|
Waiting For A Visa
''Waiting for a Visa'' is an autobiographical document written by B. R. Ambedkar during the period of 1935–36. The manuscript was published as a booklet, posthumously, on 19 March 1990, by the People's Education Society. The composition comprises a collection of anecdotes from Ambedkar himself and other individuals, intended to exemplify the practice of untouchability in Indian society. Contents The book consists of a brief introductory passage followed by six sections relating Ambedkar's experiences with untouchability, starting from his childhood. Sections 1, 2, 3 and 4 consist of Ambedkar's own experiences, while Sections 5 and 6 mainly consist of first-hand accounts of other people's experiences with untouchability, presented by Ambedkar. Introduction In a single-paragraph introduction, Ambedkar introduces the theme of the book, primarily aimed at foreigners and those who may not be familiar with the concept of untouchability. Section 1: A childhood journey to Goregaon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Education Society
People's Education Society (PES) was founded in 1972 with just over 40 students in a rented gymnasium in Bangalore, Karnataka. Today, PES has more than 18,000 students spread across multiple campuses in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th .... History People's Education Society (PES) was established under Mysore Societies Registration Act 1960 (Mysore Act No. 17 of 1960) on October 11, 1972, and was founded by Dr. M. R. Doreswamy. Mission statement Mission To provide students with a sense of history, an understanding of values and ethics, a commitment to law and morality, an appreciation of human creativity and an analytical inquiring mind. Vision To create professionally superior and ethically strong global workforce. Quality policy To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
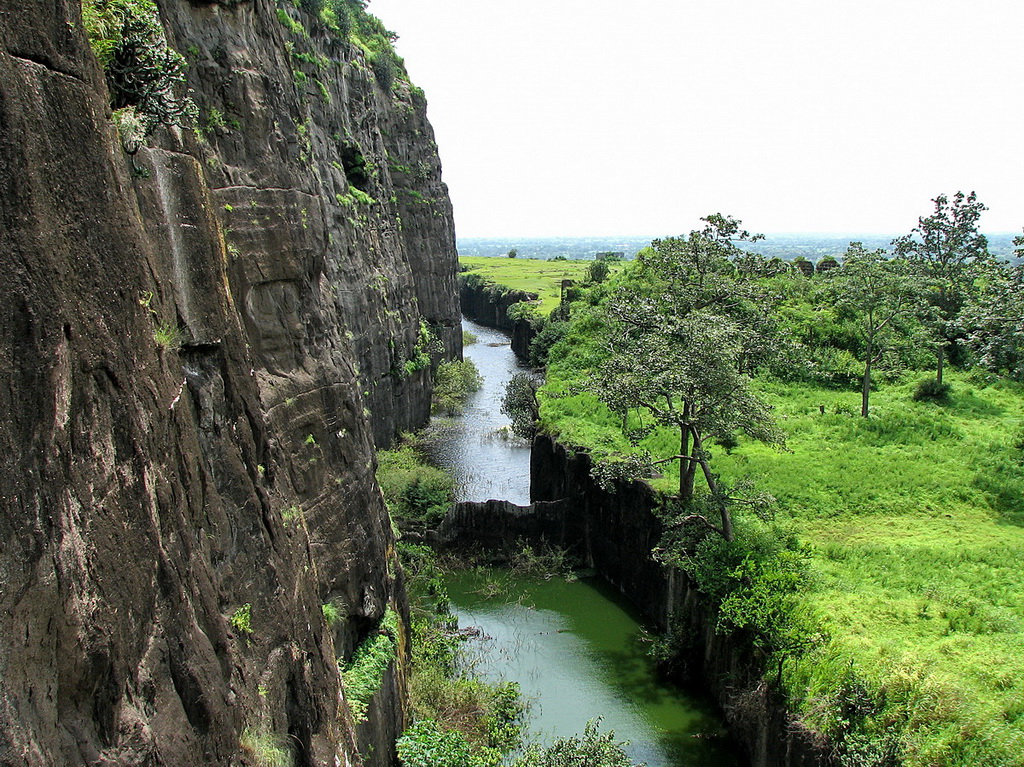
Daulatabad Fort
Daulatabad Fort, originally Deogiri Fort, is a historic fortified citadel located in Daulatabad village near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. It was the capital of the Yadavas (9th century – 14th century CE), for a brief time the capital of the Delhi Sultanate (1327–1334), and later a secondary capital of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate (1499–1636). Around the 6th century CE, Devagiri emerged as an important uplands town near present-day Sambhajinagar, along caravan routes going towards western and southern India. The historical triangular fortress in the city was initially built around 1187 by the first Yadava monarch, Bhillama V. In 1308, the city was annexed by Alauddin Khalji of the Delhi Sultanate, which ruled over some parts of the northern India. In 1327, Muhammad bin Tughluq of the Delhi Sultanate renamed Devagiri as Daulatabad and shifted his imperial capital to the city from Delhi, ordering a mass migration of Delhi's population to the now Daulatabad. However, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books By B
A book is a structured presentation of recorded information, primarily verbal and graphical, through a medium. Originally physical, electronic books and audiobooks are now existent. Physical books are objects that contain printed material, mostly of writing and images. Modern books are typically composed of many pages bound together and protected by a cover, what is known as the ''codex'' format; older formats include the scroll and the tablet. As a conceptual object, a ''book'' often refers to a written work of substantial length by one or more authors, which may also be distributed digitally as an electronic book (ebook). These kinds of works can be broadly classified into fiction (containing invented content, often narratives) and non-fiction (containing content intended as factual truth). But a physical book may not contain a written work: for example, it may contain ''only'' drawings, engravings, photographs, sheet music, puzzles, or removable content like paper dolls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kheda
Kheda is a city and a municipality in the Indian state of Gujarat. Kheda was known as Kaira during the British Raj. It was the former administrative capital of Kheda district. The city is known for tobacco farming. The nearest railway station is and the nearest airport is Ahmedabad Airport. History The name Kheda originated from the Sanskrit term ''Kshetra'' (). Khetaka is used as a name of a region surrounding the place in ancient literature. It is also mentioned as a town from 12th to 17th century. ''Ganapatha'' (dated 2nd century BCE), one of the five volumes of Pāṇini' s grammar mentions Khetaka as a name of the region. It is also mentioned as Divyanagar in 133rd chapter of '' Padmapurana''. The 7th and 8th century copper-plates of Maitraka dynasty mentions Khetaka as an administrative division as well as there are mentions of it as a place of Brahmin residence and a Rashtrakuta-controlled town in other copper-plates. There were about 750 villages under that admi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borsad
Borsad is a town and a municipality in Anand district in the state of Gujarat, India. It is located around 17 km from Anand. It is surrounded by the fertile Charotar region which largely produces tobacco, bananas, cotton, barley and other agricultural crops. Borsad was the seat of the Borsad satyagraha in 1922–23. History According to a legend Borsad was established as a hamlet by the efforts of a monk in 2nd Century A.D. and remained an important place ever since. It was declared a municipality in 1888 and in 1925, Indian political leader Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel and his allies uncovered evidence suggesting that the police were in league with local dacoits in the Borsad taluka even as the government prepared to levy a major tax for fighting dacoity in the area. More than 6,000 villagers assembled to hear Patel speak and supported the proposed agitation against the tax, which was deemed immoral and unnecessary. Patel organized hundreds of Congressmen, sent instructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talati
A village accountant or karanam (Andhra Pradesh), patwari (Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Telangana, West Bengal), patowary (Assam), talati (Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra), lekhpal (Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand) is a government role in rural areas of the Indian subcontinent. Introduced during the early 16th century, it was maintained by the British Raj. The official, as a representative of the state, is responsible for keeping land records, agricultural records and collecting taxes and acting as the revenue police in certain areas where they were given special jurisdiction. History Mughal emperor Akbar improved the ''patwari'' system, which had been introduced in the Indian subcontinent under the leadership of Sher Shah Suri. The East India Company and subsequently British crown continued with the system with some administrative changes. It denotes the office of the ''talati'' in rural Gujarat, Maharashtra and Karnataka. The office and its holder are known as Talatis, and holders of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
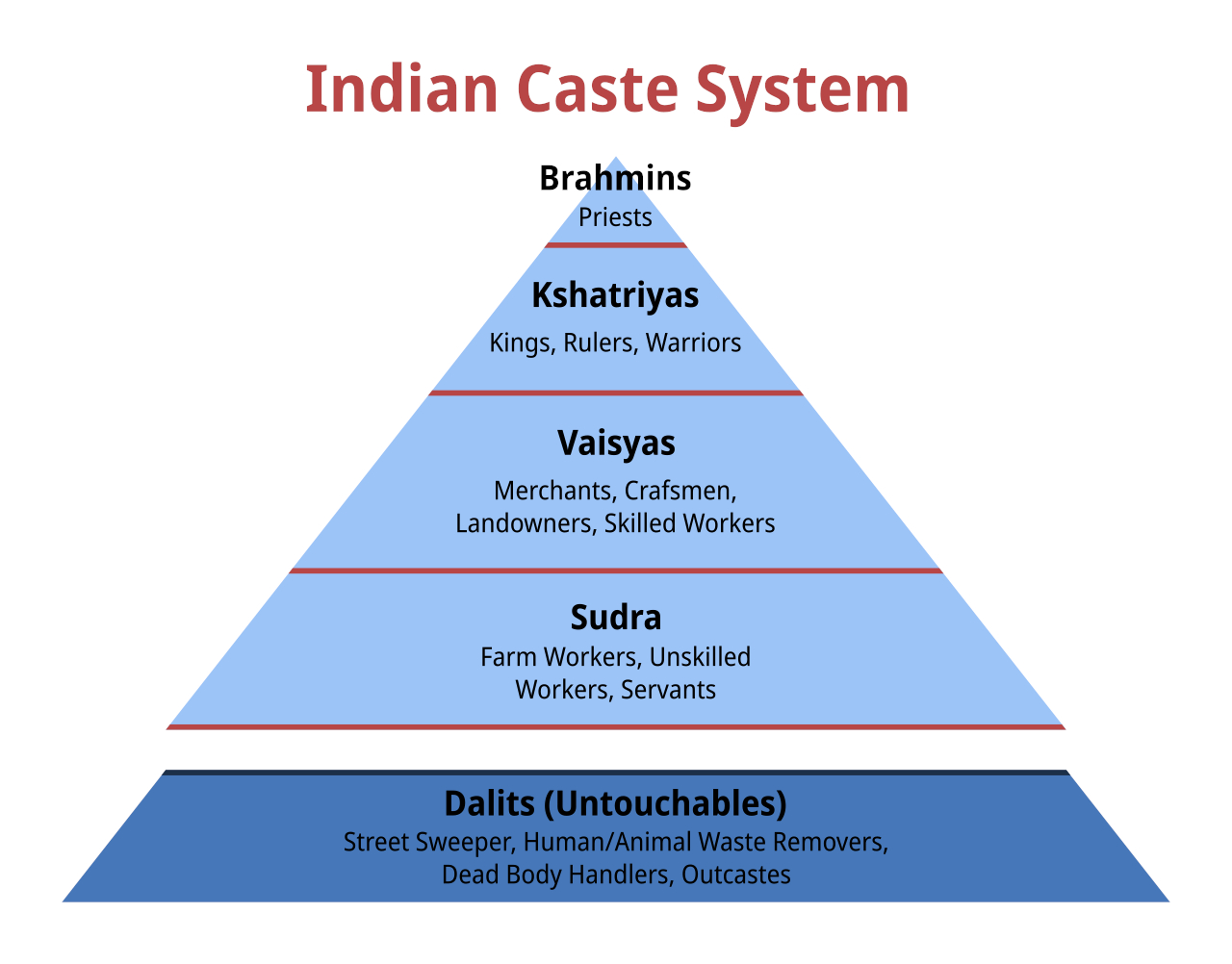
Bhangi
Chuhra, also known as Bhanghi and Balmiki, is a Dalit caste in India and Pakistan. Populated regions include the Punjab region of India and Pakistan, as well as Uttar Pradesh in India, among other parts of the Indian subcontinent such as southern India. Their traditional occupation is sweeping, a "polluting" occupation that caused them to be considered untouchables in the caste system. Originally following the Balmiki sect of Hinduism, many Chuhras converted to Sikhism, Islam and Christianity during the colonial era in India. Today, Chuhras in Indian Punjab are largely followers of Sikhism. A minority continue to follow Hinduism, which incorporates elements of Sikhism in its practices, as well as Christianity. In Pakistani Punjab 90–95% of its Christian population are Dalit Christians of the Chuhra caste; other Chuhras practice Islam or continue to follow Hinduism. Etymology and history The word "Chuhra" is derived from the word " Shudra", one of the varnas in Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and Microbiological culture, culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia. Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathiawar
Kathiawar (), also known as Saurashtra, is a peninsula in the south-western Gujarat state in India, bordering the Arabian Sea and covering about . It is bounded by the Kutch district in the north, the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest, and by the Gulf of Khambhat in the east. In the northeast, it is connected to the rest of the state and borders on the low, fertile hinterland of Ahmedabad. It is crossed by two belts of hill country and is drained radially by nine rivers which have little natural flow aside from in monsoon months, thus dams have been built on some of these. Kathiawar ports have been flourishing centres of trade and commerce since at least the 16th century. It was formerly a Saurashtra (state), state of India. Etymology and history The name Kathiawad seems to have been derived from the early settlements of Kathikas or Kathi people, Kathis who entered Gujarat from Sindh in early centuries of the Common Era. The name "Saurashtra" itself is from Sanskrit (, ), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harijan
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young India
''Young India'' was a book written by Lala Lajpat Rai in 1916 and later published by Mahatma Gandhi from 1919 to 1931. It was also the basis for Lala Lajpat Rai's contribution to the final edition of The Seven Arts in Oct 2017. Through this work, Mahatma Gandhi sought to popularize India's demand for independence or Swaraj. Gandhi used ''Young India'' to spread his unique ideology and thoughts regarding the use of nonviolence in organising movements and to urge readers to consider, organise, and plan for India's eventual independence from the British Empire. In 1933 Gandhi started publishing a weekly newspaper, '' Harijan'', in English. ''Harijan'', which means "People of God", was also Gandhi's term for the untouchable caste. The newspaper lasted until 1948. During this time Gandhi also published ''Harijan Bandu'' in Gujarati, and ''Harijan Sevak'' in Hindi Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammedan
''Mohammedan'' (also spelled ''Muhammadan'', ''Mahommedan'', ''Mahomedan'' or ''Mahometan'') is a term for a follower of Muhammad, the Islamic prophet. It is used as both a noun and an adjective, meaning belonging or relating to, either Muhammad or the religion, doctrines, institutions and practices that he established. The word was formerly common in usage, but the terms ''Muslim'' and ''Islamic'' are more common today. Though sometimes used stylistically by some Muslims, a vast majority consider the term archaic or a misnomer, as it suggests that Muslims worship Muhammad himself and not God. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' cites 1663 as the first recorded usage of the English term; the older spelling ''Mahometan'' dates back to at least 1529. The English word is derived from Neo-Latin ''Mahometanus'', from Medieval Latin ''Mahometus'', Muhammad. It meant simply a follower of Mohammad. In Western Europe, down to the 13th century or so, some Christians had the be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |