|
Vouivria
''Vouivria'' is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur, belonging to the Brachiosauridae, that lived in the area of present France during the Late Jurassic. The type species is ''Vouivria damparisensis''. History In 1926, the Solvay company began to exploit a chalkstone quarry at Belvoye, near Damparis in Franche-Comté. In April 1934, workers noticed the presence of large fossil bones in the southeastern face of the quarry. A scapula was shown to foreman Koehret who notified the company engineers Verhas and Chardin. They advised director Étienne Haerens to immediately excavate the marl lens containing the remains. Paleontologists Jean Piveteau and Raymond Ciry were asked to supervise this effort. The excavation started in May and was finished on 22 June 1934.Lapparent, A.-F. de, 1943, "Les dinosauriens jurassiques de Damparis (Jura)", ''Mémoires de la Société Géologique de France (Nouvelle Série)'' 47: 1-20 The same year, baron Jean de Dorlodot published an article ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vouivria NT
''Vouivria'' is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur, belonging to the Brachiosauridae, that lived in the area of present France during the Late Jurassic. The type species is ''Vouivria damparisensis''. History In 1926, the Solvay company began to exploit a chalkstone quarry at Belvoye, near Damparis in Franche-Comté. In April 1934, workers noticed the presence of large fossil bones in the southeastern face of the quarry. A scapula was shown to foreman Koehret who notified the company engineers Verhas and Chardin. They advised director Étienne Haerens to immediately excavate the marl lens containing the remains. Paleontologists Jean Piveteau and Raymond Ciry were asked to supervise this effort. The excavation started in May and was finished on 22 June 1934.Lapparent, A.-F. de, 1943, "Les dinosauriens jurassiques de Damparis (Jura)", ''Mémoires de la Société Géologique de France (Nouvelle Série)'' 47: 1-20 The same year, baron Jean de Dorlodot published an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiosauridae
The Brachiosauridae ("arm lizards", from Greek ''brachion'' (βραχίων) = "arm" and ''sauros'' = "lizard") are a family or clade of herbivorous, quadrupedal sauropod dinosaurs. Brachiosaurids had long necks that enabled them to access the leaves of tall trees that other sauropods would have been unable to reach. In addition, they possessed thick spoon-shaped teeth which helped them to consume tough plants more efficiently than other sauropods. They have also been characterized by a few unique traits or synapomorphies; dorsal vertebrae with 'rod-like' transverse processes and an ischium with an abbreviated pubic peduncle. ''Brachiosaurus'' is one of the best-known members of the Brachiosauridae, and was once thought to be the largest land animal to ever live. Brachiosaurids thrived in the regions which are now North and South America, Africa, Europe, and Asia. They first appear in the fossil record in the Late Jurassic Period (possibly even earlier in the Middle Jurassic) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriospondylus
''Bothriospondylus'' ("excavated vertebra") is a dubious genus of neosauropod sauropod dinosaur. It lived during the Late Jurassic. Discovery and naming The type species, ''Bothriospondylus suffossus'', was described by Richard Owen in 1875. The specific epithet ''suffossus'' means "undermined" in Latin, a reference to the fact that pleurocoels had hollowed out the sides of the vertebra. It is often incorrectly spelled as "suffosus". Owen based the species on holotype NHMUK R.44592-5, a set of four dorsal vertebrae found in Wiltshire in stratum from the Kimmeridgian, the Kimmeridge Clay. Also three unfused sacral vertebrae were referred. At the same time Owen named three other species of ''Bothriospondylus''. ''B. robustus'' was based on NHMUK R.22428, a dorsal from the same location. ''B. elongatus'' was based on a vertebra from Sussex, NHMUK R.2239, an original syntype of '' Ornithopsis hulkei''. Finally, '' Bothriospondylus magnus'' was a new name for another syntype of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987. In European lithostratigraphy, the name "Malm" indicates rocks of Late Jurassic age. In the past, ''Malm'' was also used to indicate the unit of geological time, but this usage is now discouraged to make a clear distinction between lithostratigraphic and geochronologic/chronostratigraphic units. Subdivisions The Late Jurassic is divided into three ages, which correspond with the three (faunal) stages of Upper Jurassic rock: Paleogeography During the Late Jurassic Epoch, Pangaea broke up into two supercontinents, Laurasia to the north, and Gondwana to the south. The result of this break-up was the spawning of the Atlantic Ocean. However, at this time, the Atlantic Ocean was relatively narrow. Life forms of the epoch This epoch is well known for many famous types of din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
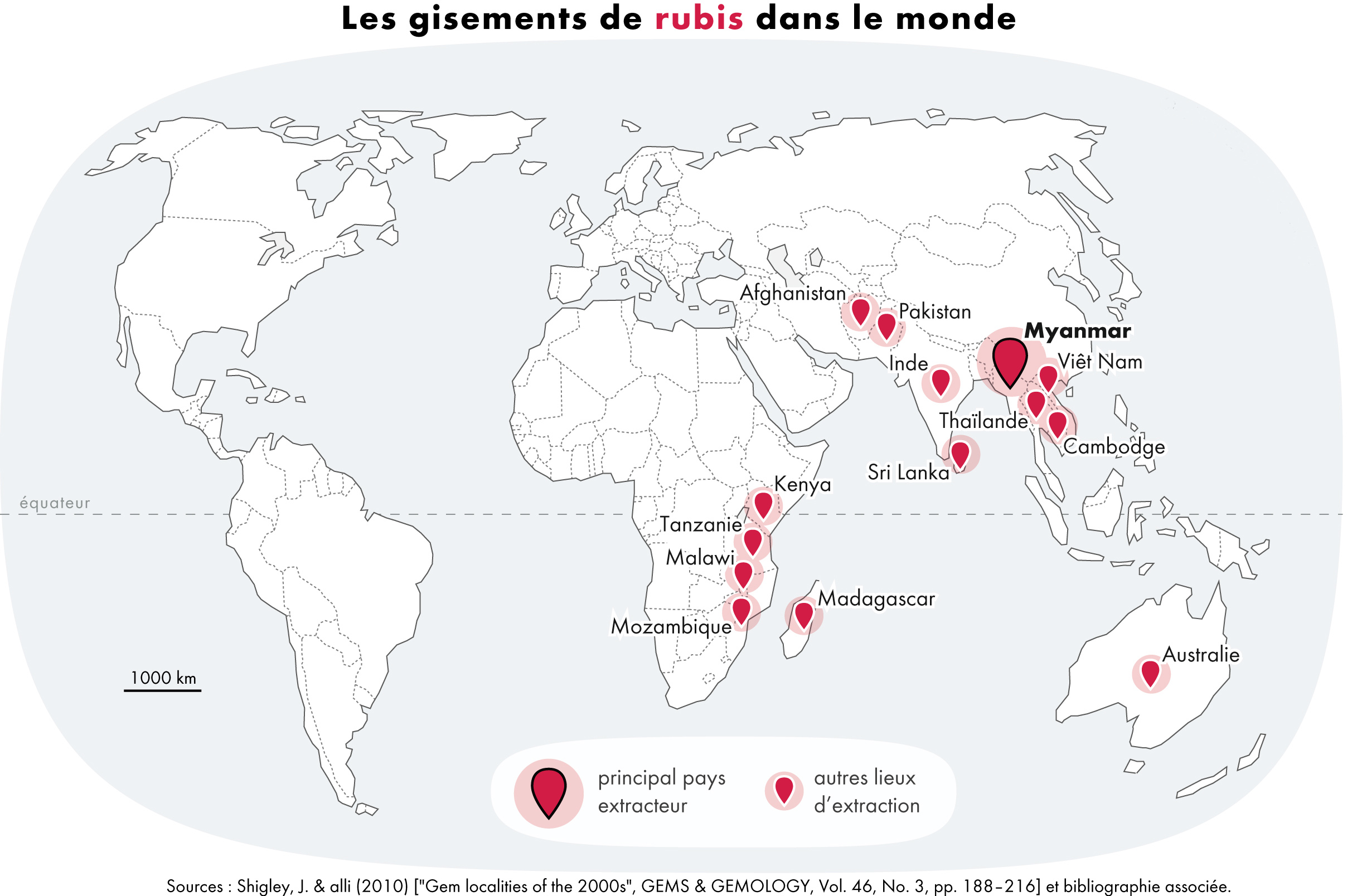
Ruby
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum (aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat (mass), carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcel Aymé
Marcel Aymé (29 March 1902 – 14 October 1967) was a French novelist and playwright, who also wrote screenplays and works for children. Biography Marcel André Aymé was born in Joigny, in the Burgundy region of France, the youngest of six children. His father, Joseph, was a blacksmith, and his mother, Emma Monamy, died when he was two years old, after the family had moved to Tours. Marcel was sent to live with his maternal grandparents in the village of Villers-Robert, a place where he would spend the next eight years, and which would serve as the model for the fictitious village of Claquebue in what is perhaps the most well-known of his novels, '' La Jument verte''. In 1906 Marcel entered the local primary school. Because his grandfather was a staunch anti-clerical republican, he was looked down upon by his classmates, many of whose parents held more traditional views. Accordingly, Marcel was not baptized before reaching the age of eight, nearly two years after the death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyvern
A wyvern ( , sometimes spelled wivern) is a legendary winged dragon that has two legs. The wyvern in its various forms is important in heraldry, frequently appearing as a mascot of schools and athletic teams (chiefly in the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada). It is a popular creature in European literature, mythology, and folklore. Today, it is often used in fantasy literature and video games. The wyvern in heraldry and folklore is rarely fire-breathing, unlike four-legged dragons. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word is a development of Middle English ''wyver'' (attested fourteenth century), from Anglo-French ''wivre'' (cf. French ''guivre'' and ''vouivre''), which originate from Latin ''vīpera'', meaning "viper", "adder", or "asp". The concluding "''–n''" had been added by the beginning of the 17th century, when John Guillim in 1610 describes the "''wiverne''" as a creature that "partake of a Fowle in the Wings and Legs ... and dot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon ( back-formation from '' taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humerus Of Vouivria
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes ( tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes ( trochlea & capitulum), and 3 fossae ( radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word "humerus" is derived from la, humerus, umerus meaning upper arm, shoulder, and is linguistically related to Gothic ''ams'' shoulder and Greek ''ōmos''. Structure Upper extremity Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |