|
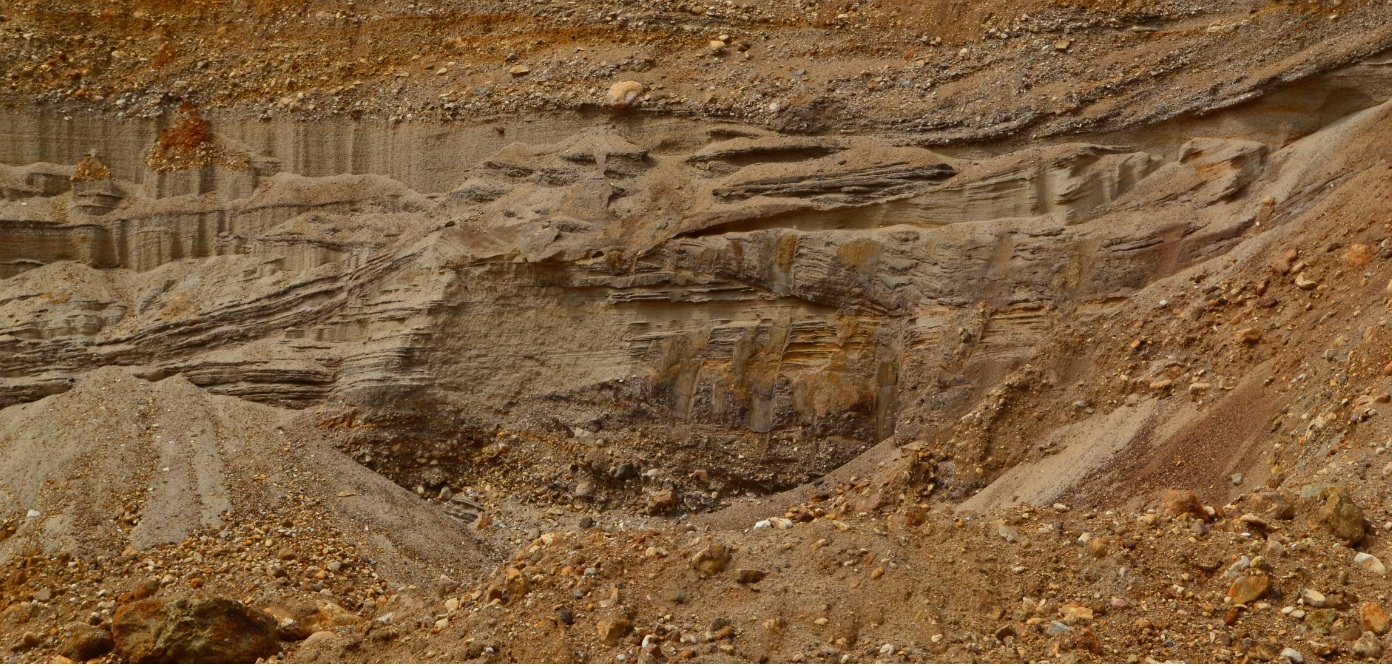
Weald Clay
Weald Clay or the Weald Clay Formation is a Lower Cretaceous sedimentary rock unit underlying areas of South East England, between the North and South Downs, in an area called the Weald Basin. It is the uppermost unit of the Wealden Group of rocks within the Weald Basin, and the upper portion of the unit is equivalent in age to the exposed portion of the Wessex Formation on the Isle of Wight. It predominantly consists of thinly bedded mudstone. The un-weathered form is blue/grey, and the yellow/orange is the weathered form, it is used in brickmaking. The formation was deposited in lagoonal, lacustrine and alluvial conditions that varied from freshwater to brackish. The climate at the time of deposition is thought to have been semi-arid, and prone to fire. The clay alternates with other subordinate lithologies, notably hard red-weathering beds of ironstone, limestone ( Sussex Marble) and sandstones, notably including the calcareous sandstone unit referred to as the Horsha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock House Brickworks
Clock House Brickworks is a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest south of Capel in Surrey. It is a Geological Conservation Review site. The pit exposes temperate and subtropical palaeoenvironments of the Lower Cretaceous Lower may refer to: * ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker * Lower (surname) * Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) * Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... Weald Clay Group. The site is particularly important for its several thousand fossil insects, including the first described social insect, a termite. There are also aquatic plants, fish and reptiles. The site is private land with no public access. References {{SSSIs Surrey Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Surrey Geological Conservation Review sites Geology of South-East England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
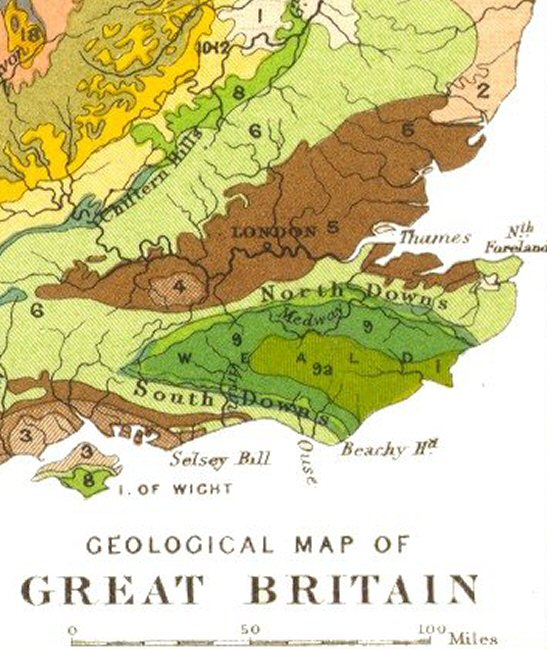
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills AONB, Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs AONB, Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsham Stone
Horsham Stone is a type of calcareous, flaggy sandstone containing millions of minute sand grains and occurring naturally in the Weald Clay of south-east England. It is also high in mica and quartz. The rock extends in an arc-like formation for several kilometres around the town of Horsham from which it takes its name, and lies just below the Weald Clay surface in bands thick. Horsham Stone is significant for its ripple-marked appearance, formed by the action of the sea similar to the ripples on the sandbanks and beaches of Sussex. Formation Sussex Stone and its limestone equivalent Sussex Marble were formed around 130 million years ago in the Lower Cretaceous period when Britain was quite different from the shape it is today. It is estimated that the latitude for Britain was approximately 30th parallel north, 30 degrees north of the equator. The fossil evidence in Horsham Stone and Sussex Marble indicate a diversity of life living on a broad, flat subtropical landscape. Towards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sussex Marble
Sussex Marble is a fossiliferous freshwater limestone material which is prevalent in the Weald Clay of parts of Kent, East Sussex and West Sussex in southeast England. It is also called Petworth Marble, Bethersden Marble or Laughton Stone in relation to villages where it was quarried, and another alternative name is winklestone. It is referred to as "marble" as it polishes very well, although it is not a true marble, geologically speaking, as it has not been subject to metamorphism. The matrix is made up of the shells of freshwater gastropods and '' viviparus'' winkles, similar to but larger than those making Purbeck Marble. The pale calcified remains of the shells are in a matrix of darker material. West Sussex has a good concentration of thin layers of Sussex Marble; beds typically measure no more than thick. There are often two beds—the lower formed of smaller-shelled gastropods than the upper—with a layer of calcareous clay between them. Historical use The Weald of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironstone
Ironstone is a sedimentary rock, either deposited directly as a ferruginous sediment or created by chemical replacement, that contains a substantial proportion of an iron ore compound from which iron (Fe) can be smelted commercially. Not to be confused with native or telluric iron, which is very rare and found in metallic form, the term ''ironstone'' is customarily restricted to hard, coarsely banded, non-banded, and non-cherty sedimentary rocks of Phanerozoic, post-Precambrian age. The Precambrian deposits, which have a different origin, are generally known as banded iron formations. The iron minerals comprising ironstones can consist either of oxides, i.e. limonite, hematite, and magnetite; carbonates, i.e. siderite; silicates, i.e. chamosite; or some combination of these minerals.U.S. Bureau of Mines Staff (1996) ''Dictionary of Mining, Mineral, & Related Terms.'' Report SP-96-1, U.S. Department of Interior, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Washington, D.C.Neuendorf, K. K. E., J. P. Mehl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSh'' and ''BSk'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as they usually cannot support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish Water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuary, estuaries, or it may occur in brackish Fossil water, fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '':wikt:brak#Dutch, brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the Osmotic power, salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it can be damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farming, shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Plain
An alluvial plain is a plain (an essentially flat landform) created by the deposition of sediment over a long period by one or more rivers coming from highland regions, from which alluvial soil forms. A ''floodplain'' is part of the process, being the smaller area over which the rivers flood at a particular time. In contrast, the alluvial plain is the larger area representing the region over which the floodplains have shifted over geological time. As the highlands erode due to weathering and water flow, the sediment from the hills is transported to the lower plain. Various creeks will carry the water further to a river, lake, bay, or ocean. As the sediments are deposited during flood conditions in the floodplain of a creek, the elevation of the floodplain will be raised. As this reduces the channel floodwater capacity, the creek will, over time, seek new, lower paths, forming a meander (a curved path). The leftover higher locations, typically natural levees at the margins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacustrine Deposits
Lacustrine deposits are sedimentary rock formations which formed in the bottom of ancient lakes. A common characteristic of lacustrine deposits is that a river or stream channel has carried sediment into the basin. Lacustrine deposits form in all lake types including rift graben lakes, oxbow lakes, glacial lakes, and crater lakes. Lacustrine environments, like seas, are large bodies of water. They share similar sedimentary deposits which are mainly composed of low-energy particle sizes. Lacustrine deposits are typically very well sorted with highly laminated beds of silts, clays, and occasionally carbonates. In regards to geologic time, lakes are temporary and once they no longer receive water, they dry up and leave a formation. Lake types Lacustrine deposits can form in every variety of basins found in nature. How each basin originates is where the distinction between lacustrine deposit types stem. Rift graben lakes are formed from crustal stretching also known as rifting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') and ''atoll lagoons''. They have also been identified as occurring on mixed-sand and gravel coastlines. There is an overlap between bodies of water classified as coastal lagoons and bodies of water classified as Estuary, estuaries. Lagoons are common coastal features around many parts of the world. Definition and terminology Lagoons are shallow, often elongated bodies of water separated from a larger body of water by a shallow or exposed shoal, reef, coral reef, or similar feature. Some authorities include fresh water bodies in the definition of "lagoon", while others explicitly restrict "lagoon" to bodies of water with some degree of salinity. The distinction between "lagoon" and "estuary" also varies between authorities. Richard A. Davis J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
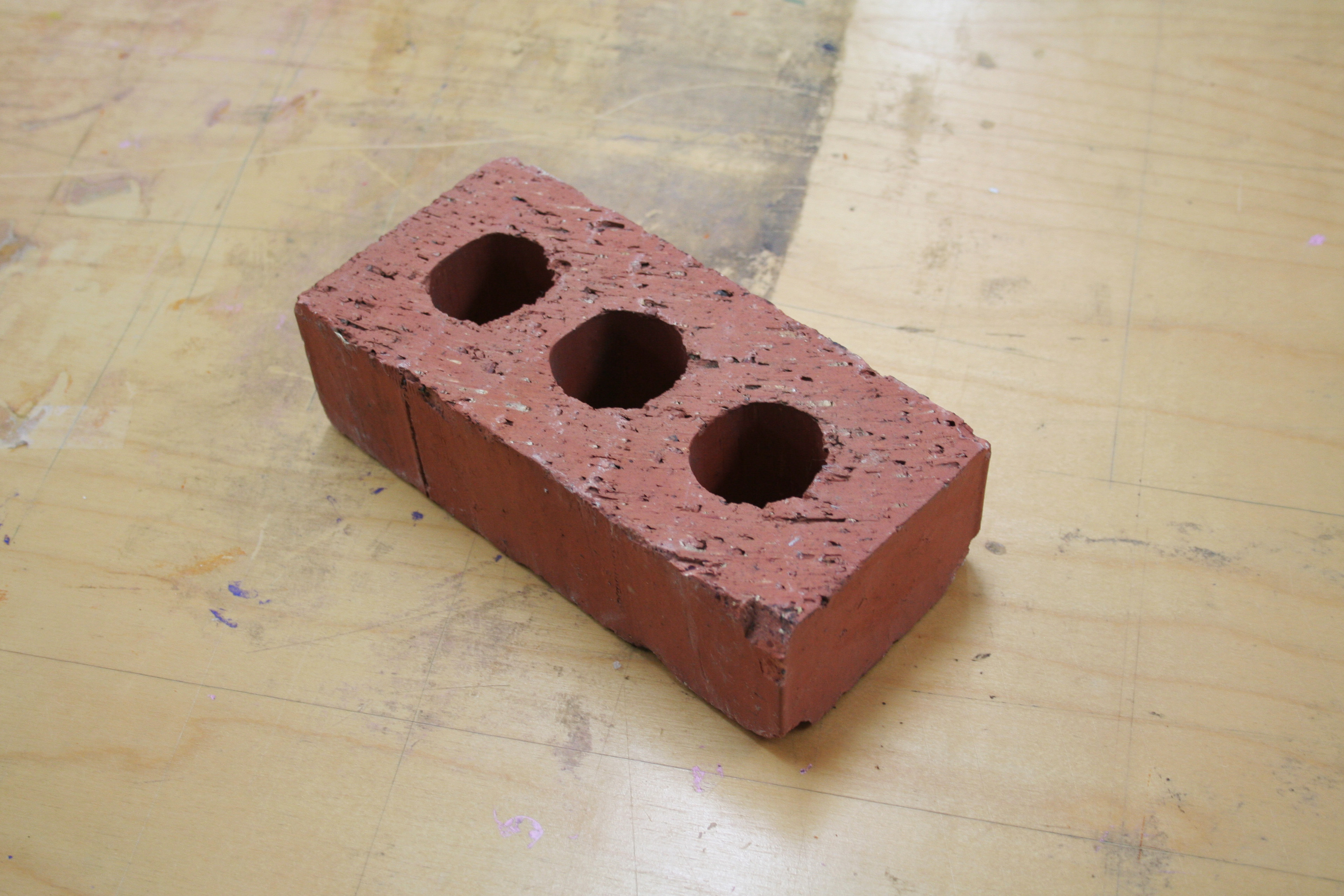
Brick
A brick is a type of construction material used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a unit primarily composed of clay. But is now also used informally to denote building units made of other materials or other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using Mortar (masonry), mortar, adhesives or by interlocking. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region, and are produced in bulk quantities. Concrete masonry unit, ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of clay or concrete, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since . Air-dried bricks, also known as mudbricks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Wight
The Isle of Wight (Help:IPA/English, /waɪt/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''WYTE'') is an island off the south coast of England which, together with its surrounding uninhabited islets and Skerry, skerries, is also a ceremonial county. The county is bordered by Hampshire across the Solent strait to the north, and is otherwise surrounded by the English Channel. Its largest settlement is Ryde, and the administrative centre is Newport, Isle of Wight, Newport. Wight has a land area of and had a population of 140,794 in 2022, making it the List of islands of England#Largest islands, largest and List of islands of England#Most populous islands, second-most populous English island. The island is largely rural, with the largest settlements primarily on the coast. These include Ryde in the north-east, Shanklin and Sandown in the south-east, and the large villages of Totland and Freshwater, Isle of Wight, Freshwater in the west. Newport is located inland at the point at which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |