|
Walter Schottky
Walter Hans Schottky ( ; ; 23 July 1886 – 4 March 1976) was a German solid-state physicist who played a major early role in developing the theory of electron and ion emission phenomena, invented the screen-grid vacuum tube in 1915 while working at Siemens, co-invented the ribbon microphone and ribbon loudspeaker along with Dr. Erwin Gerlach in 1924, and later made many significant contributions in the areas of semiconductor devices, technical physics, and technology. The Schottky effect (a thermionic emission, important for vacuum tube technology), the Schottky diode (where the depletion layer occurring in it is called the Schottky barrier), the Schottky vacancies (or Schottky defects), the Schottky anomaly (a peak value of the heat capacity) and the Mott-Schottky equation (also Langmuir-Schottky space charge law) were named after him. He conducted research on electrical noise mechanisms (shot noise), space charge, especially in electron tubes, and the barrier lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The Urban agglomeration, urban area was home to 1.45 million people (2020), while the Zurich Metropolitan Area, Zurich metropolitan area had a total population of 2.1 million (2020). Zurich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zurich Airport and Zürich Hauptbahnhof, Zurich's main railway station are the largest and busiest in the country. Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zurich was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans, who called it '. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years (although this only indicates human presence in the area and not the presence of a town that early). During the Middle Ages, Zurich gained the independent and privileged status of imperial immediacy and, in 1519 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (; ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quantum, quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918. Planck made many substantial contributions to theoretical physics, but his fame as a physicist rests primarily on his role as the originator of Quantum mechanics, quantum theory and one of the founders of modern physics, which revolutionized understanding of atomic and Subatomic particle, subatomic processes. He is known for the Planck constant, which is of foundational importance for quantum physics, and which he used to derive a set of Unit of measurement, units, today called Planck units, expressed only in terms of fundamental physical constants. Planck was twice president of the German scientific institution Kaiser Wilhelm Society. In 1948, it was renamed the Max Planck Society (Max-Planck-Gesellschaft) and nowadays includes 83 institutions representing a wide range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Defects
A Schottky defect is an excitation of the site occupations in a crystal lattice leading to point defects named after Walter H. Schottky. In ionic crystals, this defect forms when oppositely charged ions leave their lattice sites and become incorporated for instance at the surface, creating oppositely charged vacancies. These vacancies are formed in stoichiometric units, to maintain an overall neutral charge in the ionic solid. Definition Schottky defects consist of unoccupied anion and cation sites in a stoichiometric ratio. For a simple ionic crystal of type A−B+, a Schottky defect consists of a single anion vacancy (A) and a single cation vacancy (B), or v + v following Kröger–Vink notation. For a more general crystal with formula AxBy, a Schottky cluster is formed of x vacancies of A and y vacancies of B, thus the overall stoichiometry and charge neutrality are conserved. Conceptually, a Schottky defect is generated if the crystal is expanded by one unit cell, whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Barrier
A Schottky barrier, named after Walter H. Schottky, is a potential energy barrier for electrons formed at a metal–semiconductor junction. Schottky barriers have rectifier, rectifying characteristics, suitable for use as a diode. One of the primary characteristics of a Schottky barrier is the Schottky barrier height, denoted by ΦB (see figure). The value of ΦB depends on the combination of metal and semiconductor. Not all metal–semiconductor junctions form a rectifying Schottky barrier; a metal–semiconductor junction that conducts current in both directions without rectification, perhaps due to its Schottky barrier being too low, is called an ohmic contact. Physics of formation When a metal is put in direct contact with a semiconductor, a so called Schottky barrier can be formed, leading to a rectifying behavior of the electrical contact. This happens both when the semiconductor is N-type (semiconductor), n-type and its work function is smaller than the work functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action. The cat's-whisker detectors used in the early days of wireless and metal rectifiers used in early power applications can be considered primitive Schottky diodes. When sufficient forward voltage is applied, a current flows in the forward direction. A silicon p–n diode has a typical forward voltage of 600–700 mV, while the Schottky's forward voltage is 150–450 mV. This lower forward voltage requirement allows higher switching speeds and better system efficiency. Construction A metal–semiconductor junction is formed between a metal and a semiconductor, creating a Schottky barrier (instead of a semiconductor–semiconductor junction as in conventional diodes). Typical metals used ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermionic Emission
Thermionic emission is the liberation of charged particles from a hot electrode whose thermal energy gives some particles enough kinetic energy to escape the material's surface. The particles, sometimes called ''thermions'' in early literature, are now known to be ions or electrons. Thermal electron emission specifically refers to emission of electrons and occurs when thermal energy overcomes the material's work function. After emission, an opposite charge of equal magnitude to the emitted charge is initially left behind in the emitting region. But if the emitter is connected to a battery, that remaining charge is neutralized by charge supplied by the battery as particles are emitted, so the emitter will have the same charge it had before emission. This facilitates additional emission to sustain an electric current. Thomas Edison in 1880 while inventing his light bulb noticed this current, so subsequent scientists referred to the current as the Edison effect, though it wasn't un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Effect
The Schottky effect or field enhanced thermionic emission is a phenomenon in condensed matter physics named after Walter H. Schottky. In electron emission devices, especially electron guns, the thermionic electron emitter will be biased negative relative to its surroundings. This creates an electric field of magnitude ''F'' at the emitter surface. Without the field, the surface barrier seen by an escaping Fermi-level electron has height ''W'' equal to the local work-function. The electric field lowers the surface barrier by an amount Δ''W'', and increases the emission current. It can be modeled by a simple modification of the Richardson equation, by replacing ''W'' by (''W'' − Δ''W''). This gives the equation :J (F,T,W) = A_ T^2 e^ :\Delta W = \sqrt, where ''J'' is the emission current density, ''T'' is the temperature of the metal, ''W'' is the work function of the metal, ''k'' is the Boltzmann constant, ''q''e is the Elementary charge, ''ε''0 is the vacuum perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as Kitchen utensil, utensils or machines, and intangible ones such as software. Technology plays a critical role in science, engineering, and everyday life. Technological advancements have led to significant changes in society. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used during prehistory, followed by the control of fire—which in turn contributed to the Brain size, growth of the human brain and the development of language during the Pleistocene, Ice Age, according to the cooking hypothesis. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age allowed greater travel and the creation of more complex machines. More recent technological inventions, including the printing press, telephone, and the Internet, have lowered barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical Physics
Engineering physics (EP), sometimes engineering science, is the field of study combining pure science disciplines (such as physics, mathematics, chemistry or biology) and engineering disciplines (computer, nuclear, electrical, aerospace, medical, materials, mechanical, etc.). In many languages, the term technical physics is also used. It has been used since 1861 by the German physics teacher in his publications. Terminology In some countries, both what would be translated as "engineering physics" and what would be translated as "technical physics" are disciplines leading to academic degrees. In China, for example, with the former specializing in nuclear power research (i.e. nuclear engineering), and the latter closer to engineering physics. In some universities and their institutions, an engineering physics (or applied physics) major is a discipline or specialization within the scope of engineering science, or applied science. Several related names have existed since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Device
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material (primarily silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors) for its function. Its conductivity lies between conductors and insulators. Semiconductor devices have replaced vacuum tubes in most applications. They conduct electric current in the solid state, rather than as free electrons across a vacuum (typically liberated by thermionic emission) or as free electrons and ions through an ionized gas. Semiconductor devices are manufactured both as single discrete devices and as integrated circuit (IC) chips, which consist of two or more devices—which can number from the hundreds to the billions—manufactured and interconnected on a single semiconductor wafer (also called a substrate). Semiconductor materials are useful because their behavior can be easily manipulated by the deliberate addition of impurities, known as dopin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. The driver is a linear motor connected to a diaphragm, which transmits the motor's movement to produce sound by moving air. An audio signal, typically originating from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is electronically amplified to a power level sufficient to drive the motor, reproducing the sound corresponding to the original unamplified signal. This process functions as the inverse of a microphone. In fact, the ''dynamic speaker'' driver—the most common type—shares the same basic configuration as a dynamic microphone, which operates in reverse as a generator. The dynamic speaker was invented in 1925 by Edward W. Kellogg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
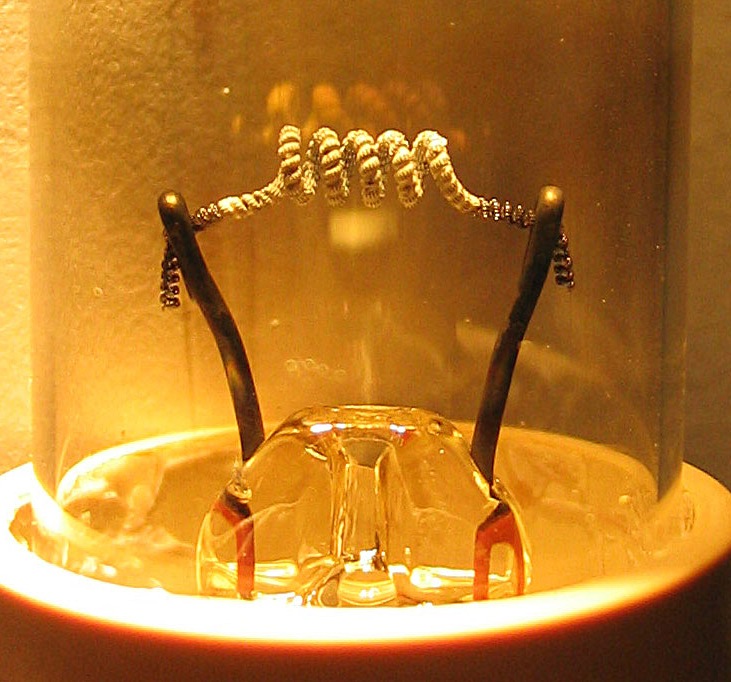
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |