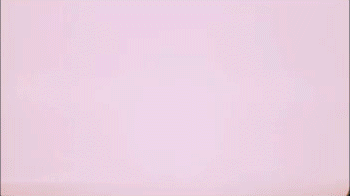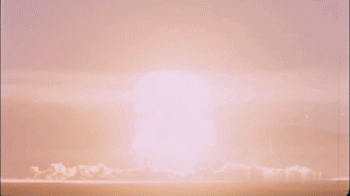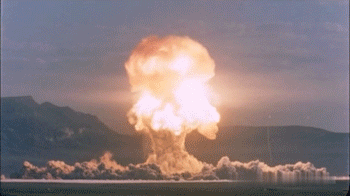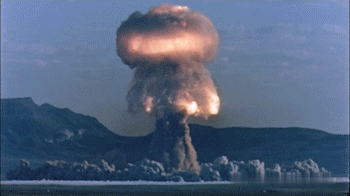|
W9 (nuclear Warhead)
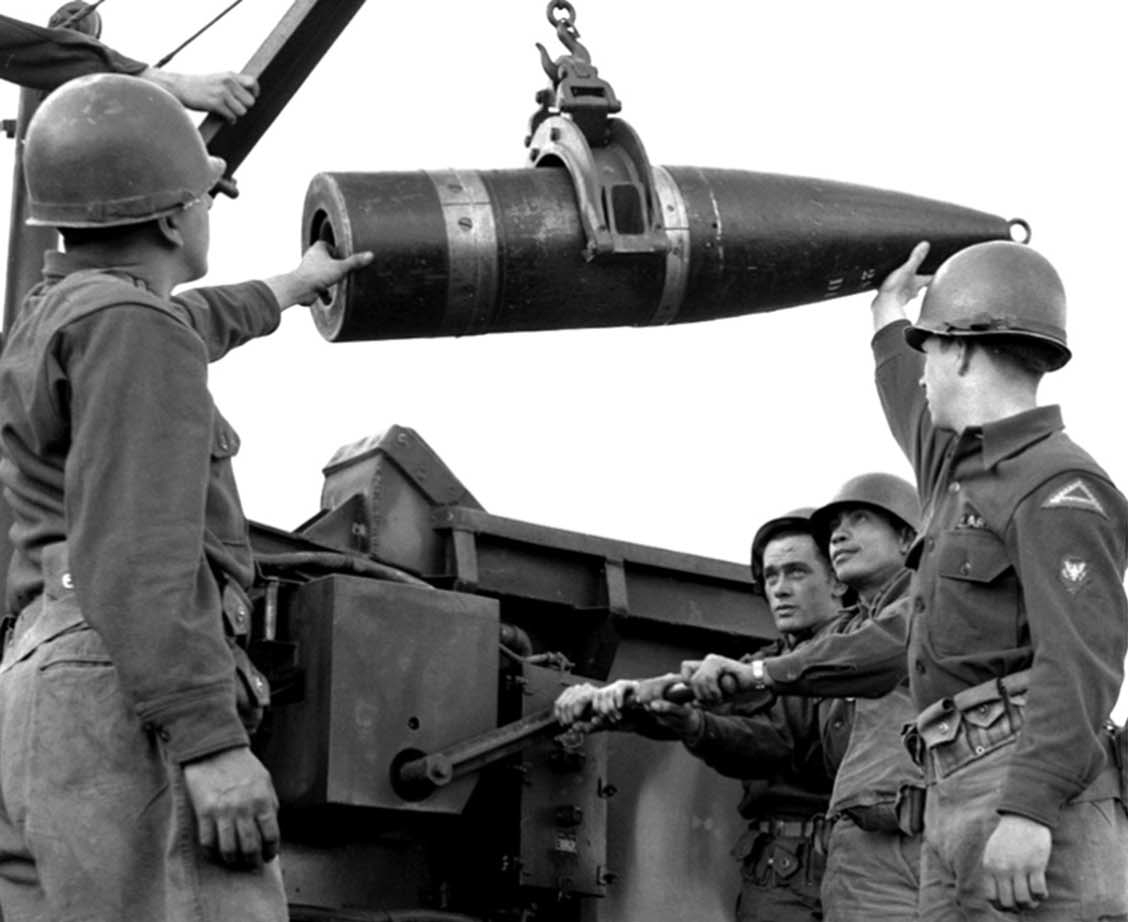
The W9 was an American nuclear artillery shell fired from a special howitzer. It was produced starting in 1952 and all were retired by 1957, being superseded by the W19 (nuclear artillery shell), W19. Description The W9 was in diameter, long, and weighed . It had an explosive yield of . The W9 was a gun-type fission weapon, gun-type nuclear weapon, using around of enriched uranium, highly enriched uranium in one large rings assembly and one smaller ''bullet'', which was fired down a tube by conventional explosives into the rings assembly to achieve critical mass and detonate the weapon. The W9 units which were retired in 1957 were recycled into lower yield T-4 Atomic Demolition Munitions. These were the first (semi) man-portable nuclear weapons. Tests The W9 is only the second gun-type nuclear weapon known to have been detonated; the first was the Little Boy nuclear weapon used in World War II. The W9 artillery shell was test fired once, fired from the "Atomic Annie" M6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W33 (nuclear Weapon)
The W33 (also known as the Mark 33, T317 and M422) was an American nuclear artillery shell designed for use in the M110 howitzer and M115 howitzer. A total of 2,000 W33 projectiles were produced, with the first production warheads entering the stockpile in 1957. The W33 remained in service until 1992. The warhead used enriched uranium (code named ''oralloy'') as its nuclear fissile material and could be used in two different yield configurations. This required the assembly and insertion of different pits, with the amount of fissile materials used controlling whether the destructive yield was low or high. The highest-yield version of the W33 may have been a boosted fission weapon. History Development of the W33 was authorized by the Army Ordnance Corps in June 1953. It was believed that a shell capable of being fired by a standard mobile field howitzer would be more effective while also providing a psychological effect in ground warfare. The design would also include considera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
W9 AFAP
W9 may refer to: Transportation * Wizz Air UK (IATA code: W9) * Air Bagan (former IATA code: W9), a former airline of Myanmar * London Buses route W9, England Other uses * Form W-9, used by the US federal government for tax purposes * W9, a postcode district in the W postcode area, England * W9 (TV channel), a French television channel * W9 (nuclear warhead), an American nuclear artillery shell * Japanese minesweeper ''W-9'', several ships * Niland Geyser Niland Geyser (nicknamed the "Slow One" and formally designated W9) is a moving mudpot or mud spring outside Niland, California in the Salton Trough in an area of geological instability due to the San Andreas Fault, formed due to carbon dioxide ... (scientific designation), California, US See also * 9W (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Warheads Of The United States
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: *Nuclear engineering *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator * Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society *Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music * "Nuclear" (band), chilean thrash metal band * "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album * ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC Films * ''Nuclear'' (film), a 2022 documentary by Oliver Stone. See also *Nucleus (other) *Nucleolus *Nucleation *Nucleic acid *Nucular ''Nucular'' is a common, proscribed pronunciation of the word "nuclear". It is a rough phonetic spelling of . The ''Oxford English Dictionary''s entry dates the word's first published appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Weapons
This is a list of nuclear weapons listed according to country of origin, and then by type within the states. The United States, Russia, China and India are known to possess a nuclear triad, being capable to deliver nuclear weapons by land, sea and air. United States American nuclear weapons of all types – bombs, warheads, shells, and others – are numbered in the same sequence starting with the Mark 1 and () ending with the W91 (which was cancelled prior to introduction into service). All designs which were formally intended to be weapons at some point received a number designation. Pure test units which were experiments (and not intended to be weapons) are not numbered in this sequence. Early weapons were very large and could only be used as free fall bombs. These were known by "Mark" designators, like the Mark 4 which was a development of the Fat Man weapon. As weapons became more sophisticated they also became much smaller and lighter, allowing them to be used in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Artillery
Nuclear artillery is a subset of limited-nuclear weapon yield, yield tactical nuclear weapons, in particular those weapons that are launched from the ground at battlefield targets. Nuclear artillery is commonly associated with shell (projectile), shells delivered by a cannon, but in a technical sense short-range artillery rockets or tactical ballistic missiles are also included. The development of nuclear artillery was part of a broad push by nuclear weapons countries to develop nuclear weapons which could be used tactically against enemy armies in the field (as opposed to strategic uses against cities, military bases, and heavy industry). Nuclear artillery was both developed and deployed by a small group of State (polity), states, including the United States, the Soviet Union, and France. The United Kingdom planned and partially developed such weapon systems (the Blue Water (missile), Blue Water missile and the Yellow Anvil, Yellow Anvil artillery shell) but did not put them i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom Cloud
A mushroom cloud is a distinctive mushroom-shaped flammagenitus cloud of debris, smoke, and usually condensed water vapour resulting from a large explosion. The effect is most commonly associated with a nuclear explosion, but any sufficiently energetic detonation or deflagration will produce a similar effect. They can be caused by powerful conventional weapons, including thermobaric weapons such as the Father of All Bombs, ATBIP and GBU-43/B MOAB. Some Eruption column, volcanic eruptions and impact events can produce natural mushroom clouds. Mushroom clouds result from the sudden formation of a large volume of lower-density gases at any altitude, causing a Rayleigh–Taylor instability. The buoyant mass of gas rises rapidly, resulting in turbulent vortices curling downward around its edges, forming a temporary vortex ring that draws up a central column, possibly with smoke, debris, condensed water vapor, or a combination of these, to form the "mushroom stem". The mass of gas plu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui has been the city's mayor since April 2011. The Hiroshima metropolitan area is the second largest urban area in the Chugoku Region of Japan, following the Okayama metropolitan area. Hiroshima was founded in 1589 as a Jōkamachi, castle town on the Ōta River river delta, delta. Following the Meiji Restoration in 1868, Hiroshima rapidly transformed into a major urban center and industrial hub. In 1889, Hiroshima officially gained city status. The city was a center of military activities during the Empire of Japan, imperial era, playing significant roles such as in the First Sino-Japanese War, the Russo-Japanese War, and the two world wars. Hiroshima was the first military target of a nuclear weapon in history. This occurred on August 6, 1945, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Plumbbob
Operation Plumbbob was a series of nuclear tests that were conducted between May 28 and October 7, 1957, at the Nevada Test Site, following ''Project 57'', and preceding '' Project 58/58A''. Background The operation consisted of 29 explosions, of which only two did not produce any nuclear yield. Twenty-one laboratories and government agencies were involved. While most ''Operation Plumbbob'' tests contributed to the development of warheads for intercontinental and intermediate range missiles, they also tested air defense and anti-submarine warheads with smaller yields. They included 43 military effects tests on civil and military structures, radiation and bio-medical studies, and aircraft structural tests. ''Operation Plumbbob'' had the tallest tower tests to date in the U.S. nuclear testing program as well as high-altitude balloon tests. One nuclear test involved the largest troop maneuver ever associated with U.S. nuclear testing. Approximately 18,000 members of the U.S. Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Nougat
Operation Nougat was a series of 44 nuclear tests conducted (with one exception) at the Nevada Test Site in 1961 and 1962, immediately after the Soviet Union abrogated a testing moratorium, with the US' ''Mink'' test shot taking place the day before the Soviets test-detonated the Tsar Bomba. Most tests were limited-yield underground test shots. New designs would be further developed in atmospheric testing during '' Operation Dominic I and II''. '' Operation Dominic I and II'' would follow ''Operation Nougat'', with some testing overlap. '' Operation Hardtack II'' preceded Nougat and the testing moratorium. Tests Antler Antler was the first shot fired as part of the resumption of nuclear testing by the United States. Fired 15 September 1961, containment was immediately lost when the shot vented via the tunnel portal, destroying much of the test data. This was a recurring problem for tunnel tests of the era. The problem was thought to be caused by water above the blast zone drai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada Test Site
The Nevada National Security Sites (N2S2 or NNSS), popularized as the Nevada Test Site (NTS) until 2010, is a reservation of the United States Department of Energy located in the southeastern portion of Nye County, Nevada, about northwest of the city of Las Vegas. Formerly known as the Nevada Proving Grounds of the United States Army, the site was acquired in 1951 to be the testing venue for the American nuclear devices. The first atmospheric test was conducted at the site's Frenchman Flat area by the United States Atomic Energy Commission (USAEC) on January 27, 1951. About 928 nuclear tests were conducted here through 1994, when the United States stopped its underground nuclear testing. The site consists of about of desert and mountainous terrain. Some 1,100 buildings in 28 areas are connected by of paved roads, of unpaved roads, ten heliports, and two airstrips. The site is privately managed and operated by Mission Support and Test Services LLC, a joint venture of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Artillery
Nuclear artillery is a subset of limited-nuclear weapon yield, yield tactical nuclear weapons, in particular those weapons that are launched from the ground at battlefield targets. Nuclear artillery is commonly associated with shell (projectile), shells delivered by a cannon, but in a technical sense short-range artillery rockets or tactical ballistic missiles are also included. The development of nuclear artillery was part of a broad push by nuclear weapons countries to develop nuclear weapons which could be used tactically against enemy armies in the field (as opposed to strategic uses against cities, military bases, and heavy industry). Nuclear artillery was both developed and deployed by a small group of State (polity), states, including the United States, the Soviet Union, and France. The United Kingdom planned and partially developed such weapon systems (the Blue Water (missile), Blue Water missile and the Yellow Anvil, Yellow Anvil artillery shell) but did not put them i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |