|
Watercolor
Watercolor (American English) or watercolour (Commonwealth English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences), also ''aquarelle'' (; from Italian diminutive of Latin 'water'), is a painting method"Watercolor may be as old as art itself, going back to the Stone Age when early ancestors combined earth and charcoal with water to create the first wet-on-dry picture on a cave wall." in which the paints are made of pigments suspended in a water-based solution. ''Watercolor'' refers to both the List of art media, medium and the resulting work of art, artwork. Aquarelles painted with water-soluble colored ink instead of modern water colors are called (Latin for "aquarelle made with ink") by experts. However, this term has now tended to pass out of use. The conventional and most common Support (art), support—material to which the paint is applied—for watercolor paintings is watercolor paper. Other supports or substrates include stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painting
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual arts, visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, Composition (visual art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
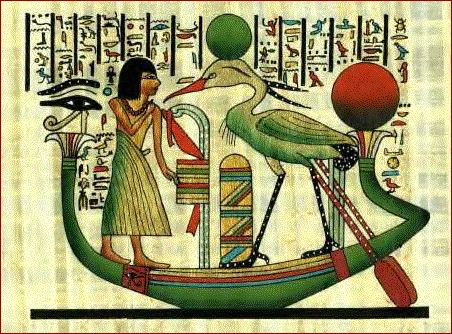
Watercolor Paper
Watercolor paper (or watercolour paper) is paper or substrate onto which an artist applies watercolor paints, pigments, or dyes. Many types of paper are manufactured specifically for watercolour painting. The paper may be made of pulp (paper), wood pulp exclusively, or mixed with cotton fibers. cotton paper, Pure cotton watercolor paper is also used but it is more expensive than pulp-based paper. Some watercolourists prefer an acid-free medium. Watercolor paper may be hot-pressed, cold-pressed, or rough. Paper traditionally comes in either 90, 140, or 300 lb weights. Prices range from affordable to more expensive and higher quality. History Papyrus was used as a 'paper' onto which the Egyptians applied their water-based paints or pigments."Ancient Egyptians used water-soluble translucent paints to decorate papyrus scrolls. They used such earth pigments as ochres and siennas, as well as minerals like reds, cinnabar, blue azure, green malachite, and so on, with gum arabic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brush Painting
Ink wash painting ( zh, t=水墨畫, s=水墨画, p=shuǐmòhuà) is a type of Chinese ink brush painting which uses washes of black ink, such as that used in East Asian calligraphy, in different concentrations. It emerged during the Tang dynasty of China (618–907), and overturned earlier, more realistic techniques. It is typically monochrome, using only shades of black, with a great emphasis on virtuoso brushwork and conveying the perceived "spirit" or "essence" of a subject over direct imitation. Ink wash painting flourished from the Song dynasty in China (960–1279) onwards, as well as in Japan after it was introduced by Zen Buddhist monks in the 14th century. Some Western scholars divide Chinese painting (including ink wash painting) into three periods: times of representation, times of expression, and historical Oriental art. Chinese scholars have their own views which may be different; they believe that contemporary Chinese ink wash paintings are the pluralistic conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Bol
Hans Bol or Jan Bol (16 December 1534 – 20 November 1593), was a Southern Netherlands, Flemish painter, Miniature art, miniature painter, print artist and draftsman.Hans Bol at the Netherlands Institute for Art History He is known for his Landscape art, landscapes, allegorical and biblical scenes, and genre paintings executed in a late Northern Mannerist style. After a successful career in Flanders, he left his home country for the Dutch Republic during the Fall of Antwerp, Siege of Antwerp. His landscape work had an important influence on the next generation of Dutch landscape painters. His prints after his own designs as well as those of Flemish masters such as Pieter Brueghel the Elder contributed to the spread of their themes in the Northern Netherlands.Larry Silver, 'Peasant Scenes and Landscapes: The Rise of Pictorial Genres in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paint
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based, and each has distinct characteristics. Primitive forms of paint were used tens of thousands of years ago in cave paintings. Clean-up solvents are also different for water-based paint than oil-based paint. Water-based paints and oil-based paints will cure differently based on the outside ambient temperature of the object being painted (such as a house). History Paint was used in some of the earliest known human artworks. Some cave paintings drawn with red or yellow ochre, hematite, manganese oxide, and charcoal may have been made by early ''Homo sapiens'' as long as 40,000 years ago. Paint may be even older. In 2003 and 2004, South African archeologists reported finds in Blombos Cave of a 100,000-y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compound, inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic chemistry, inorganic, organic chemistry, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Art Media
Media, or mediums, are the core types of material (or related other tools) used by an artist, composer, designer, etc. to create a work of art. For example, a visual artist may broadly use the media of painting or sculpting, which themselves have more specific media within them, such as watercolor paints or marble. The following is a list of artistic categories and the media used within each category: Architecture *Cement, concrete, mortar * Cob *Glass *Metal *Stone, brick *Wood Carpentry *Adhesives *Wood (timber) Ceramics *Bone china *Clay * Glaze *Porcelain *Pottery *Terracotta *Tile Drawing Common drawing materials *Acrylic paint *Chalk *Charcoal *Colored pencil *Conté *Crayon * Encaustic *Fresco *Glitter * Gouache *Graphite * Ink * Intaglio *Oil paint * Glass paint *Pastel *Pixel *Printmaking * Sketch *Tempera *Watercolor Common supports (surfaces) for drawing *Canvas *Card stock *Concrete *Fabric *Glass *Human body *Metal *Paper *Papyrus *Parchment *Plast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Painting
Chinese painting () is one of the oldest continuous artistic traditions in the world. Painting in the traditional style is known today in Chinese as , meaning "national painting" or "native painting", as opposed to Western styles of art which became popular in China in the 20th century. It is also called ''danqing'' (). Traditional painting involves essentially the same techniques as Chinese calligraphy, calligraphy and is done with a Ink and wash painting, brush dipped in black ink or Chinese pigment, coloured pigments; oils are not used. As with calligraphy, the most popular materials on which paintings are made are paper and silk. The finished work can be mounted on scrolls, such as hanging scrolls or handscrolls. Traditional painting can also be done on album sheets, walls, lacquerware, folding screens, and other media. The two main techniques in Chinese painting are: * Gongbi (工筆), meaning "meticulous", uses highly detailed brushstrokes that delimit details very precise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support (art)
In visual arts, the support is a solid surface onto which the painting is placed, typically a canvas or a panel. Support is technically distinct from the overlaying ground, but sometimes the latter term is used in a broad sense of "support" to designate any surface used for painting, for example, paper for watercolor or plaster for fresco. The support for an oil painting can be either rigid or flexible, both providing certain opportunities and challenges for the artist. In order to get both the stability and the desired texture, painters for finished paintings usually use canvas that are pre-stretched on a solid frame or panel (so-called stretchers usually made of stretcher bars). These ''stretched canvas'' became popular in Venice in the 17th century. Since these supports are expensive, studies are frequently executed on pieces of canvas or paper. ''Canvas board'', a piece of canvas mounted onto a paper board, provides another low-cost alternative for sketches. The hardwoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illustrated Manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is decorated with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers and liturgical books such as psalters and courtly literature, the practice continued into secular texts from the 13th century onward and typically include proclamations, enrolled bills, laws, charters, inventories, and deeds. The earliest surviving illuminated manuscripts are a small number from late antiquity, and date from between 400 and 600 CE. Examples include the Vergilius Romanus, Vergilius Vaticanus, and the Rossano Gospels. The majority of extant manuscripts are from the Middle Ages, although many survive from the Renaissance. While Islamic manuscripts can also be called illuminated and use essentially the same techniques, comparable Far Eastern and Mesoamerican works are described as ''painted''. Most manuscripts, illuminated or not, were written on parchment until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Painting
is one of the oldest and most highly refined of the Japanese visual arts, encompassing a wide variety of genres and styles. As with the history of Japanese arts in general, the long history of Japanese painting exhibits synthesis and competition between native Japanese aesthetics and the adaptation of imported ideas, mainly from Chinese painting, which was especially influential at a number of points; significant Western influence only comes from the 19th century onwards, beginning at the same time as Japanese art was influencing that of the West. Areas of subject matter where Chinese influence has been repeatedly significant include Buddhist religious painting, ink-wash painting of landscapes in the Chinese literati painting tradition, calligraphy of sinograms, and the painting of animals and plants, especially birds and flowers. However, distinctively Japanese traditions have developed in all these fields. The subject matter that is widely regarded as most characterist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inkstick
Inksticks () or ink cakes are a type of solid Chinese ink used traditionally in several Chinese and East Asian art forms such as calligraphy and brush painting. Inksticks are made mainly of soot and animal glue, sometimes with incense or medicinal scents added. To make ink, the inkstick is ground against an inkstone with a small quantity of water to produce a dark liquid which is then applied with an ink brush. By adjusting the strength and duration of the ink grinding process, artists and calligraphers may adjust the concentration of the produced ink to suit their tastes. Along with the inkstone, ink brush, and paper, the inkstick is considered one of the Four Treasures of the Study of classical Chinese literary culture. History The earliest artifacts of Chinese inks can be dated back to 12th century BC, with charred materials, plant dyes, and animal-based inks being occasionally used, mineral inks being most common. Mineral inks based on materials such as graphite were ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |