|
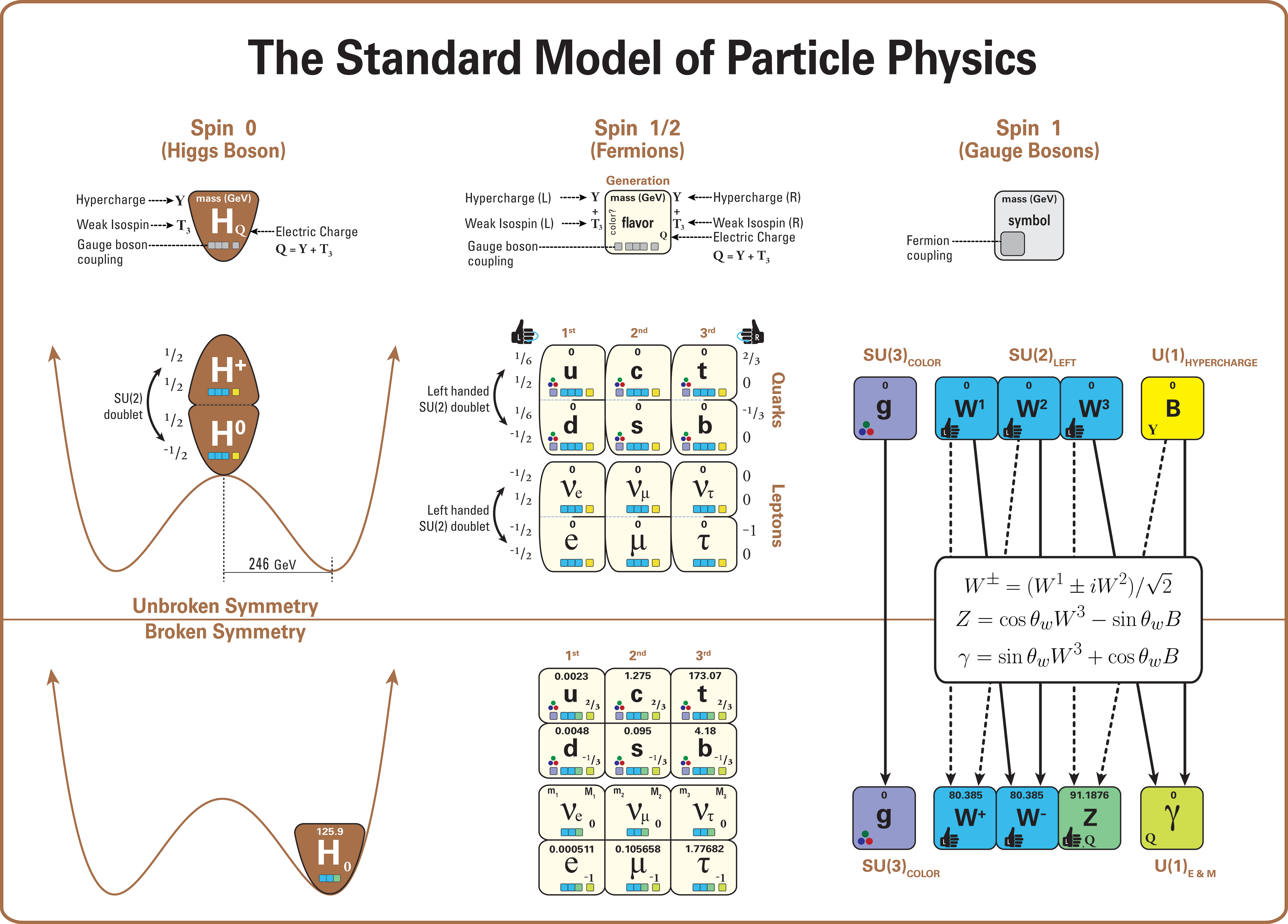
Weak Hypercharge
In the Standard Model (mathematical formulation), Standard Model of electroweak interactions of particle physics, the weak hypercharge is a quantum number relating the electric charge and the third component of weak isospin. It is frequently denoted Y_\mathsf and corresponds to the gauge symmetry U(1). It is Conservation law (physics), conserved (only terms that are overall weak-hypercharge neutral are allowed in the Lagrangian). However, one of the interactions is with the Higgs field. Since the Higgs field vacuum expectation value is nonzero, particles interact with this field all the time even in vacuum. This changes their weak hypercharge (and weak isospin ). Only a specific combination of them, \ Q = T_3 + \tfrac\, Y_\mathsf\ (electric charge), is conserved. Mathematically, weak hypercharge appears similar to the Gell-Mann–Nishijima formula for the hypercharge of strong interactions (which is not conserved in weak interactions and is zero for leptons). In the electroweak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom Quark
The bottom quark, beauty quark, or b quark, is an elementary particle of the third generation. It is a heavy quark with a charge of − ''e''. All quarks are described in a similar way by electroweak interaction and quantum chromodynamics, but the bottom quark has exceptionally low rates of transition to lower-mass quarks. The bottom quark is also notable because it is a product in almost all top quark decays, and is a frequent decay product of the Higgs boson. Name and history The bottom quark was first described theoretically in 1973 by physicists Makoto Kobayashi and Toshihide Maskawa to explain CP violation. The name "bottom" was introduced in 1975 by Haim Harari. The evidence for the bottom quark was first obtained in 1977 by the Fermilab E288 experiment team led by Leon M. Lederman, when proton-nucleon collisions produced bottomonium decaying to pairs of muons. The discovery was confirmed about a year later by the PLUTO and DASP2 Collaborations at the elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strange Quark
The strange quark or s quark (from its symbol, s) is the third lightest of all quarks, a type of elementary particle. Strange quarks are found in subatomic particles called hadrons. Examples of hadrons containing strange quarks include kaons (), strange D mesons (), Sigma baryons (), and other strange particles. According to the IUPAP, the symbol s is the official name, while "strange" is to be considered only as a mnemonic. The name sideways has also been used because the s quark (but also the other three remaining quarks) has an isospin, I value of 0 while the u ("up") and d ("down") quarks have values of + and − respectively. Along with the charm quark, it is part of the generation (physics), second generation of matter. It has an electric charge of elementary charge, ''e'' and a bare mass of . Like all quarks, the strange quark is an elementary particle, elementary fermion with Spin (physics), spin spin-1/2, , and experiences all four fundamental interactions: gravit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higgs Field
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the excited state, quantum excitation of the Higgs field, one of the field (physics), fields in particle physics theory. In the Standard Model, the Higgs particle is a massive scalar boson that Coupling (physics), couples to (interacts with) particles whose mass arises from their interactions with the Higgs Field, has zero Spin (physics), spin, even (positive) Parity (physics), parity, no electric charge, and no color charge, colour charge. It is also very unstable, particle decay, decaying into other particles almost immediately upon generation. The Higgs field is a scalar field with two neutral and two electrically charged components that form a complex doublet (physics), doublet of the weak isospin SU(2) symmetry. Its "Spontaneous symmetry breaking#Sombrero potential, sombrero potential" leads it to take a nonzero value everywhere (inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Down Quark
The down quark (symbol: d) is a type of elementary particle, and a major constituent of matter. The down quark is the second-lightest of all quarks, and combines with other quarks to form composite particles called hadrons. Down quarks are most commonly found in atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei, where it combines with up quarks to form protons and neutrons. The proton is made of one down quark with two up quarks, and the neutron is made up of two down quarks with one up quark. Because they are found in every single known atom, down quarks are present in all everyday matter that we interact with. The down quark is part of the generation (physics), first generation of matter, has an electric charge of − elementary charge, ''e'' and a Quark#Mass, bare mass of . Like all quarks, the down quark is an elementary fermion with Spin (physics), spin spin-1/2, , and experiences all four fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interactions, and strong interactions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Model (mathematical Formulation)
This article describes the mathematics of the Standard Model of particle physics, a gauge quantum field theory containing the internal symmetries of the unitary product group . The theory is commonly viewed as describing the fundamental set of particles – the leptons, quarks, gauge bosons and the Higgs boson. The Standard Model is renormalizable and mathematically self-consistent; however, despite having huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some unexplained phenomena. In particular, although the physics of special relativity is incorporated, general relativity is not, and the Standard Model will fail at energies or distances where the graviton is expected to emerge. Therefore, in a modern field theory context, it is seen as an effective field theory. Quantum field theory The standard model is a quantum field theory, meaning its fundamental objects are ''quantum fields'', which are defined at all points in spacetime. Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson
In particle physics, a boson ( ) is a subatomic particle whose spin quantum number has an integer value (0, 1, 2, ...). Bosons form one of the two fundamental classes of subatomic particle, the other being fermions, which have half odd-integer spin (1/2, 3/2, 5/2, ...). Every observed subatomic particle is either a boson or a fermion. Paul Dirac coined the name ''boson'' to commemorate the contribution of Satyendra Nath Bose, an Indian physicist. Some bosons are elementary particles occupying a special role in particle physics, distinct from the role of fermions (which are sometimes described as the constituents of "ordinary matter"). Certain elementary bosons (e.g. gluons) act as force carriers, which give rise to forces between other particles, while one (the Higgs boson) contributes to the phenomenon of mass. Other bosons, such as mesons, are composite particles made up of smaller constituents. Outside the realm of particle physics, multiple identical composite bosons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weinberg Angle (relation Between Coupling Constants)
The weak mixing angle or Weinberg angle is a parameter in the Weinberg–Salam theory (by Steven Weinberg and Abdus Salam) of the electroweak interaction, part of the Standard Model of particle physics, and is usually denoted as . It is the angle by which spontaneous symmetry breaking rotates the original and vector boson plane, producing as a result the boson, and the photon. Its measured value is slightly below 30°, but also varies, very slightly increasing, depending on how high the relative momentum of the particles involved in the interaction is that the angle is used for. Details The algebraic formula for the combination of the and vector bosons (i.e. 'mixing') that simultaneously produces the massive and the massless photon A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Conjugation
In physics, charge conjugation is a transformation that switches all particles with their corresponding antiparticles, thus changing the sign of all charges: not only electric charge but also the charges relevant to other forces. The term C-symmetry is an abbreviation of the phrase "charge conjugation symmetry", and is used in discussions of the symmetry of physical laws under charge-conjugation. Other important discrete symmetries are P-symmetry (parity) and T-symmetry (time reversal). These discrete symmetries, C, P and T, are symmetries of the equations that describe the known fundamental forces of nature: electromagnetism, gravity, the strong and the weak interactions. Verifying whether some given mathematical equation correctly models nature requires giving physical interpretation not only to continuous symmetries, such as motion in time, but also to its discrete symmetries, and then determining whether nature adheres to these symmetries. Unlike the continuous symm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicity (particle Physics)
In physics, helicity is the projection of the spin onto the direction of momentum. Mathematically, ''helicity'' is the sign of the projection of the spin vector onto the momentum vector: "left" is negative, "right" is positive. Overview The angular momentum J is the sum of an orbital angular momentum L and a spin S. The relationship between orbital angular momentum L, the position operator r and the linear momentum (orbit part) p is : \mathbf = \mathbf\times\mathbf , so L's component in the direction of p is zero. Thus, helicity is just the projection of the spin onto the direction of linear momentum. The helicity of a particle is positive ("right-handed") if the direction of its spin is the same as the direction of its motion and negative ("left-handed") if opposite. Helicity is conserved. That is, the helicity commutes with the Hamiltonian, and thus, in the absence of external forces, is time-invariant. It is also rotationally invariant, in that a rotation applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak Isospin
In particle physics, weak isospin is a quantum number relating to the electrically charged part of the weak interaction: Particles with half-integer weak isospin can interact with the bosons; particles with zero weak isospin do not. Weak isospin is a construct parallel to the idea of isospin under the strong interaction. Weak isospin is usually given the symbol or , with the third component written as or is more important than ; typically "weak isospin" is used as short form of the proper term "3rd component of weak isospin". It can be understood as the eigenvalue of a charge operator. Notation This article uses and for weak isospin and its projection. Regarding ambiguous notation, is also used to represent the 'normal' (strong force) isospin, same for its third component a.k.a. or . Aggravating the confusion, is also used as the symbol for the Topness quantum number. Conservation law The weak isospin conservation law relates to the conservation of \ T_3\ ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin (spin 1/2, spin , Spin (physics)#Higher spins, spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles include all quarks and leptons and all composite particles made of an even and odd, odd number of these, such as all baryons and many atoms and atomic nucleus, nuclei. Fermions differ from bosons, which obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Some fermions are elementary particles (such as electrons), and some are composite particles (such as protons). For example, according to the spin-statistics theorem in Theory of relativity, relativistic quantum field theory, particles with integer Spin (physics), spin are bosons. In contrast, particles with half-integer spin are fermions. In addition to the spin characteristic, fermions have another specific property: they possess conserved baryon or lepton quantum numbers. Therefore, what is usually referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |