|
Warsaw Water Filters
Warsaw Water Filters, also known as Lindley's Filters (Polish – "Filtry Lindleya"), is one of three Warsaw waterworks, and is located in Ochota between Koszykowa, Krzywickiego, Filtrowa and Raszyńska streets. The waterworks was finished in 1886 using William Lindley's design. Since 1973, Warsaw Filters has been on the antiquities list. Construction Warsaw Filters was founded by the Mayor of Warsaw, Russian general Sokrates Starynkiewicz (Russian – Сократ Старинкевич). After his approval in 1881, construction started. The design by William Lindley consisted of the River Pump Station and a Filter Station on the left bank of the Vistula. During the construction, all available technologies were used, with even minor details made of high-quality resources. Basic materials used while building Filters were waterproof bricks, granite and sandstone. The first processed water was distributed to Warsaw citizens on July 3, 1886, from filters consisting of a group of slo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praga
Praga is a district of Warsaw, Poland. It is on the east bank of the river Vistula. First mentioned in 1432, until 1791 it formed a separate town with its own city charter. History The historical Praga was a small settlement located at the eastern bank of the Vistula river, directly opposite the towns of Old Warsaw and Mariensztat, both being parts of Warsaw now. First mentioned in 1432, it derived its name from the Polish verb ''prażyć'', meaning ''to burn'' or ''to roast'', as it occupied a forested area that was burnt out to make place for the village. Separated from Warsaw by a wide river, it developed independently of the nearby city, and on 10 February 1648 king Władysław IV of Poland granted Praga with a city charter. However, as it was mostly a suburb and most buildings were wooden, the town was repeatedly destroyed by fires, floods and foreign armies. Currently the only surviving historical monument from that epoch is the Church of Our Lady of Loreto. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narodowy Instytut Dziedzictwa
The National Institute of Cultural Heritage of Poland ( pl, Narodowy Instytut Dziedzictwa NID) is a Polish governmental institution responsible for documenting cultural property and the intangible cultural heritage, as well as for supporting and coordinating their protection."National Institute of Cultural Heritage" English-language websiteNarodowy Instytut Dziedzictwa, "O NID" ("About NID") Heritage lists The Institute coordinates at the national level the Registry of Cultural Property lists, maintained at the regional level by the voivodeship offices for cultural property protection (''wojewódzkie urzędy ochrony zabytów'') according to the ''Ordinance No 32'' of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomnik Historii
Historic Monument ( pl, pomnik historii) is one of several categories of objects of cultural heritage (in the singular, ''zabytek'') in Poland. To be recognized as a Polish historic monument, an object must be declared such by the President of Poland. The term "historic monument" was introduced into Polish law in 1990, and the first Historic Monuments were declared by President Lech Wałęsa in 1994. List The National Heritage Board of Poland The National Institute of Cultural Heritage of Poland ( pl, Narodowy Instytut Dziedzictwa NID) is a Polish governmental institution responsible for documenting cultural property and the intangible cultural heritage, as well as for supporting and ... maintains the official list. References {{reflist Objects of cultural heritage in Poland Law of Poland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historical Monuments (Poland)
Historic Monument ( pl, pomnik historii) is one of several categories of objects of cultural heritage in Poland, objects of cultural heritage (in the singular, ''zabytek'') in Poland. To be recognized as a Polish historic monument, an object must be declared such by the President of Poland. The term "historic monument" was introduced into Polish law in 1990, and the first Historic Monuments were declared by President Lech Wałęsa in 1994. List The National Heritage Board of Poland maintains the official list. References {{reflist Objects of cultural heritage in Poland Law of Poland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
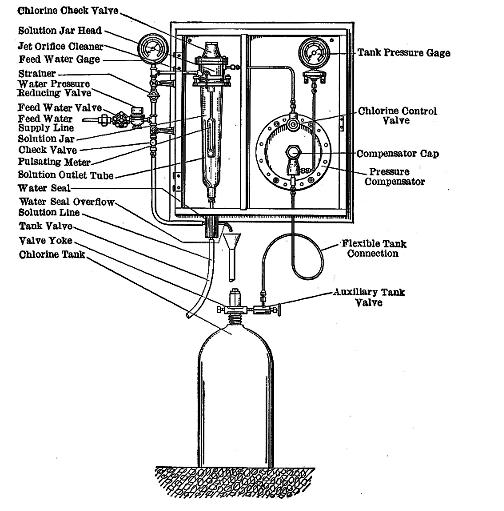
Water Chlorination
Water chlorination is the process of adding chlorine or chlorine compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to water. This method is used to kill bacteria, viruses and other microbes in water. In particular, chlorination is used to prevent the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid. History In a paper published in 1894, it was formally proposed to add chlorine to water to render it "germ-free". Two other authorities endorsed this proposal and published it in many other papers in 1895. Early attempts at implementing water chlorination at a water treatment plant were made in 1893 in Hamburg, Germany. In 1897 the town of Maidstone, England was the first to have its entire water supply treated with chlorine. Permanent water chlorination began in 1905, when a faulty slow sand filter and a contaminated water supply caused a serious typhoid fever epidemic in Lincoln, England. Alexander Cruickshank Houston used chlorination of the water to stop the epidem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expansion Vessel
An expansion tank or expansion vessel is a small tank used to protect closed (not open to atmospheric pressure) water heating systems and domestic hot water systems from excessive pressure. The tank is partially filled with air, whose compressibility cushions shock caused by water hammer and absorbs excess water pressure caused by thermal expansion. Description The modern vessel is a small container or tank divided in two by a rubber diaphragm. One side is connected to the pipe work of the heating system and therefore contains water. The other, the dry side, contains air under pressure, and normally a Schrader valve (car-tire type valve stem) for checking pressures and adding air. When the heating system is empty or at the low end of the normal range of working pressure, the diaphragm is pushed against the water inlet; as the water pressure increases, the diaphragm moves, compressing the air on its other side. An older style of expansion tank was larger, oriented horizontally, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imhoff Tank
The Imhoff tank, named for German engineer Karl Imhoff (1876–1965), is a chamber suitable for the reception and processing of sewage. It may be used for the clarification of sewage by simple settling and sedimentation, along with anaerobic digestion of the extracted sludge. It consists of an upper chamber in which sedimentation takes place, from which collected solids slide down inclined bottom slopes to an entrance into a lower chamber in which the sludge is collected and digested. The two chambers are otherwise unconnected, with the more liquid sewage flowing only through the upper sedimentation chamber and only a slow flow of sludge in the lower digestion chamber. The lower chamber requires separate biogas vents and pipes for the removal of digested sludge, typically after 6–9 months of digestion. The Imhoff tank is in effect a two-story septic tank and retains the septic tank's simplicity while eliminating many of its drawbacks, which largely result from the mixing of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powiśle, Warsaw
Powiśle (pronounced ; literally ''along-the-Vistula'') is a neighbourhood in Warsaw's borough of Śródmieście (Downtown). It is located between the Vistula river and its escarpment. Historically, it is composed of three neighbourhoods: central Powiśle, Mariensztat to the north (just below the Warsaw's Old Town) and Solec to the south. In the 17th and 18th centuries the area was mostly inhabited by the poor. Little changed in the 19th century when the neighbourhood became slightly industrialized. It retained the character of a city slum until its almost complete destruction during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944. It was inhabited by the unemployed and craftsmen of all types, factory and port workers, smiths, coalers, sand vendors, fishermen and prostitutes. As such it was similar in character to London Docklands. After the war, the area became partially rebuilt and the area of Mariensztat became the first neighbourhood of Warsaw to be reconstructed. Currently there are plans to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
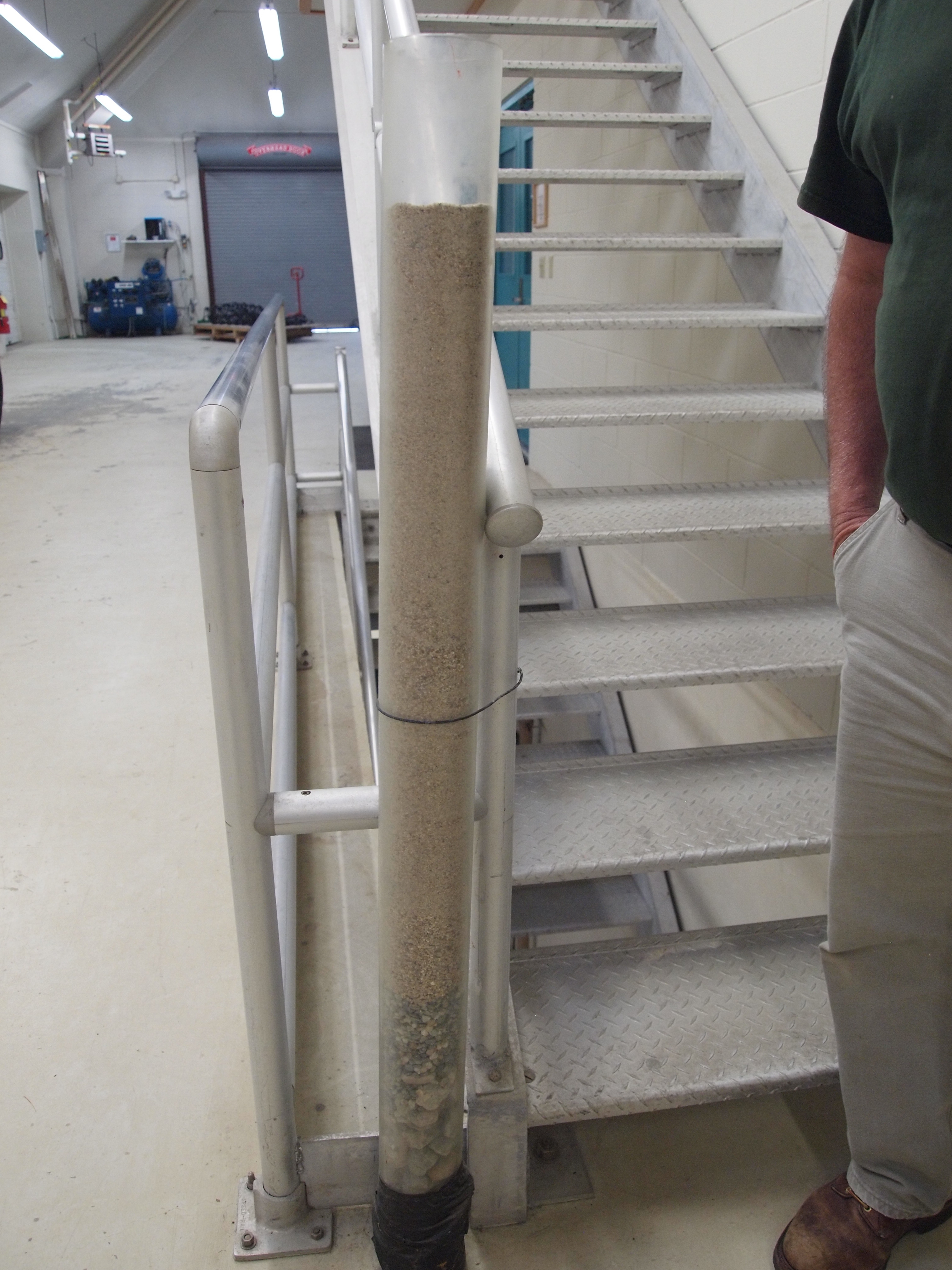
Slow Sand Filter
Slow sand filters are used in water purification for treating raw water to produce a potable product. They are typically deep, can be rectangular or cylindrical in cross section and are used primarily to treat surface water. The length and breadth of the tanks are determined by the flow rate desired by the filters, which typically have a loading rate of per square metre per hour. Slow sand filters differ from all other filters used to treat drinking water in that they work by using a complex biological film that grows naturally on the surface of the sand. The sand itself does not perform any filtration function but simply acts as a substrate, unlike its counterparts for ultraviolet and pressurized treatments. Although they are often preferred technology in many developing countries because of their low energy requirements and robust performance, they are also used to treat water in some developed countries, such as the UK, where they are used to treat water supplied to London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |