|
WR 124
WR 124 is a Wolf–Rayet star in the constellation of Sagitta surrounded by a ring nebula of expelled material known as M1-67. It is one of the fastest runaway stars in the Milky Way with a radial velocity around . It was discovered by Paul W. Merrill in 1938, identified as a high-velocity Wolf–Rayet star. It is listed in the General Catalogue of Variable Stars as QR Sagittae with a range of 0.08 magnitudes. Distance A 2010 study of WR 124 directly measured the expansion rate of the M1-67 nebula expelled from the star using Hubble Space Telescope camera images taken 11 years apart, and compared that to the expansion velocity measured by the Doppler shift of the nebular emission lines. This yielded a distance of , which is less than previous studies, and the resulting luminosity of 150,000 times the Sun () is much lower than previously calculated. The luminosity is also lower than predicted by models for a star of this spectral class. Previous studies had found distances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolometric Luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object. In SI units, luminosity is measured in joules per second, or watts. In astronomy, values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the luminosity of the Sun, ''L''⊙. Luminosity can also be given in terms of the astronomical magnitude system: the absolute bolometric magnitude (''M''bol) of an object is a logarithmic measure of its total energy emission rate, while absolute magnitude is a logarithmic measure of the luminosity within some specific wavelength range or filter band. In contrast, the term ''brightness'' in astronomy is generally used to refer to an object's apparent brightness: that is, how bright an object appears to an observer. Apparent brightness depends on both the lumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
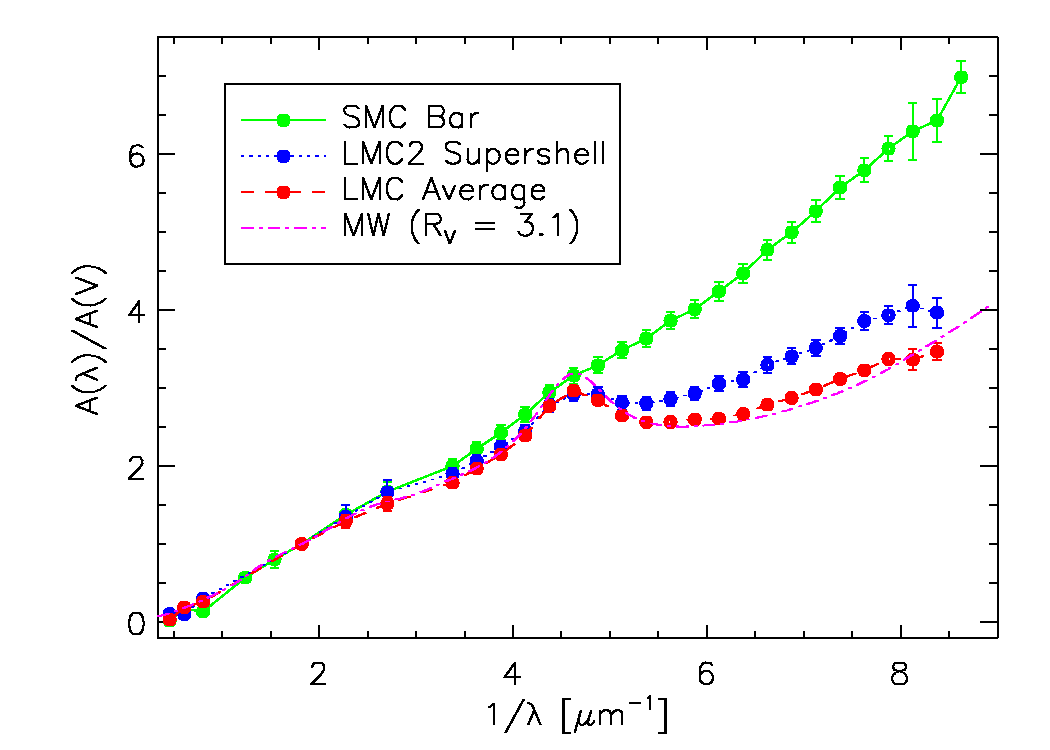
Extinction (astronomy)
In astronomy, extinction is the absorption and scattering of electromagnetic radiation by dust and gas between an emitting astronomical object and the observer. Interstellar extinction was first documented as such in 1930 by Robert Julius Trumpler. However, its effects had been noted in 1847 by Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and its effect on the colors of stars had been observed by a number of individuals who did not connect it with the general presence of galactic dust. For stars that lie near the plane of the Milky Way and are within a few thousand parsecs of the Earth, extinction in the visual band of frequencies (photometric system) is roughly 1.8 magnitudes per kiloparsec. For Earth-bound observers, extinction arises both from the interstellar medium (ISM) and the Earth's atmosphere; it may also arise from circumstellar dust around an observed object. Strong extinction in earth's atmosphere of some wavelength regions (such as X-ray, ultraviolet, and infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it were viewed from a distance of exactly , without extinction (or dimming) of its light due to absorption by interstellar matter and cosmic dust. By hypothetically placing all objects at a standard reference distance from the observer, their luminosities can be directly compared among each other on a magnitude scale. As with all astronomical magnitudes, the absolute magnitude can be specified for different wavelength ranges corresponding to specified filter bands or passbands; for stars a commonly quoted absolute magnitude is the absolute visual magnitude, which uses the visual (V) band of the spectrum (in the UBV photometric system). Absolute magnitudes are denoted by a capital M, with a subscript representing the filter band used for mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaia Early Data Release 3
The ''Gaia'' catalogues are star catalogues created using the results obtained by ''Gaia'' space telescope. The catalogues are released in stages that will contain increasing amounts of information; the early releases also miss some stars, especially fainter stars located in dense star fields. Data from every data release can be accessed at the ''Gaia'' archive. Initial Gaia Source List The Initial Gaia Source List (IGSL) is a star catalogue of 1.2 billion objects created in support of the ''Gaia'' mission. The mission should have delivered a catalogue based entirely on its own data. For the first catalogue, Gaia DR1, a way was needed to be able to assign the observations to an object and to compare them with the objects from other star catalogues. For this purpose, a separate catalog of objects from several other catalogues was compiled, which roughly represents the state of knowledge of astronomy at the beginning of the Gaia mission. Attitude Star Catalog The Attitude Star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects when observed from different positions, so parallax can be used to determine distances. To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder. Parallax also affects opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydrostatic equilibrium, where outward thermal pressure from the hot core is balanced by the inward pressure of gravitational collapse from the overlying layers. The strong dependence of the rate of energy ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object. In SI units, luminosity is measured in joules per second, or watts. In astronomy, values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the luminosity of the Sun, ''L''⊙. Luminosity can also be given in terms of the astronomical magnitude system: the absolute bolometric magnitude (''M''bol) of an object is a logarithmic measure of its total energy emission rate, while absolute magnitude is a logarithmic measure of the luminosity within some specific wavelength range or filter band. In contrast, the term ''brightness'' in astronomy is generally used to refer to an object's apparent brightness: that is, how bright an object appears to an observer. Apparent brightness depends on both the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |