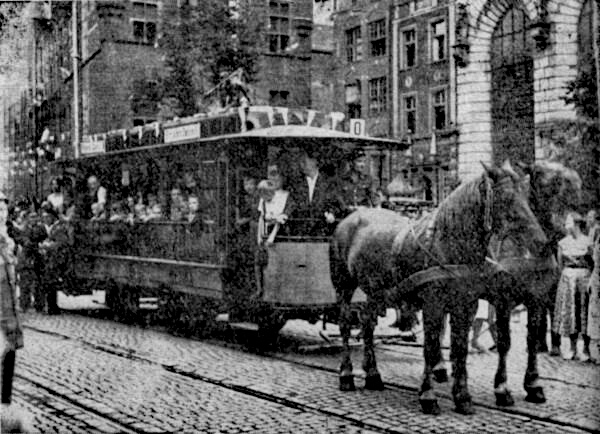|
Wagon
A wagon (or waggon) is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by Working animal#Draft animals, draft animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people. Wagons are immediately distinguished from carts (which have two wheels) and from lighter four-wheeled vehicles primarily for carrying people, such as carriages. Common animals which pull wagons are horses, mules, and oxen. One animal or several, often in pairs or teams may pull wagons. However, there are examples of human-propelled wagons, such as Corf (mining), mining corfs. A wagon was formerly called a wain and one who builds or repairs wagons is a Wainwright (occupation), wainwright. More specifically, a wain is a type of horse- or oxen-drawn, load-carrying vehicle, used for agricultural purposes rather than transporting people. A wagon or cart, usually four-wheeled; for example, a haywain, normally has four wheels, but the term has now acquired s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conestoga Wagon
The Conestoga wagon, also simply known as the Conestoga, is a horse-drawn freight wagon that was used exclusively in North America, primarily the United States, in the 18th and 19th centuries. Such wagons were probably first used by Pennsylvania Dutch settlers in the early 18th century. Named for the Conestoga River, such wagons were in use as early as 1717. Conestoga wagons are larger, heavier versions of covered wagons, covered by Hemp#Fiber, hemp cloths stretched over hoops, with large wheels for traveling over primitive roads, and curved sides and floor to keep the contents centered. They were pulled by a team of four to six horses. The first examples of this type may have been built at home by farmers but later were produced commercially by wainwright (occupation), wagon makers and wheelwrights. Conestoga wagons were used to carry up to of produce or manufactured goods between farms and towns. They were most often used in the northeast United States, especially Pennsylvani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Wagon Road
The Great Wagon Road, also known as the Philadelphia Wagon Road, is a historic trail in the eastern United States that was first traveled by indigenous tribes, and later explorers, settlers, soldiers, and travelers. It extended from British Pennsylvania to North Carolina, through the Great Appalachian Valley, and from there to Georgia. History The heavily traveled Great Wagon Road was the primary route for the early settlement of the Southern United States, particularly the " backcountry". Although a wide variety of settlers traveled southward on the road, two dominant cultures emerged. The German Palatines and Scotch-Irish immigrants arrived in huge numbers because of bloody religious conflicts and persecution of Protestants by monarchies in Great Britain and Europe. The mostly Protestant German Palatines (also known as Pennsylvania Dutch) tended to find rich farmland and work it zealously to become stable and prosperous. The other group, mostly Protestant Presbyterians know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covered Wagon
A covered wagon, also called a prairie wagon, whitetop, or prairie schooner, is a horse-drawn or ox-drawn wagon used for passengers or freight hauling. It has a canvas, tarpaulin, or waterproof sheet which is stretched over removable wooden bows (also called hoops or tilts) and lashed to the body of the wagon. They were a popular style of vehicle for overland migrations. Conestoga wagon The Conestoga wagon was a heavy American wagon of English and German type from the late 18th century and into the 19th century. It was used for freight and drawn by teams of horses or oxen depending on load. The covered canvas top was supported on eight to twelve angled bows, rather than upright. Capacity was around 4 to 5 tons with no springs. Though it was boat-shaped it did not float. It was used in eastern North America for freight hauling, with some used for southward migration through the Appalachian valleys and along the Great Wagon Road. It was too heavy for use west of the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ox-wagon
An ox-wagon or bullock wagon is a four-wheeled vehicle pulled by oxen (draught cattle). It was a traditional form of transport, especially in Southern Africa but also in New Zealand and Australia. Ox-wagons were also used in the United States. The first recorded use of an ox-wagon was around 1670, but they continue to be used in some areas up to modern times. Design Ox-wagons are typically drawn by teams of oxen, harnessed in pairs. This gave them a very wide turning circle, the legacy of which are the broad, pleasant boulevards of cities such as Bulawayo, Zimbabwe, which are wide, and Grahamstown, South Africa, which are "wide enough to turn an ox-wagon". The wagon itself is made of various kinds of wood, with the rims of the wheels being covered with tyres of iron, and since the middle of the 19th century the axles have also been made of iron. The back wheels are usually substantially larger than the front ones and rigidly connected to the tray of the vehicle. The front wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse-drawn Vehicle
A horse-drawn vehicle is a piece of equipment pulled by one or more horses. These vehicles typically have two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have mostly been replaced by automobiles and other forms of self-propelled transport but are still in use today. General Horses were domesticated circa 2000 BCE. Before that oxen were used. Historically, a wide variety of arrangements of horses and vehicles have been used, from chariot racing, which involved a small vehicle and four horses abreast, to horsecars or trollies, which used two horses to pull a car that was used in cities before electric trams were developed. A two-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle is a cart (see various types below, both for carrying people and for goods). Four-wheeled vehicles have many names – one for heavy loads is most commonly called a wagon. Very light carts and wagons can also be pulled by Donkey, donkeys (much smaller than horses), pony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriage
A carriage is a two- or four-wheeled horse-drawn vehicle for passengers. In Europe they were a common mode of transport for the wealthy during the Roman Empire, and then again from around 1600 until they were replaced by the motor car around 1900. They were generally owned by the rich, but second-hand private carriages became common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping or, on those made in recent centuries, steel springs. There are numerous names for different types. Two-wheeled carriages are usually owner-driven. Coaches are a special category within carriages. They are carriages with four corner posts and a fixed roof. Two-wheeled war chariots and transport vehicles such as four-wheeled wagons and two-wheeled carts were forerunners of carriages. In the 21st century, horse-drawn carriages are occasionally used for public parades by royalty and for traditional formal ceremonies. Simplified modern versio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-mule Team
Twenty-mule teams were teams of eighteen mules and two horses attached to large wagons that transported borax out of Death Valley from 1883 to 1898. They traveled from mining, mines across the Mojave Desert to the nearest Rail transport, railroad spur, away in Mojave, California, Mojave. The routes were from the Harmony and Amargosa Borax Works to Daggett, California, and later Mojave, California. After Harmony and Amargosa shut down in 1888, the mule team's route was moved to the mines at Borate, east of Calico, San Bernardino County, California, Calico, back to Daggett. There they worked from 1891 until 1898 when they were replaced by the Borate and Daggett Railroad. The wagons were among the largest ever pulled by draft animals, designed to carry 10 short tons (9 tonne, metric tons) of borax ore at a time. History In 1877, six years before twenty-mule teams would be introduced in Death Valley, ''Scientific American'' reported that Francis Marion Smith and his brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Axle Assembly
Turning radius was a longstanding problem with wagons, dictated by the distance between the front wagon wheels and the bed of the wagon—namely, the point where the rotating wheels collide with the side of the wagon when turning. Many earlier designs required a very large turning radius; however, shrinking the width of the bed means decreasing the size of the load. As this is a problem that carts (by virtue of their two-wheeled nature) do not face, this factor, combined with their lighter weight, meant that carts were long preferred over wagons for many uses. The general solutions to this problem involved several modifications to the front-axle assembly. The front axle assembly of a wagon consists of an axle, a pair of wheels and a round plate with a kingpin in its centre that sits halfway between the wheels, which may be mounted on spindles. A round plate with a hole in its centre is located on the underside of the wagon. The plate on the wagon, in turn, sits on the plate on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving (horse)
Driving means guiding a horse in Horse harness, harness to pull a load such as a horse-drawn vehicle, a farm implement, or other load. Horses, pony, ponies, donkeys, mules, and Working animal#Draft animals, other animals can be driven. Typical horse-drawn vehicles are wagons, carriages, carts, and sleighs. Driving activities include pleasure driving, racing, farm work, Horse show, showing horses, and other competitions. Styles For horse training purposes, "driving" may also include the practice of ''long-lining'' (''long reining''), wherein a horse is driven without a cart by a handler walking behind or behind and to the side of the animal. This technique is used in the early stages of training horses for riding as well as for driving. Horses, mules and donkeys are driven in horse harness, harness in many different ways. For working purposes, they can pull a plow or other farm equipment designed to be pulled by animals. In many parts of the world they still pull carts, wagons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullocky
A bullocky is an Australian English term for the driver of a bullock team. The American term is bullwhacker. Bullock drivers were also known as teamsters or carriers. History Bullock teams were in use in Sydney in 1795 when they were used for hauling building materials. The early explorers, Hume and Hovell in 1824 and Charles Sturt, later in 1828-9, also used bullock teams during their explorations.Chisholm, Alec H. (ed.), The Australian Encyclopaedia, Vol. 2, "Bullock-driving", Halstead Press, Sydney, 1963 Before the gold rushes in Australia, in the mid 19th century, bullock drays carried essential food and station supplies to isolated country areas. On return trips they transported wheat, wool, sugar cane, and timber by drays drawn by teams of draught animals (either bullocks or horses) to shipping ports before the advent of rail. They travelled constantly across the landscape, servicing the pastoral stations and settlements far from regional transport hubs and urban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teamster
A teamster in American English is a truck driver; a person who drives teams of draft animals; or a member of the International Brotherhood of Teamsters, a labor union. In some places, a teamster was called a carter, the name referring to the bullock cart. Originally the term ''teamster'' meant a person who drove a team, usually of oxen, horses, or mules, pulling a wagon, replacing the earlier ''teamer''. This term was common by the time of the Mexican–American War (1848) and the Indian Wars throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries on the American frontier. Another name for the occupation was ''bullwhacker'', related to driving oxen. A teamster might also drive pack animals, such as a muletrain, in which case he was also called a muleteer or muleskinner. Today this person may be called an outfitter or packer. In Australian English, a teamster was also called a bullocker or bullocky and was sometimes used to denote a carrier. From the Revolutionary War at le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |