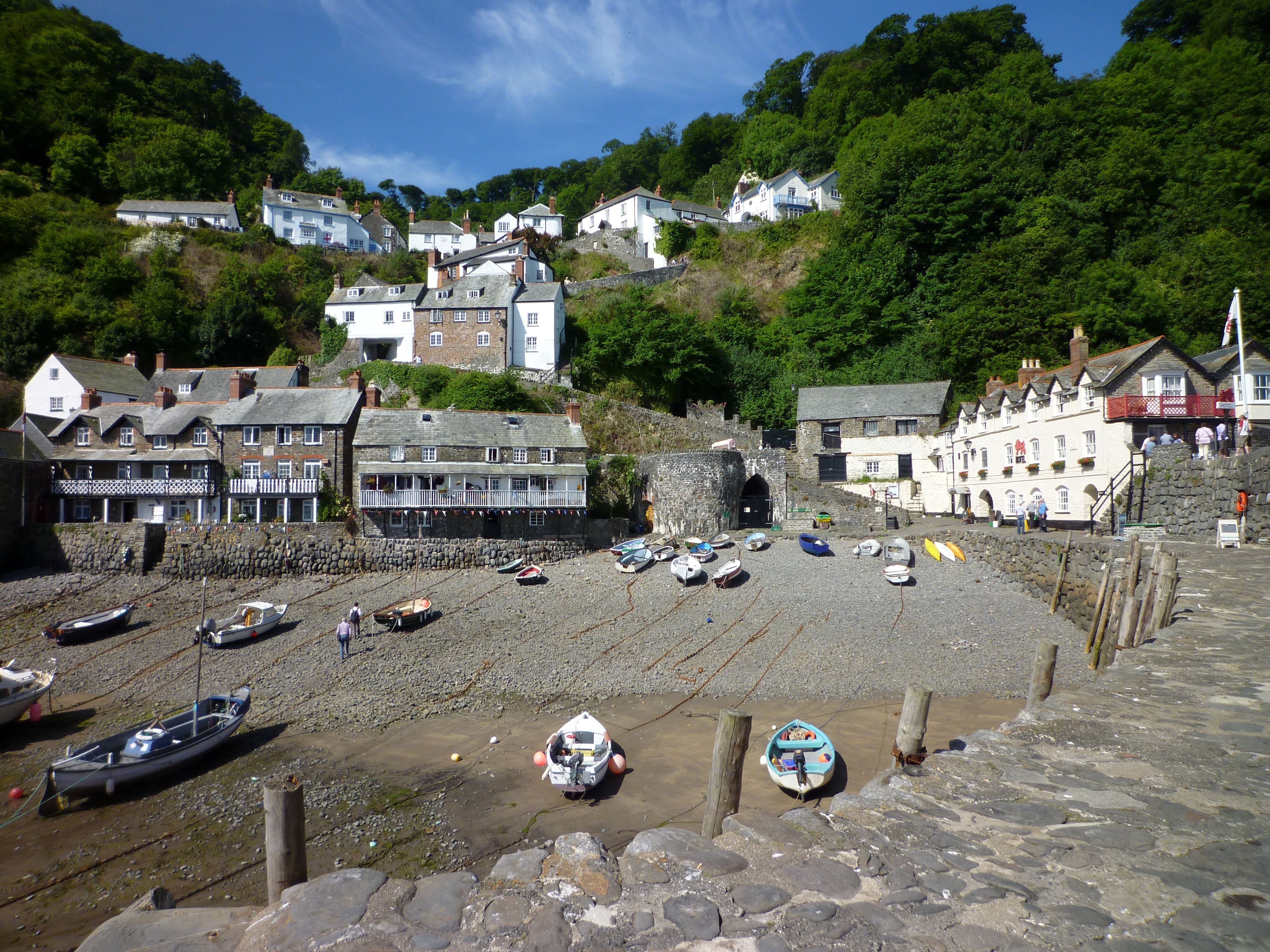
Clovelly
Clovelly () is a privately-owned harbour village in the Torridge district of Devon, England. The settlement and surrounding land belongs to John Rous who inherited it from his mother in 1983. He belongs to the Hamlyn family who have managed the village since 1738. The village, which is built into the wooded sea cliffs of the north Devon shore, has a steep pedestrianised cobbled main street with traditional architecture. Due to the gradients, donkeys (now mostly replaced with sledges) have been used to move goods and cargo from Clovelly Bay. Visitors to the village entering via the visitor centre are required to pay an entrance fee which covers parking, entrance to two museums, Clovelly Court gardens, and an audiovisual history guide. The village is a tourist destination and is host to an annual Lobster and Crab festival. At the 2011 census, the parish population was 443, a decrease of 50 on the 2001 census. The island of Lundy is part of the electoral ward of Clovelly B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newquay
Newquay ( ; kw, Tewynblustri) is a town on the north coast in Cornwall, in the south west of England. It is a civil parish, seaside resort, regional centre for aerospace industries, spaceport and a fishing port on the North Atlantic coast of Cornwall, approximately north of Truro and west of Bodmin. The town is bounded to the south by the River Gannel and its associated salt marsh, and to the north-east by the Porth Valley. The western edge of the town meets the Atlantic at Fistral Bay. The town has been expanding inland (south) since the former fishing village of New Quay began to grow in the second half of the nineteenth century. In 2001, the census recorded a permanent population of 19,562, increasing to 20,342 at the 2011 census. Recent estimates suggest that the total population for the wider Newquay area (Newquay and St Columb Community Network Area ) was 27,682 in 2017, projected to rise to 33,463 by 2025. History Prehistoric period There are some pre-histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Columb Major
St Columb Major is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Often referred to locally as ''St Columb'', it is approximately southwest of Wadebridge and east of Newquay Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 200 ''Newquay & Bodmin'' The designation ''Major'' distinguishes it from the nearby settlement and parish of St Columb Minor on the coast. An electoral ward simply named ''St Columb'' exists with a population at the 2011 census of 5,050. The town is named after the 6th-century AD Saint Columba of Cornwall, also known as Columb. Twice a year the town plays host to "hurling", a medieval game once common throughout Cornwall but now only played in St Columb and St Ives.It is also played irregularly and less frequently at Bodmin, but nowhere else. It is played on Shrove Tuesday and again on the Saturday eleven days later. The game involves two teams of unlimited numbers (the 'townsmen' and the 'countrymen' of St Columb parish) who endeavour to carry a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mawgan
St Mawgan or St Mawgan in Pydar ( kw, Lanherne) is a village and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The population of this parish at the 2011 census was 1,307. The village is situated four miles northeast of Newquay, and the parish also includes the hamlet of Mawgan Porth.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 200 ''Newquay & Bodmin'' The surviving manor house known as Lanherne House is an early 16th-century grade I listed building. The nearby Royal Air Force station, RAF St Mawgan, takes its name from the village and is next to Newquay Cornwall Airport. The River Menalhyl runs through St Mawgan village and the valley is known as ''The Vale of Lanherne''. It was the subject of a poem by poet Henry Sewell Stokes. History There is evidence of Bronze Age and Iron Age settlements, though the village history proper is considered to start from the arrival of the Welsh missionary St Mawgan (or Meugan) and his followers in the 6th century when they set up a monaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Pole (antiquary)
Sir William Pole (1561–1635) of Colcombe House in the parish of Colyton, and formerly of Shute House in the parish of Shute (adjoining Colcombe), both in Devon, was an English country gentleman and landowner, a colonial investor, Member of Parliament and, most notably, a historian and antiquarian of the County of Devon. Career Pole was baptised on 27 August 1561 at Colyton, Devon, the son of William Pole, Esquire (c.1514 – 1587), MP, by his wife Katherine Popham (died 1588), daughter of Alexander Popham of Huntworth, Somerset by his wife Joan Stradling. Katherine was the sister of John Popham (1531–1607), Lord Chief Justice. In 1560 his father had purchased Shute House, near Colyton and Axminster, Devon. He entered the Inner Temple in 1578, was placed on the Commission of the Peace for Devonshire, served as Sheriff of Devon in 1602–3, and was MP in 1586 for Bossiney, Cornwall. He was knighted by King James I at Whitehall Palace on 15 February 1606. He paid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filleigh
Filleigh is a small village, civil parish and former manor in North Devon, on the southern edge of Exmoor, west of South Molton. The village centre's street was, until the 1980s opening of the North Devon Link Road, the main highway between the North Devon administrative centre of Barnstaple and South Molton, leading westwards to Taunton. Much of the village's land is contained within grade I listed park and garden, Castle Hill, which straddles both sides of the Link Road providing a glimpse of some of it. History Manor De Filleigh The manor was held in the 14th century by a family which took its name from the manor, de Filleigh. The family also held lands within the neighbouring settlements of East Buckland, Bray and Charles. Denzell On default of male heirs, the manor passed by marriage to the Denzell (or Densyll etc.) family. This family originated from Denzell manor in St Mawgan parish, near St Columb Major, near Newquay, Cornwall. The senior line became extinct in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
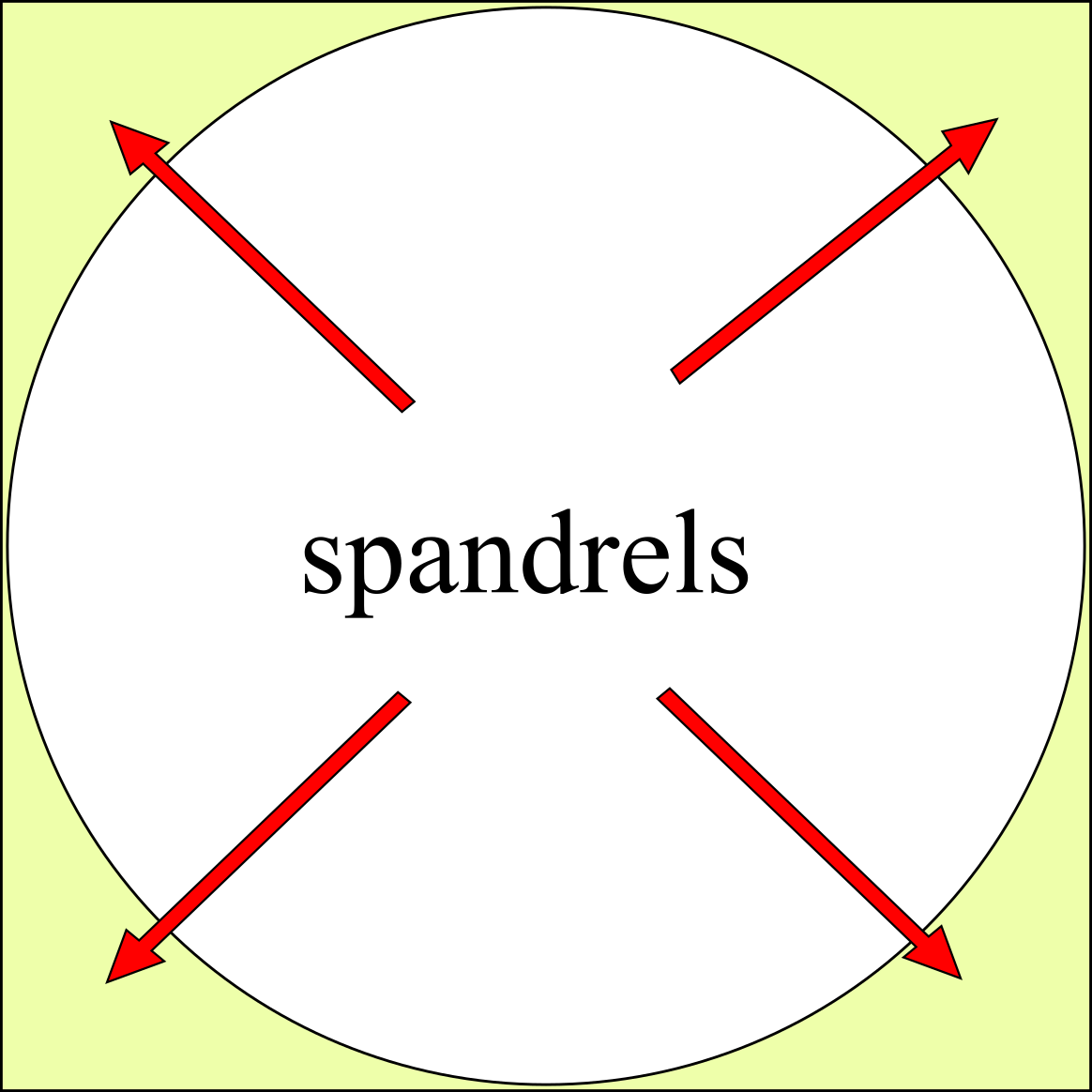
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crozier
A crosier or crozier (also known as a paterissa, pastoral staff, or bishop's staff) is a stylized staff that is a symbol of the governing office of a bishop or abbot and is carried by high-ranking prelates of Roman Catholic, Eastern Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and some Anglican, Lutheran, United Methodist and Pentecostal churches. In Western Christianity the usual form has been a shepherd's crook, curved at the top to enable animals to be hooked. In Eastern Christianity, it is found in two common forms: tau-shaped, with curved arms, surmounted by a small cross; or a pair of sculptured serpents or dragons curled back to face each other, with a small cross between them. Other typical insignia of prelates are the mitre, the pectoral cross, and the episcopal ring. History The origin of the crozier as a staff of authority is uncertain, but there were many secular and religious precedents in the ancient world. One example is the lituus, the traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a saltire in heraldic terminology. The cross has been widely recognized as a symbol of Christianity from an early period.''Christianity: an introduction'' by Alister E. McGrath 2006 pages 321-323 However, the use of the cross as a religious symbol predates Christianity; in the ancient times it was a pagan religious symbol throughout Europe and western Asia. The effigy of a man hanging on a cross was set up in the fields to protect the crops. It often appeared in conjunction with the female-genital circle or oval, to signify the sacred marriage, as in Egyptian amul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexter And Sinister
''Dexter'' and ''sinister'' are terms used in heraldry to refer to specific locations in an escutcheon bearing a coat of arms, and to the other elements of an achievement. ''Dexter'' (Latin for 'right') indicates the right-hand side of the shield, as regarded by the bearer, i.e. the bearer's proper right, and to the left as seen by the viewer. ''Sinister'' (Latin for 'left') indicates the left-hand side as regarded by the bearer – the bearer's proper left, and to the right as seen by the viewer. In vexillology, the equivalent terms are ''hoist'' and '' fly''. Significance The dexter side is considered the side of greater honour, for example when impaling two arms. Thus, by tradition, a husband's arms occupy the dexter half of his shield, his wife's paternal arms the sinister half. The shield of a bishop shows the arms of his see in the dexter half, his personal arms in the sinister half. King Richard II adopted arms showing the attributed arms of Edward the Confessor in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartering (heraldry)
Quartering is a method of joining several different coats of arms together in one shield by dividing the shield into equal parts and placing different coats of arms in each division. Typically, a quartering consists of a division into four equal parts, two above and two below (''party per cross''). Occasionally the division is instead along both diagonals ( party per saltire'') again creating four parts but now at top, bottom, left, and right. An example of ''party per cross'' is the Sovereign Arms of the United Kingdom, as used outside Scotland, which consists of four quarters, displaying the Arms of England, Scotland and Ireland, with the coat for England repeated at the end. (In the royal arms as used in Scotland, the Scottish coat appears in the first and fourth quarters and the English one second.). An example of ''party per saltire'' is the arms of the medieval Kingdom of Sicily which also consists of four sections, with top and bottom displaying the coat of the Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |