|
Waste Management In Japan
Waste management in Japan today emphasizes not just the efficient and sanitary collection of waste, but also reduction in waste produced and recycling of waste when possible. This has been influenced by its history, particularly periods of significant economic expansion, as well as its geography as a mountainous country with limited space for landfills. Important forms of waste disposal include incineration, recycling and, to a smaller extent, landfills and land reclamation. Although Japan has made progress since the 1990s in reducing waste produced and encouraging recycling, there is still further progress to be made in reducing reliance on incinerators and the garbage sent to landfills. Challenges also exist in the processing of electronic waste and debris left after natural disasters. History There was no centralized systems or legislation for managing waste at the beginning of the Meiji Era. In 1900, two measures were introduced to improve sanitation and avoid epidemics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Economic Miracle
The Japanese economic miracle refers to Japan's record period of economic growth between the post-World War II era and the end of the Cold War. During the economic boom, Japan rapidly became the world's second-largest economy (after the United States). By the 1990s, Japan's population demographics had begun to stagnate, and the workforce was no longer expanding as quickly as it had in the previous decades despite per-worker productivity remaining high. Background This economic miracle was the result of post-World War II Japan and West Germany benefitting from the Cold War. The American government reformed Japanese society during the occupation of Japan, making political, economic and civic changes. It occurred chiefly due to the economic interventionism of the Japanese government and partly due to the aid and assistance of the U.S. aid to Asia. After World War II, the U.S. established a significant presence in Japan to slow the expansion of Soviet influence in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Electric Vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an electric propulsion system (hybrid vehicle drivetrain). The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional vehicle or better performance. There is a variety of HEV types and the degree to which each function as an electric vehicle (EV) also varies. The most common form of HEV is the hybrid electric car, although hybrid electric trucks (pickups and tractors), buses, boats and aircraft also exist. Modern HEVs make use of efficiency-improving technologies such as regenerative brakes which convert the vehicle's kinetic energy to electric energy, which is stored in a battery or supercapacitor. Some varieties of HEV use an internal combustion engine to turn an electrical generator, which either recharges the vehicle's batteries or directly powers its electric drive motors; this combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
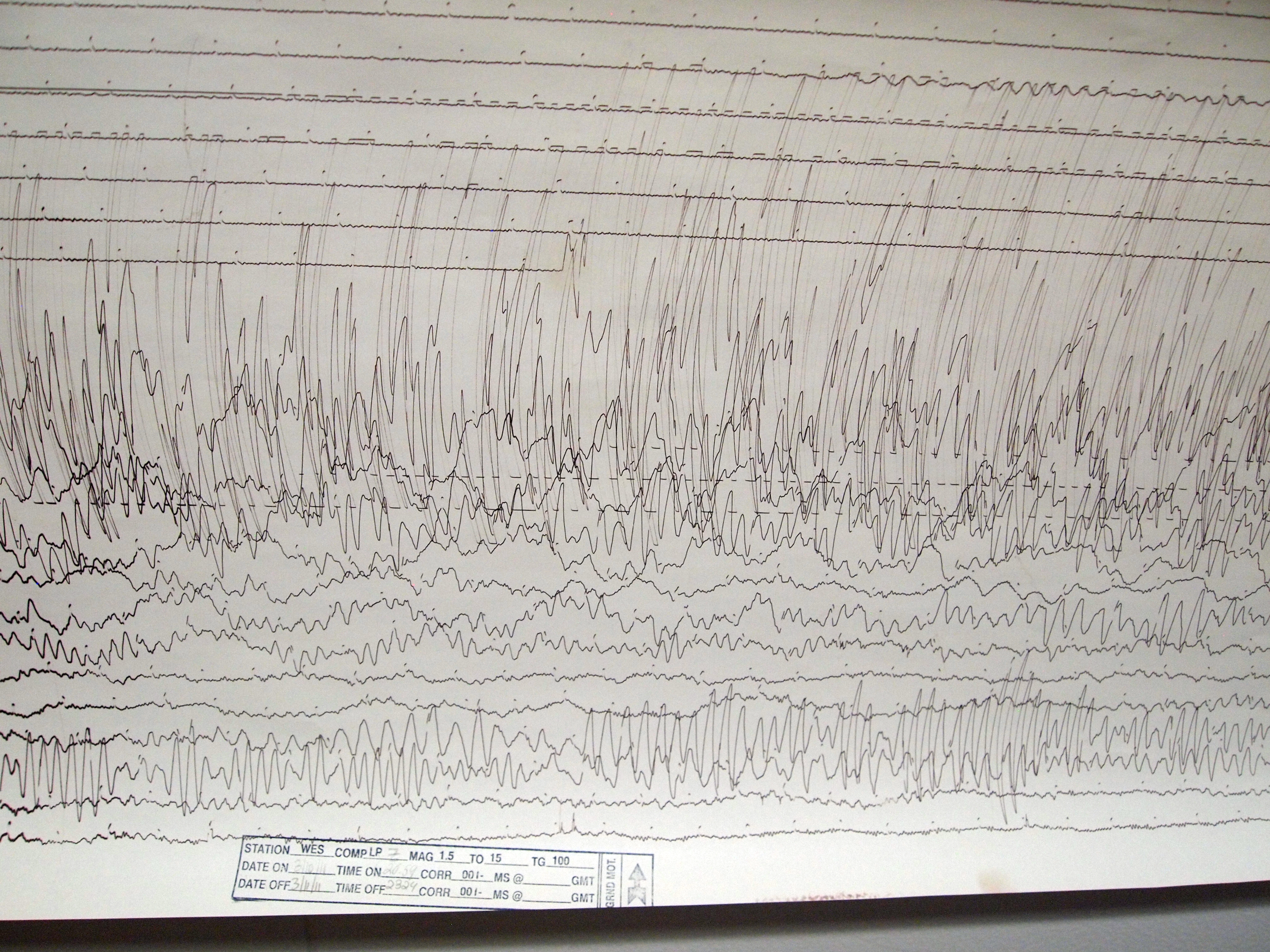
Sendai
is the capital city of Miyagi Prefecture, the largest city in the Tōhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,091,407 in 525,828 households, and is one of Japan's 20 designated cities. The city was founded in 1600 by the ''daimyō'' Date Masamune. It is nicknamed the ; there are Japanese zelkova trees lining many of the main thoroughfares such as and . In the summer, the Sendai Tanabata Festival, the largest Tanabata festival in Japan, is held. In winter, the trees are decorated with thousands of lights for the , lasting through most of December. On 11 March 2011, coastal areas of the city suffered catastrophic damage from a magnitude 9.0 offshore earthquake,UK Foreign Office 9.0 assessment [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake And Tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the , among other names. The disaster is often referred to in both Japanese and English as simply 3.11 (read in Japanese). It was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful earthquake in the world since modern record-keeping began in 1900. The earthquake triggered powerful tsunami waves that may have reached heights of up to in Miyako in Tōhoku's Iwate Prefecture, Yomiuri Shimbun evening edition 2-11-04-15 page 15, nearby Aneyoshi fishery port (姉吉漁港)(Google map E39 31 57.8, N 142 3 7.6) 2011-04-15大震災の津波、宮古で38.9 m…明治三陸上回るby okayasu Akio (岡安 章夫) and which, in the Sendai area, travele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
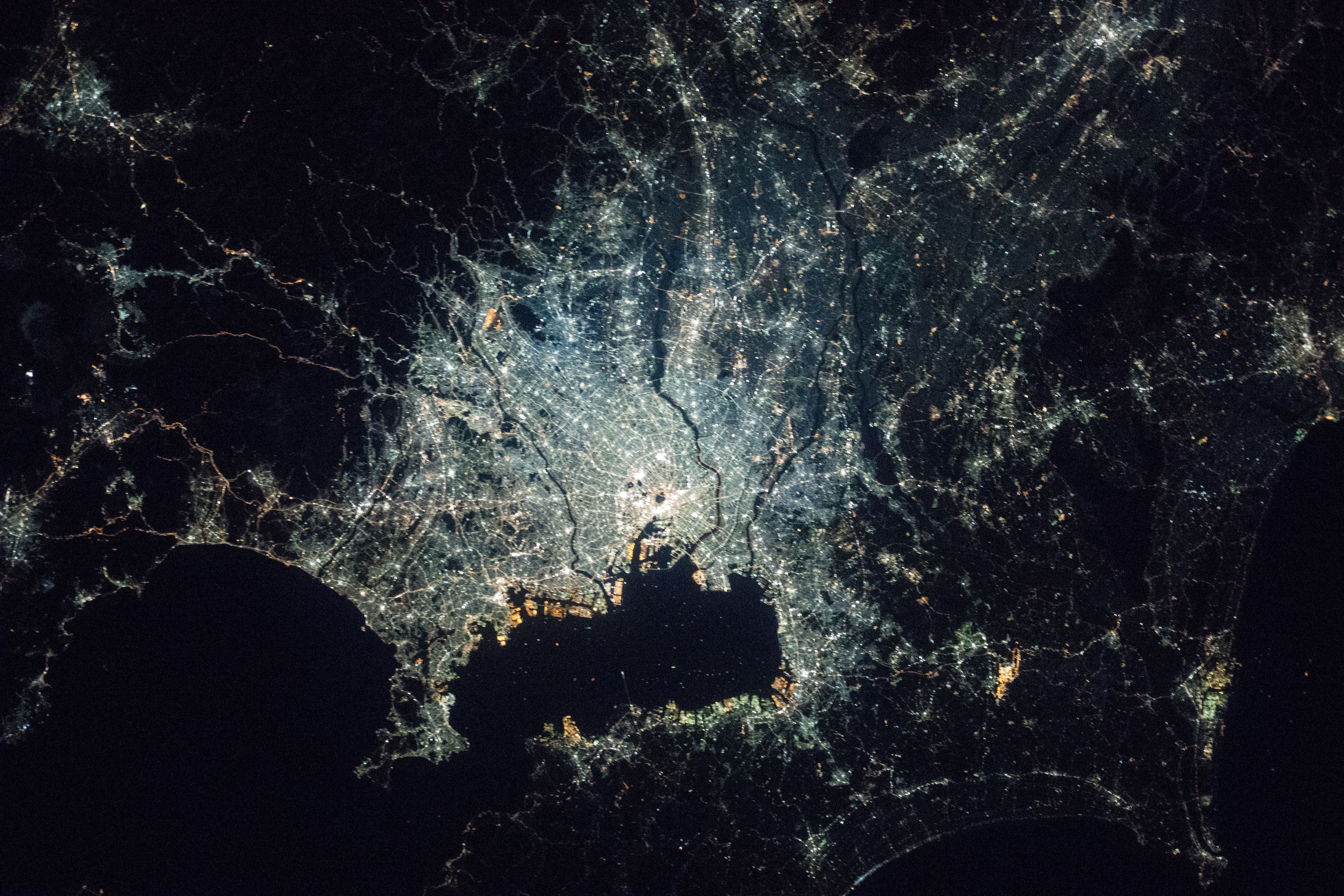
Tokyo Bay
is a bay located in the southern Kantō region of Japan, and spans the coasts of Tokyo, Kanagawa Prefecture, and Chiba Prefecture. Tokyo Bay is connected to the Pacific Ocean by the Uraga Channel. The Tokyo Bay region is both the most populous and largest industrialized area in Japan. Names In ancient times, Japanese knew Tokyo Bay as the . By the Azuchi–Momoyama period (1568–1600) the area had become known as after the city of Edo. The bay took its present name in modern times, after the Imperial court moved to Edo and renamed the city Tokyo in 1868. Geography Tokyo Bay juts prominently into the Kantō Plain. It is surrounded by the Bōsō Peninsula in Chiba Prefecture to the east and the Miura Peninsula in Kanagawa Prefecture to the west. The shore of Tokyo Bay consists of a diluvial plateau and is subject to rapid marine erosion. Sediments on the shore of the bay make for a smooth, continuous shoreline. Boundaries In a narrow sense, Tokyo Bay is the area n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Breakwater
The is a breakwater and artificial island located in Tokyo Bay, adjacent to the Tokyo Gate Bridge. History The Central Breakwater was first constructed in 1973 and has been used as a site for waste disposal from Tokyo since then, forming two artificial islands in Tokyo Bay known as the and the . The islands had a combined area of 377 hectares in 2011 and are expected to ultimately reach an area of 989 hectares. Jurisdiction dispute Jurisdiction over the Central Breakwater islands was disputed between the special wards of Koto and Ota for 4 decades. Under Japanese law, any boundary dispute may be submitted to the prefectural government (in this case, the Tokyo metropolitan government) for resolution; a similar dispute with regard to the nearby Odaiba and Ariake area was resolved in 1982 by splitting the area between the three special wards that claimed it. Koto has argued that the garbage used to create the landfill was hauled through Koto and that making the island part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic Recycling
Plastic recycling is the reprocessing of plastic waste into new products. When performed correctly, this can reduce dependence on landfill, conserve resources and protect the environment from plastic pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Although recycling rates are increasing, they lag behind those of other recoverable materials, such as aluminium, glass and paper. Since the beginning of plastic production in the 20th century, until 2015, the world has produced some 6.3 billion tonnes of plastic waste, only 9% of which has been recycled, and only ~1% has been recycled more than once. Additionally, 12% was incinerated and the remaining 79% disposed of to landfill or to the environment including the sea. Recycling is necessary because almost all plastic is non- biodegradable and thus builds-up in the environment, where it can cause harm. For example, approximately 8 million tons of waste plastic enter the Earth's oceans every year, causing damage to the aquatic ecosystem an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel And Tin Cans
A steel can, tin can, tin (especially in British English, Australian English, Canadian English and South African English), steel packaging, or can is a container for the distribution or storage of goods, made of thin metal. Many cans require opening by cutting the "end" open; others have removable covers. They can store a broad variety of contents: food, beverages, oil, chemicals, etc. Steel cans are made of tinplate (tin-coated steel) or of tin-free steel. In some dialects, even aluminium cans are called "tin cans". Steel cans are highly recyclable, unlike materials like plastic, with around 65% of steel cans being recycled. History The tin canning process was conceived by the Frenchman Philippe de Girard, who got a British merchant Peter Durand to patent the idea in 1810. The canning concept was based on experimental food preservation work in glass containers the year before by the French inventor Nicholas Appert. Durand did not pursue food canning, but, in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminum Can
An Aluminum can (British English: Tin can) is a single-use container for packaging made primarily of aluminum. It is commonly used for food and beverages such as milk and soup but also for products such as oil, chemicals, and other liquids. Global production is 180 billion annually and constitutes the largest single use of aluminum globally. Usage Use of aluminum in cans began in 1957. Aluminum offers greater malleability, resulting in ease of manufacture; this gave rise to the two-piece can, where all but the top of the can is simply stamped out of a single piece of aluminum, rather than constructed from two pieces of steel. The inside of the can is lined by spray coating an epoxy lacquer or polymer to protect the aluminum from being corroded by acidic contents such as carbonated beverages and imparting a metallic taste to the beverage. The epoxy may contain bisphenol A. A label is either printed directly on the side of the can or will be glued to the outside of the curved s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Some Of The Different Types Of Bags That Must Be Bought For Different Types Of Recyclable Waste In Japan , German pop duo
{{disambig ...
Some may refer to: *''some'', an English word used as a determiner and pronoun; see use of ''some'' *The term associated with the existential quantifier *"Some", a song by Built to Spill from their 1994 album ''There's Nothing Wrong with Love'' *Socialist-oriented market economy, the Vietnamese economic system occasionally abbreviated SOME *Social market economy, the German socioeconomic model abbreviated SOME *So Others Might Eat (SOME), a Washington, D.C.-based non-profit organization *SoMe, short for social media * ''Some'' (film), a 24 film * "Some" (song), a duet by Junggigo and Soyou *Some & Any Some & Any was a German pop duo, formed during the eighth season of the German television talent show ''Popstars''. The group consisted of then-18-year-old Vanessa Meisinger and 20-year-old half-Brazilian, half-Swiss Leonardo Ritzmann. The seaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar ( mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Mercury is used in thermometers, barometers, manometers, sphygmomanometers, float valves, mercury switches, mercury relays, fluorescent lamps and other devices, though concerns about the element's toxicity have led to mercury thermometers and sphygmomanometers being largely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxins And Dioxin-like Compounds
Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds (DLCs) are a group of chemical compounds that are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environmental pollutant, environment. They are mostly by-products of burning or various industrial processes - or, in case of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl, PCBs and polybrominated biphenyl, PBBs, unwanted minor components of intentionally produced mixtures. Some of them are highly toxic, but the toxicity among them varies 30,000-fold. They are grouped together because their mechanism of action is the same. They activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AH receptor), albeit with very different binding affinities, leading to high differences in toxicity and other effects. They include: * Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, Polychlorinated dibenzo''-p-''dioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins. PCDDs are derivatives of dibenzodioxin, dibenzo''-p-''dioxin. There are 75 PCDD congener (chemistry), congeners, differing in the number and location of chlorine atoms, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |