|
Wairakei
Wairakei is a small settlement and Geothermal activity, geothermal area 8-kilometres (5 mi) north of Taupō, in the centre of the North Island of New Zealand, on the Waikato River. It is part of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and features several natural geysers, hot pools, boiling mud pools, and the Wairakei Power Station, a major geothermal electric power generating station. The station was the second large-scale geothermal facility worldwide, and was commissioned in 1958. It was listed in the book ''70 Wonders Of The Modern World'' published in 2000 by Reader's Digest to record ''The Eventful 20th Century''. The settlement, referred to as Wairakei Village, was constructed to house the workers of both the power station and the neighbouring Aratiatia hydro power station. From 31 October 2022 it had buses to Taupō, Mondays to Fridays. Demographics Statistics New Zealand describes Wairakei Village as a rural settlement, which covers . and had an estimated population of as of with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wairakei Power Station
The Wairakei Power Station is a geothermal power station near the Wairakei Geothermal Field in New Zealand. Wairakei lies in the Taupō Volcanic Zone. History The power station was built in 1958, the first of its type (wet steam) in the world, and it is currently owned and operated by Contact Energy. A binary cycle power plant was constructed in 2005 to use lower-temperature steam that had already gone through the main plant. This increased the total capacity of the power station to 181 MW. The Wairakei power station is due to be phased out in 2027, replaced by the Te Mihi Power Station, Te Mihi geothermal power station. The Poihipi Power Station was built in 1996 at a nearby site in the same field. Units Wairakei A station * Unit 1 – 11.2 MW intermediate pressure * Unit 4 – 11.2 MW intermediate pressure * Unit 7 – 11.2 MW low pressure * Unit 8 – 11.2 MW low pressure * Unit 9 – 11.2 MW low pressure * Unit 10 – 11.2 MW low pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taupō
Taupō (), sometimes written Taupo, is a town located in the central North Island of New Zealand. It is situated on the edge of Lake Taupō, which is the largest freshwater lake in New Zealand. Taupō was constituted as a borough in 1953. It has been the seat of Taupō District Council since the council was formed in 1989. Taupō is the largest urban area of the Taupō District, and the second-largest urban area in the Waikato, Waikato region, behind Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton. It has a population of approximately Taupō is known for its natural beauty, with the surrounding area offering a range of outdoor recreational activities such as hiking, fishing, skiing, and water sports. Visitors can also enjoy a variety of attractions, including the Wairakei Power Station, Huka Falls, and the Tongariro National Park. Naming The name ''Taupō'' is from the Māori language and is a shortened version of ''Taupō-nui-a-Tia''. The longer name was first given to the cliff at Pākā B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craters Of The Moon (geothermal Site)
Craters of the Moon Thermal Area (or ''Karapiti'' in Māori language) is a region with geothermal activity north of Taupō, New Zealand. It is a part of Wairakei, the largest geothermal field in New Zealand, with a surface area of about 25 km2, which lies in the Taupō Volcanic Zone. The name springs from the many hydrothermal eruption craters, which are in part barren and which have bright colours. Combined with the numerous steam vents, constantly shifting, collapsing and reforming giving the whole area desolate appearance, and the sulphur smell, the whole area has an “unearthly” atmosphere. The craters are a relatively recent feature of the area and appeared as a result of human activity in the region. The site is Crown Land, administered by the Department of Conservation (New Zealand), Department of Conservation, with help from the ''Craters of the Moon Trust'', a volunteer organisation that provides information for visitors and passive vehicle security. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato River
The Waikato River is the longest river in New Zealand, running for through the North Island. It rises on the eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu, joining the Tongariro River system and flowing through Lake Taupō, New Zealand's largest lake. It then drains Taupō at the lake's northeastern edge, creates the Huka Falls, and flows northwest through the Waikato Plains. It empties into the Tasman Sea south of Auckland, at Port Waikato. It gives its name to the Waikato region that surrounds the Waikato Plains. The present course of the river was largely formed about 17,000 years ago. Contributing factors were climate warming, forest being reestablished in the river headwaters and the deepening, rather than widening, of the existing river channel. The channel was gradually eroded as far up river as Piarere, leaving the old Hinuera channel through the Hinuera Gap high and dry. The remains of the old course are seen clearly at Hinuera, where the cliffs mark the ancient river edges. The Wai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taupō Volcanic Zone
The Taupō Volcanic Zone (TVZ) is a volcano, volcanic area in the North Island of New Zealand. It has been active for at least the past two million years and is still highly active. Mount Ruapehu marks its south-western end and the zone runs north-eastward through the Taupō and Rotorua areas and offshore into the Bay of Plenty. It is part of a larger Central Volcanic Region that extends to the Coromandel Peninsula and has been active for four million years. The zone is contained within the Tectonics, tectonic intra-arc continental Taupō Rift and this rift volcanic zone is widening unevenly east–west, with the greatest rate of widening at the Bay of Plenty coast, the least at Mount Ruapehu and a rate of about per year at Taupō. The zone is named after Lake Taupō, the flooded caldera of the largest volcano in the zone, the Taupō Volcano and contains a large central North Island Volcanic Plateau, volcanic plateau as well as other landforms. Activity There are numerous vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taupō District
Taupō District is a territorial authority district in New Zealand. It covers 6,333 km² of land, and a further 610 km² of lake area, including Lake Taupō, New Zealand's largest lake, and Lake Rotoaira. The district stretches from the small town of Mangakino in the northwest to the Tongariro National Park in the south, and east into the Kaingaroa Forest. The district's population is largely located in the two main centres, Taupō and Tūrangi. Local government The district is governed by Taupō District Council. The vast majority of the district also falls within the jurisdiction of Waikato Regional Council, although parts are within the jurisdiction of the Bay of Plenty Regional Council and Manawatū-Whanganui Regional Council, and a tiny sliver is within the territory of the Hawke's Bay Regional Council. History Little is known about early Māori settlement near Taupō, although Ngāti Tūwharetoa have been the main iwi of the area for several hundred years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato Regional Council
The Waikato () is a Regions of New Zealand, region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipā District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki Plains, Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the northern King Country, much of the Taupō District, and parts of the Rotorua Lakes District. It is governed by the Waikato Regional Council. The Waikato stretches from Coromandel Peninsula in the north, to the north-eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu in the south, and spans the North Island from the west coast, through the Waikato and Hauraki to Coromandel Peninsula on the east coast. Broadly, the extent of the region is the Waikato River catchment. Other major catchments are those of the Waihou River, Waihou, Piako River, Piako, Awakino River (Waikato), Awakino and Mōkau River, Mōkau rivers. The region is bounded by Auckland Region, Auckland on the north, Bay of Plenty Region, Bay of Plen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 New Zealand Census
The 2018 New Zealand census, which took place on Tuesday 6 March 2018, was the thirty-fourth national census in New Zealand. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,699,755 – an increase of 457,707 (10.79%) over the 2013 census. Results from the 2018 census were released to the public on 23 September 2019, from the Statistics New Zealand website. The most recent New Zealand census was held in March 2023. History Background The ''Census Act 1877'' required censuses to be held every fifth year and is well embedded in legislation and government systems. Since 1881, censuses have been held every five years, with the exceptions of those in 1931 and 1941 and the one in 2011 which was cancelled due to the February 2011 earthquake in Christchurch, which displaced many Canterbury residents from their homes only a few weeks before census day. It was rescheduled for March 2013, so the 2013 census is the previous census completed before this one. Issues and controversies In Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Sign Language
New Zealand Sign Language or NZSL () is the main language of the deaf community in New Zealand. It became an official language of New Zealand in April 2006 under the New Zealand Sign Language Act 2006. The purpose of the act was to create rights and obligations in the use of NZSL throughout the legal system and to ensure that the Deaf community had the same access to government information and services as everybody else. According to the 2013 Census, over 20,000 New Zealanders know NZSL. New Zealand Sign Language has its roots in British Sign Language (BSL), and may be technically considered a dialect of British, Australian and New Zealand Sign Language (BANZSL). There are 62.5% similarities found in British Sign Language and NZSL, compared with 33% of NZSL signs found in American Sign Language. Like other natural sign languages, it was devised by and for deaf people, with no linguistic connection to a spoken or written language. NZSL uses the same two-handed manual alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
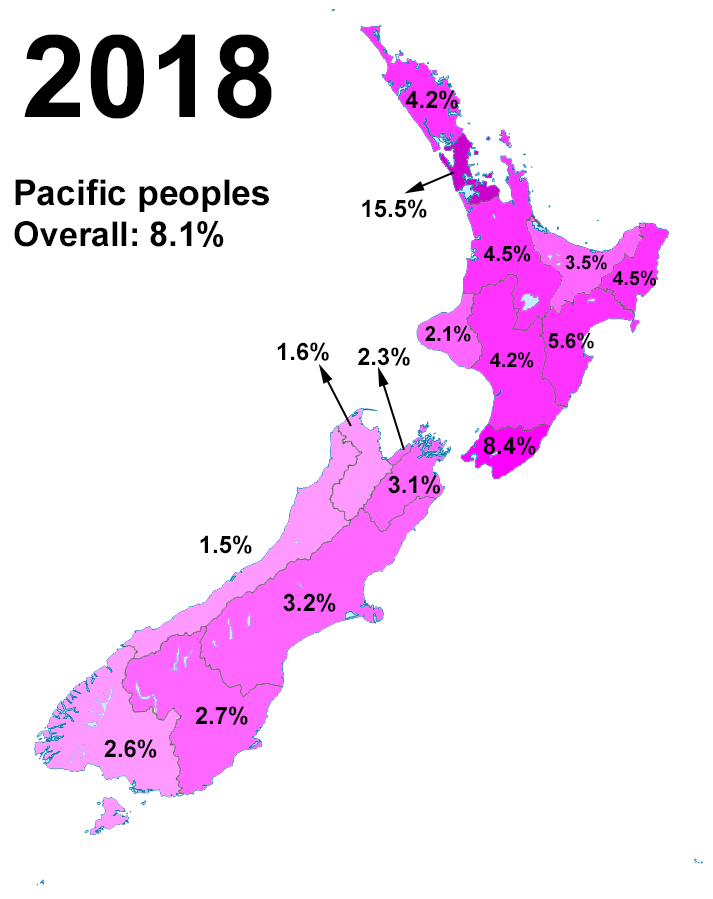
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |