|
Wasp Point
Wasp Point () is a projecting point in the middle of the southwest coast of Thule Island, South Sandwich Islands. It was named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1971 after the American sealing vessel in which Captain Benjamin Morrell of Stonington, CT, visited the island An island or isle is a piece of subcontinental land completely surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be ... in 1823. Next to Longton Point on Cook Island, it is the southernmost landmass of the South Sandwich Islands and the southernmost landmass worldwide north of the 60th parallel south and therefore the southernmost landmass outside of the Antarctic Treaty System. References Headlands of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands {{SouthGeorgia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thule Island
Thule Island, also called Morrell Island, is one of the southernmost of the South Sandwich Islands, part of the grouping known as Southern Thule. It is named, on account of its remote location, after the mythical land of Thule, said by ancient geographers to lie at the extreme end of the Earth. The alternative name Morrell Island is after Benjamin Morrell, an American explorer and whaling captain. It was espied by James Cook and his '' Resolution'' crew on 31 January 1775 during his attempt to find Terra Australis. Geography Thule Island is approximately triangular in shape and in area with a long, panhandle-like peninsula called Hewison Point, , extending to the southeast. Steep slopes ascend to a summit caldera with the peak of Mount Larsen at above sea level. Mount Larsen is named after the Antarctic explorer and whaler Carl Anton Larsen. On the southwestern end lies Wasp Point. Off Hewison Point lies the small islet of Twitcher Rock, the southernmost land on Earth exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Sandwich Islands
) , anthem = "God Save the King" , song_type = , song = , image_map = South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in United Kingdom.svg , map_caption = Location of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Ocean , mapsize = 255px , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = , established_title2 = Separation from Falkland Islands , established_date2 = 3 October 1985 , official_languages = English , demonym = , capital = King Edward Point , coordinates = , largest_settlement = capital , largest_settlement_type = largest settlement , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , government_type = Directly administered dependency under a constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Commissioner , leader_name2 = Alison Blake , national_representation = Government of the United Kingdom , national_representation_type1 = Minister , national_representation1 = Zac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee
The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI). Such names are formally approved by the Commissioners of the BAT and SGSSI respectively, and published in the BAT Gazetteer and the SGSSI Gazetteer maintained by the Committee. The BAT names are also published in the international Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica maintained by SCAR. The Committee may also consider proposals for new place names for geographical features in areas of Antarctica outside BAT and SGSSI, which are referred to other Antarctic place-naming authorities, or decided by the Committee itself if situated in the unclaimed sector of Antarctica. Names attributed by the committee * Anvil Crag, named for descriptive features *Anckorn Nunataks, named after J. F. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
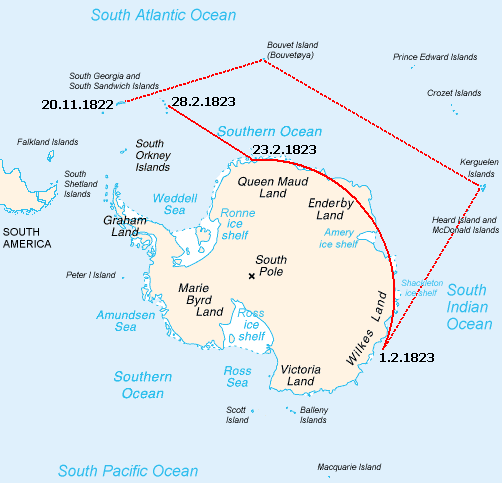
Benjamin Morrell
Benjamin Morrell (July 5, 1795 – 1838 or 1839?) was an American sea captain, explorer and trader who made a number of voyages, mainly to the Atlantic, the Southern Ocean and the Pacific Islands. In a ghost-written memoir, ''A Narrative of Four Voyages'', which describes his sea-going life between 1823 and 1832, Morrell included numerous claims of discovery and achievement, many of which have been disputed by geographers and historians, and in some cases have been proved false. He ended his career as a fugitive, having wrecked his ship and misappropriated parts of the salvaged cargo. Morrell had an eventful early career, running away to sea at the age of 17 and being twice captured and imprisoned by the British during the War of 1812. He subsequently sailed before the mast for several years before being appointed as chief mate, and later as captain, of the New York sealer ''Wasp''. In 1823 he took ''Wasp'' for an extended voyage into subantarctic waters, and on his return made u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island or isle is a piece of subcontinental land completely surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges Delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental islands and oceanic islands. There are also artificial islands (man-made islands). There are about 900,000 official islands in the world. This number consists of all the officially-reported islands of each country. The total number of islands in the world is unknown. There may be hundreds of thousands of tiny islands that are unknown and uncounted. The number of sea islands in the world is estimated to be more than 200,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longton Point
Cook Island is the central and largest island of the Southern Thule island group, part of the South Sandwich Islands in the far south Atlantic Ocean. Southern Thule was discovered by a British expedition under Captain James Cook in 1775. Cook Island was named for Cook by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, which explored the South Sandwich Islands in 1819–1820. The island was surveyed in 1930 by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel on ''Discovery II'', who charted and named many of its features. Other names were later applied by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC). Geography Cook Island measures about wide. It is heavily glaciated and uninhabited. Its highest peak, Mount Harmer, rises to . Mount Holdgate rises at the southeast end of the island. Working clockwise from the northwest, the following points are found on the island's coast. All were named by DI personnel unless otherwise specified. Resolution Point is a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60th Parallel South
The 60th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 60 degrees south of Earth's equatorial plane. No land lies on the parallel—it crosses nothing but ocean. The closest land is a group of rocks north of Coronation Island (Melson Rocks or Governor Islands) of the South Orkney Islands, which are about 54 km south of the parallel, and Thule Island and Cook Island of the South Sandwich Islands, which both are about 57 km north of the parallel (Thule island slightly closer). The parallel marks the northern limit of the Southern Ocean (though some organisations and countries, notably Australia, have other definitions) and of the Antarctic Treaty System. It also marks the southern boundary of the South Pacific Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone and the Latin American Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zone. At this latitude the sun is visible for 18 hours, 52 minutes during the December solstice and 5 hours, 52 minutes during the June solstice. On December 21, the sun is at 53.83 degrees up in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |