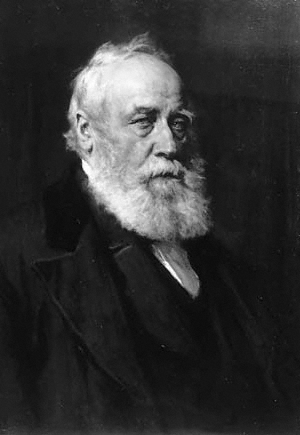|
W.F. Skene
William Forbes Skene Writer to the Signet, WS FRSE Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, FSA(Scot) Doctor of Civil Law, DCL Legum Doctor, LLD (7 June 1809 – 29 August 1892), was a Scotland, Scottish lawyer, historian and antiquary. He co-founded the Scottish legal firm Skene Edwards which was prominent throughout the 20th century but disappeared in 2008 when it merged with Morton Fraser. Life He was born in Inverey, the second son of Sir Walter Scott's friend, James Skene (1775–1864), of Rubislaw, near Aberdeen, and his wife, Jane Forbes, daughter of Sir William Forbes, 6th Baronet of Pitsligo. The family moved to Edinburgh in 1817, originally living with his uncle, Andrew Skene then from 1820 living at 126 Princes Street facing Edinburgh Castle.Edinburgh Post Office Directory 1820 He was educated at the Royal High School, Edinburgh, High School in Edinburgh. He was then apprenticed as a lawyer first to Francis Wilson WS at Parliament Square then to Henry Jardine WS also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Skene
Andrew Skene FRSE (1784–1835) was a Scottish advocate who rose to the highest level for his profession: Solicitor General for Scotland. Life He was born in Aberdeen on 28 February 1784 the son of Prof George Skene of Rubislaw FRSE MD (1741-1803), Professor of Natural Philosophy at Marischal College and Jane Moir of Stoneywood. In 1811 he was appointed Counsel for the City of Aberdeen in place of John Burnett Judge Admiral, for all legal matters in Scotland. In 1823 he was a co-founder of the Bannatyne Club along with his brother-in-law Sir Henry Jardine and Sir Walter Scott. In 1829 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh his proposer being Alexander Maconochie, Lord Meadowbank. He was elected Solicitor General for Scotland in 1834, replacing Henry Cockburn, Lord Cockburn. He lived at 74 Great King Street in Edinburgh's Second New Town and died there on 2 April 1835, aged only 51. He is buried in New Calton Burial Ground on the east side of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Potato Famine
The Highland Potato Famine () was a period of 19th-century Scottish Highland history (1846 to roughly 1856) over which the agricultural communities of the Hebrides and the western Scottish Highlands () saw their potato crop (upon which they had become over-reliant) repeatedly devastated by potato blight. It was part of the wider food crisis facing Northern Europe caused by potato blight during the mid-1840s, whose most famous manifestation is the Great Irish Famine, but compared with its Irish counterpart, it was much less extensive (the population seriously at risk was never more than 200,000 – and often much less) and took many fewer lives as prompt and major charitable efforts by the rest of the United Kingdom ensured relatively little starvation. The terms on which charitable relief was given, however, led to destitution and malnutrition amongst its recipients. A government enquiry could suggest no short-term solution other than reduction of the population of the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but from c. 1841 and for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Session
The Court of Session is the highest national court of Scotland in relation to Civil law (common law), civil cases. The court was established in 1532 to take on the judicial functions of the royal council. Its jurisdiction overlapped with other royal, state and church courts but as those were disbanded, the role of the Court of Session ascended. The Acts of Union 1707, Acts of Union which established the Kingdom of Great Britain on 1 May 1707 provided that the court will "remain in all time coming" as part of Scotland's separate Scots law, legal system. Cases at trial court, first instance are heard in the Outer House by a single judge. The Inner House hears appeals from the Outer House and all other courts and tribunals in Scotland. Only Scottish advocates and solicitor-advocates may argue cases before the court. The Court of Session has sat at Parliament House, Edinburgh, Parliament House since 1707. The Scottish Courts and Tribunals Service and the Principal Clerk of Session ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Literature
Celtic literature is the body of literature written in one of the Celtic languages, or else it may popularly refer to literature written in other languages which is based on the traditional narratives found in early Celtic literature. Background In the strictly academic context of Celtic studies, the term Celtic literature is used by Celticists to denote any number of bodies of literature written in a Celtic language, encompassing the Irish, Welsh, Cornish, Manx, Scottish Gaelic, and Breton languages in either their modern or earlier forms. Alternatively, the term is often used in a popular context to refer to literature that is written in a non-Celtic language but originates nonetheless from the Celtic nations or else displays subjects or themes identified as "Celtic". Examples of this literature include the medieval Arthurian romances written in the French language, which drew heavily from Celtic sources, or in a modern context literature in the English language by wr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philology
Philology () is the study of language in Oral tradition, oral and writing, written historical sources. It is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics with strong ties to etymology. Philology is also defined as the study of literary texts and oral and written records, the establishment of their authentication, authenticity and their original form, and the determination of their meaning. A person who pursues this kind of study is known as a philologist. In older usage, especially British, philology is more general, covering comparative linguistics, comparative and historical linguistics. Classical philology studies classical languages. Classical philology principally originated from the Library of Pergamum and the Library of Alexandria around the fourth century BC, continued by Greeks and Romans throughout the Roman Empire, Roman and Byzantine Empire. It was eventually resumed by European scholars of the Renaissance humanism, Renaissance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Languages
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves Pezron, who made the explicit link between the Celts described by classical writers and the Welsh and Breton languages. During the first millennium BC, Celtic languages were spoken across much of Europe and central Anatolia. Today, they are restricted to the northwestern fringe of Europe and a few diaspora communities. There are six living languages: the four continuously living languages Breton, Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Welsh, and the two revived languages Cornish and Manx. All are minority languages in their respective countries, though there are continuing efforts at revitalisation. Welsh is an official language in Wales and Irish is an official language across the island of Ireland and of the European Union. Welsh is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh University
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the town council under the authority of a royal charter from King James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's four ancient universities and the sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played a crucial role in Edinburgh becoming a leading intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the " Athens of the North". The three main global university rankings ( ARWU, THE, and QS) place the University of Edinburgh within their respective top 40. It is a member of several associations of research-intensive universities, including the Coimbra Group, League of European Research Universities, Russell Group, Una Europa, and Universitas 21. In the fiscal year ending 31 July 2024, the university had a total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of St Andrews
The University of St Andrews (, ; abbreviated as St And in post-nominals) is a public university in St Andrews, Scotland. It is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest of the four ancient universities of Scotland and, following the universities of University of Oxford, Oxford and University of Cambridge, Cambridge, the third-oldest university in the English-speaking world. St Andrews was founded in 1413 when the Avignon Pope, Avignon Antipope Benedict XIII issued a papal bull to a small founding group of Augustinians, Augustinian clergy. Along with the universities of University of Glasgow, Glasgow, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, and University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, St Andrews was part of the Scottish Enlightenment during the 18th century. St Andrews is made up of a variety of institutions, comprising three colleges — United College, St Andrews, United College (a union of St Salvator's and St Leonard's Colleges), St Mary's College, St Andrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Jardine
Sir Henry Jardine of Harwood WS FRSE (30 January 1766 – 11 August 1851) was a solicitor, antiquarian and a founder member of the Bannatyne Club in 1823, with his friend Sir Walter Scott. Life He was born in Edinburgh on 30 January 1766. He was the son of Reverend John Jardine (1716–1766), "second charge" minister of the Tron Kirk on the Royal Mile and Dean of the Chapel Royal, and Jean Drummond, daughter of George Drummond, the Lord Provost of Edinburgh. His father died when Henry was 4 months old but his grandfather George Drummond provided assistance. He attended the High School in Edinburgh and then studied law at the University of Edinburgh. After graduation he was apprenticed to John Davidson WS based on Castlehill on the Royal Mile. He qualified as a Writer to the signet in 1790.Kay's Originals vol.2 p.327 In 1790 he was winner of the Edinburgh Arrow as finest archer in the Royal Company of Archers. He became a Writer to the Signet in 1790 and in 1793 beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh had a population of in , making it the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city in Scotland and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous in the United Kingdom. The Functional urban area, wider metropolitan area had a population of 912,490 in the same year. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament, the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland, and the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarch in Scotland. It is also the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. The city has long been a cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |