|
W. W. Ryland
William Wynne Ryland (1732 or July 173829 August 1783) was an English engraver, who pioneered stipple engraving and was executed for forgery. Life and work Ryland was born in London, the eldest of seven sons of Edward Ryland (died 1771), an engraver and copper-plate printer. He studied engraving under Ravenet in London, and, in Paris, drawing under François Boucher and engraving under Jacques-Philippe Le Bas. After spending five years on the continent he returned to England, and having engraved portraits of George III and Lord Bute (after Ramsay), and a portrait of Queen Charlotte and the Princess Royal after Francis Cotes , he was appointed engraver to the king, a position that carried a salary of £200 per annum. In 1766 he became a member of the Incorporated Society of Artists, and he exhibited with them and in the Royal Academy. In his later life Ryland abandoned line engraving, and introduced chalk-engraving, in which the line is composed of stippled dots, and in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Winne Ryland Engraved 1768 By D P Parset After P Falconet
William is a masculine given name of Norman French origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Liam, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the German given name ''Wilhelm''. Both ultimately descend from Proto-Germanic ''*Wiljahelmaz'', with a direct cognate also in the Old Norse name ''Vilhjalmr'' and a West Germanic borrowing into Medieval Latin ''Willelmus''. The Proto-Germanic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Engraving
Line engraving is a term for engraved images printed on paper to be used as prints or illustrations. The term is mainly used in connection with 18th- or 19th-century commercial illustrations for magazines and books or reproductions of paintings. It is not a technical term in printmaking, and can cover a variety of techniques, giving similar results. Steel engraving is an overlapping term, for images that in fact are often mainly in etching, mostly used for banknotes, illustrations for books, magazines and decorative prints, often reproductive, from about 1820 to the early 20th century, when the technique became less used. ''Copperplate engraving'' is another somewhat outdated term for engravings. With photography long established, engravings made today are nearly all artistic ones in printmaking, but the technique is not as common as it used to be; more than other printmaking techniques, engraving requires great skill and much practice, even for an experienced artist. Techniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Francis Buller, 1st Baronet
Sir Francis Buller, 1st Baronet (17 March 1746 – 5 June 1800) of Churston Court in the parish of Churston Ferrers, of nearby Lupton in the parish of Brixham, and of Prince Hall on Dartmoor, all in Devon, was an English judge. Origins Buller was born at Downes House in the parish of Crediton in Devon, a younger son of James Buller (1717–1765), of Downes and of King's Nympton Park, both in Devon and of Morval in Cornwall, a Member of Parliament for Cornwall, by his second wife Lady Jane Bathurst, daughter of Allen Bathurst, 1st Earl Bathurst. As his elder brothers inherited the substantial family estates, Buller as a younger son was obliged to make his own fortune, which he achieved both from his brilliant legal career and from having married a wealthy heiress. Career Legal career After an education at The King's School, Ottery St Mary in Devon, and at Christ's Hospital, London, in February 1763 he entered the Inner Temple as a pupil of William Henry Ashurst, speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Bailey
The Central Criminal Court of England and Wales, commonly referred to as the Old Bailey after the street on which it stands, is a criminal court building in central London, one of several that house the Crown Court of England and Wales. The street outside follows the route of the ancient wall around the City of London, which was part of the fortification's '' bailey'', hence the metonymic name. The Old Bailey has been housed in a succession of court buildings on the street since the sixteenth century, when it was attached to the medieval Newgate gaol. The current main building block was completed in 1902, designed by Edward William Mountford; its architecture is recognised and protected as a Grade II* listed building. An extension South Block was constructed in 1972, over the former site of Newgate gaol which was demolished in 1904. The Crown Court sitting in the Old Bailey hears major criminal cases from within Greater London. In exceptional cases, trials may be referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
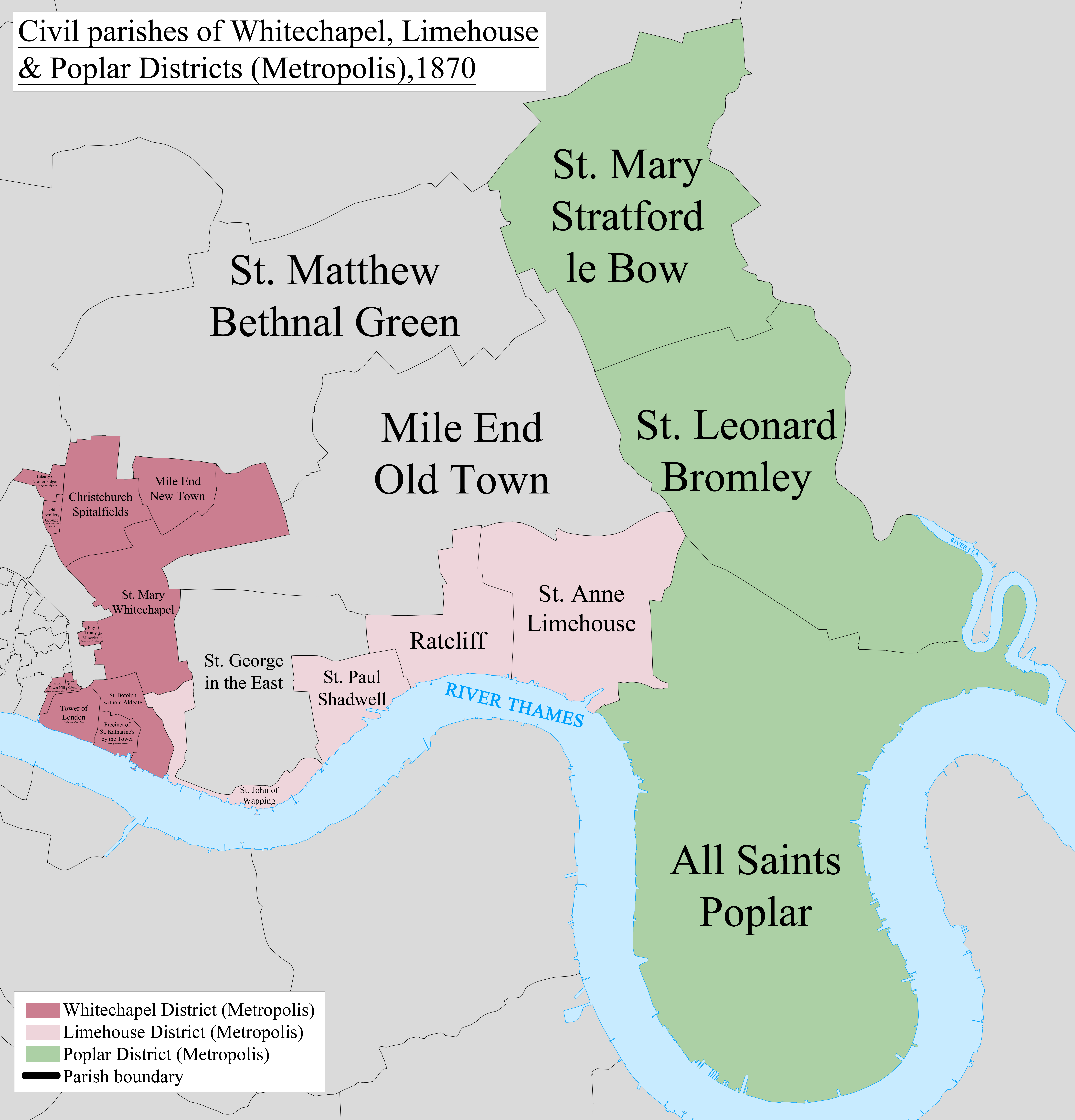
Stepney
Stepney is a district in the East End of London in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The district is no longer officially defined, and is usually used to refer to a relatively small area. However, for much of its history the place name applied to a much larger manor and parish. Stepney Green is a remnant of a larger area of Common Land formerly known as Mile End Green. The area was built up rapidly in the 19th century, mainly to accommodate immigrant workers and displaced London poor, and developed a reputation for poverty, overcrowding, violence and political dissent. It was severely damaged during the Blitz, with over a third of housing totally destroyed; and then, in the 1960s, slum clearance and development replaced most residential streets with tower blocks and modern housing estates. Some Georgian architecture and Victorian era terraced housing survive in patches: for example Arbour Square, the eastern side of Stepney Green, and the streets around Matlock Street. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knightsbridge
Knightsbridge is a residential and retail district in central London, south of Hyde Park. It is identified in the London Plan as one of two international retail centres in London, alongside the West End. Toponymy Knightsbridge is an ancient name, spelt in a variety of ways in Saxon and Old English, such as ''Cnihtebricge'' (c. 1050); ''Knichtebrig'' (1235); ''Cnichtebrugge'' (13th century); and ''Knyghtesbrugg'' (1364). The meaning is "bridge of the young men or retainers," from the Old English ''cniht'' (genitive case plural –a) and ''brycg''. ''Cniht'', in pre-Norman days, did not have the later meaning of a warrior on horseback, but simply meant a youth. The allusion may be to a place where ''cnihtas'' congregated: bridges and wells seem always to have been favourite gathering places of young people, and the original bridge was where one of the old roads to the west crossed the River Westbourne. However, there is possibly a more specific reference to the important ''cnih ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strand, London
Strand (or the Strand) is a major thoroughfare in the City of Westminster, Central London. It runs just over from Trafalgar Square eastwards to Temple Bar, where the road becomes Fleet Street in the City of London, and is part of the A4, a main road running west from inner London. The road's name comes from the Old English ''strond'', meaning the edge of a river, as it historically ran alongside the north bank of the River Thames. The street was much identified with the British upper classes between the 12th and 17th centuries, with many historically important mansions being built between the Strand and the river. These included Essex House, Arundel House, Somerset House, Savoy Palace, Durham House and Cecil House. The aristocracy moved to the West End during the 17th century, and the Strand became known for its coffee shops, restaurants and taverns. The street was a centre point for theatre and music hall during the 19th century, and several venues remain on the St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornhill, London
Cornhill (formerly also Cornhil) is a ward and street in the City of London, the historic nucleus and financial centre of modern London. The street runs between Bank Junction and Leadenhall Street. The hill from which it takes its name is one of the three ancient hills of London; the others are Tower Hill, site of the Tower of London, and Ludgate Hill, crowned by St Paul's Cathedral. The highest point of Cornhill is at above sea level. History Cornhill is one of the traditional divisions of the City. The street contains two of the City churches designed by Sir Christopher Wren: St. Michael, Cornhill, and St Peter upon Cornhill, reputed to occupy the oldest Christianised site in London. Both are on the site of the Roman forum of ''Londinium''. At its other end it meets Threadneedle Street, Poultry, Lombard Street and others at Bank junction. Sir Thomas Gresham's original Royal Exchange fronted onto Cornhill, but its successor on the site, designed by William Tite, fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angelica Kauffman
Maria Anna Angelika Kauffmann ( ; 30 October 1741 – 5 November 1807), usually known in English as Angelica Kauffman, was a Swiss Neoclassical painter who had a successful career in London and Rome. Remembered primarily as a history painter, Kauffmann was a skilled portraitist, landscape and decoration painter. She was, along with Mary Moser, one of two female painters among the founding members of the Royal Academy in London in 1768. Early life Kauffman was born at Chur in Graubünden, Switzerland. Her family moved to Morbegno in 1742, then Como in Lombardy in 1752 at that time under Austrian rule. In 1757 she accompanied her father to Schwarzenberg in Vorarlberg/Austria where her father was working for the local bishop. Her father, Joseph Johann Kauffmann, was a relatively poor man but a skilled Austrian muralist and painter, who was often travelling for his work. He trained Angelica and she worked as his assistant, moving through Switzerland, Austria, and Italy. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Master
In art history, "Old Master" (or "old master")Old Masters Department Christies.com. refers to any painter of skill who worked in Europe before about 1800, or a painting by such an artist. An " old master print" is an original (for example an or etching) made by an artist in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardinal Stephen Langton, to make peace between the unpopular king and a group of rebel barons, it promised the protection of church rights, protection for the barons from illegal imprisonment, access to swift justice, and limitations on feudal payments to the Crown, to be implemented through a council of 25 barons. Neither side stood behind their commitments, and the charter was annulled by Pope Innocent III, leading to the First Barons' War. After John's death, the regency government of his young son, Henry III of England, Henry III, reissued the document in 1216, stripped of some of its more radical content, in an unsuccessful bid to build political support for their cause. At the end of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(cropped).jpg)

.jpg)

_01.jpg)

.jpg)