|
Voskhod (rocket)
The Voskhod rocket (, ''"ascent"'', ''"dawn"'') was a derivative of the Soviet Union, Soviet R-7 Semyorka, R-7 ICBM designed for the human spaceflight Voskhod programme, programme but later used for launching Zenit (satellite), Zenit reconnaissance satellites. It was essentially an 8K78/8K78M minus the Blok L stage and spec-wise was a halfway between the two boosters, with the former's older, lower-spec engines and the latter's improved Blok I design. Its first flight was on 16 November 1963 when it successfully launched a Zenit satellite from LC-1/5 at Baikonur. Boosters used in the Voskhod program had a man-rated version of the RD-0107 engine; this version was known as the RD-0108. Starting in 1966, the 11A57 adopted the standardized 11A511 core with the more powerful 8D74M first stage engines, however the Blok I stage continued using the RD-0107 engine rather than the RD-0110. Around 300 were flown from Baikonur and Plesetsk through 1976, almost all of them used to launch Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human-rating Certification
Human-rating certification, also known as man-rating or crew-rating, is the certification of a spacecraft or launch vehicle as capable of safely transporting humans. There is no one particular standard for human-rating a spacecraft or launch vehicle, and the various entities that launch or plan to launch such spacecraft specify requirements for their particular systems to be human-rated. NASA One entity that applies human rating is the US government civilian space agency, NASA. NASA's human-rating requires not just that a system be designed to be tolerant of failure and to protect the crew even if an unrecoverable failure occurs, but also that astronauts aboard a human-rated spacecraft have some control over it. This set of technical requirements and the associated certification process for crewed space systems are in addition to the standards and requirements for all of NASA's space flight programs. The development of the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station pre-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-0107
The RD-0110 (, and its derivatives, the RO-8, RD-0108, RD-461) is a rocket engine burning liquid oxygen and kerosene in a gas generator combustion cycle. It has four fixed nozzles and the output of the gas generator is directed to four secondary vernier nozzles to provide attitude control for the stage. It has an extensive flight history with its initial versions having flown more than . History OKB-154 of S.A. Kosberg was tasked with developing an engine for the unmanned Molniya Block-I stage. Thus, the RD-0107 was developed in the 1960 to 1961 period, based on the RD-0106 (GRAU Index: 8D715) engine that powered the SS-8 Sasin ICBM, also designed by OKB-154. It also leveraged the experience in the field from the Vostok Block-E RD-0105/ RD-0109 development. The engine had its debut flight on 10 October 1960, and the last Molniya flight was on 22 October 1967. For the crewed carrying Voskhod Block-I, a version of the engine that complied with the human rating 3K Regulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod Program
The Voskhod programme (, , ''Ascent'' or ''Dawn'') was the second Soviet human spaceflight project. Two one-day crewed missions were flown using the Voskhod spacecraft and rocket, one in 1964 and one in 1965, and two dogs flew on a 22-day mission in 1966. Voskhod development was both a follow-on to the Vostok programme and a recycling of components left over from that programme's cancellation following its first six flights. The Voskhod programme was superseded by the Soyuz programme. Design The Voskhod spacecraft was basically a Vostok spacecraft that had a backup, solid-fueled retrorocket added to the top of the descent module. As it was much heavier, the launch vehicle would be the 11A57, a Molniya 8K78M with the Blok L stage removed and later the basis of the Soyuz booster. The ejection seat was removed and two or three crew couches were added to the interior at a 90-degree angle to that of the Vostok crew position. However, the position of the in-flight controls was not chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1974 In Spaceflight
On 29 March 1974 Mariner 10 ''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets. ''Marin ... became the first spacecraft to fly by Mercury, that saw a spacecraft for the first and last time in the 20th century. Orbital launches , colspan=8, January , - , colspan=8, February , - , colspan=8, March , - , colspan=8, April , - , colspan=8, May , - , colspan=8, June , - , colspan=8, July , - , colspan=8, August , - , colspan=8, September , - , colspan=8, October , - , colspan=8, November , - , colspan=8, December , - Suborbital launches , colspan=8, January-March , - , colspan=8, April-June , - , colspan=8, July-September , - , colspan=8, October-December , - Deep Space Rendezvous EVAs Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1973 In Spaceflight
1973 saw the launch of the first American Space station known as Skylab on a Saturn V rocket. Launches , colspan=8, January , - , colspan=8, February , - , colspan=8, March , - , colspan=8, April , - , colspan=8, May , - , colspan=8, June , - , colspan=8, July , - , colspan=8, August , - , colspan=8, September , - , colspan=8, October , - , colspan=8, November , - , colspan=8, December , - Deep Space Rendezvous EVAs References Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1973 1973 in spaceflight, Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1965 In Spaceflight
Orbital and Suborbital launches Deep Space Rendezvous EVAs Orbital launch statistics By country By rocket By orbit References U.S. ''Aeronautics and Space Report 1965'' Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1965 1965 in spaceflight, Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1964 In Spaceflight
Orbital and Suborbital launches Deep Space Rendezvous Orbital launch statistics By country By rocket By orbit References Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1964 Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1963 In Spaceflight
Orbital and Suborbital launches Deep space rendezvous Notable creations of orbital debris Orbital launch statistics By country By rocket By orbit References Footnotes {{DEFAULTSORT:1963 In Spaceflight Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod Rocket
The Voskhod rocket (, ''"ascent"'', ''"dawn"'') was a derivative of the Soviet R-7 ICBM designed for the human spaceflight programme but later used for launching Zenit reconnaissance satellite A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The ...s. It was essentially an 8K78/8K78M minus the Blok L stage and spec-wise was a halfway between the two boosters, with the former's older, lower-spec engines and the latter's improved Blok I design. Its first flight was on 16 November 1963 when it successfully launched a Zenit satellite from LC-1/5 at Baikonur. Boosters used in the Voskhod program had a man-rated version of the RD-0107 engine; this version was known as the RD-0108. Starting in 1966, the 11A57 adopted the standardized 11A511 core with the more powerful 8D74M first stage en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
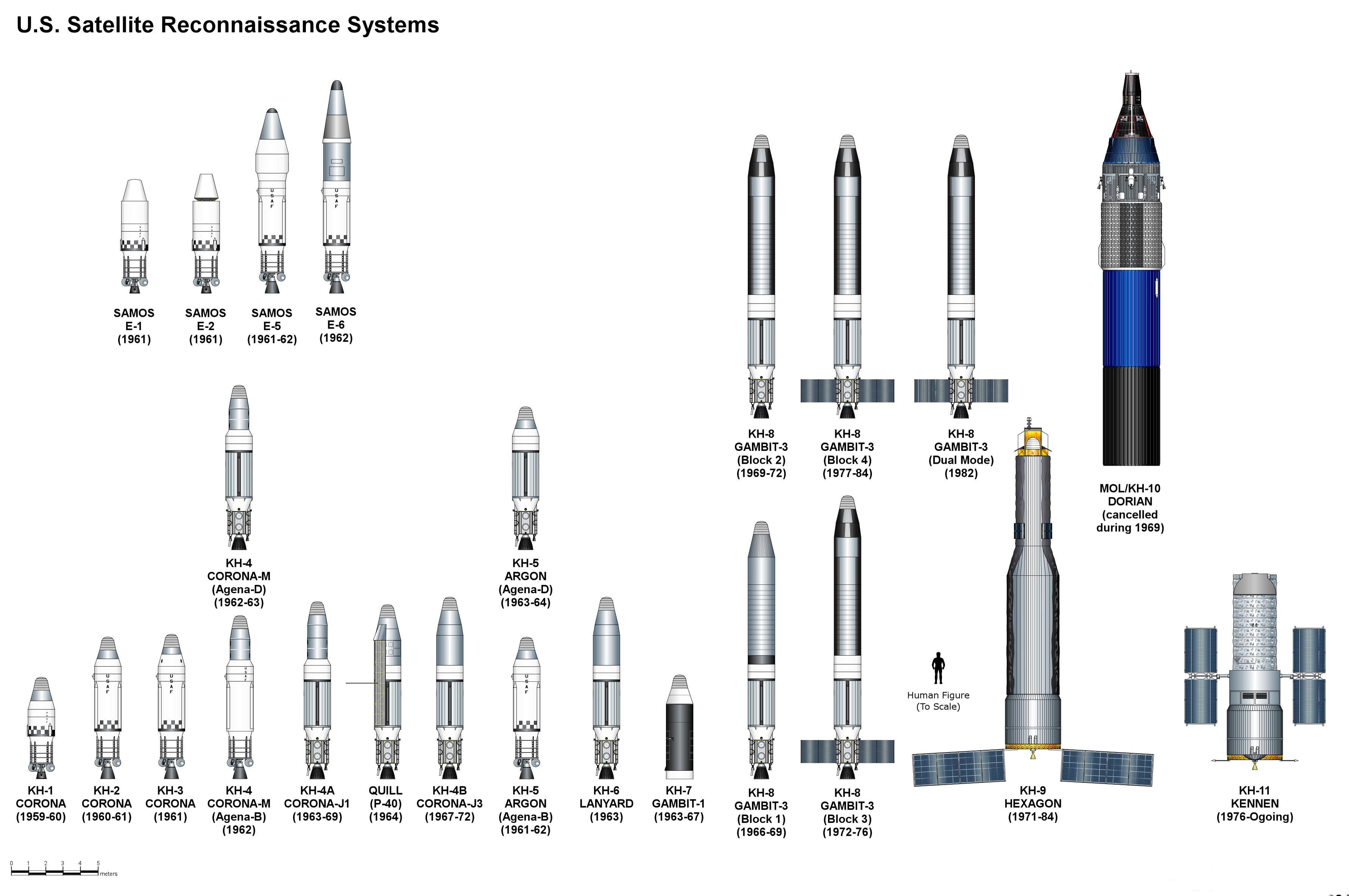
Reconnaissance Satellite
A reconnaissance satellite or intelligence satellite (commonly, although unofficially, referred to as a spy satellite) is an Earth observation satellite or communications satellite deployed for military or intelligence applications. The first generation type (i.e., Corona and Zenit) took photographs, then ejected canisters of photographic film which would descend back down into Earth's atmosphere. Corona capsules were retrieved in mid-air as they floated down on parachutes. Later, spacecraft had digital imaging systems and downloaded the images via encrypted radio links. In the United States, most information available about reconnaissance satellites is on programs that existed up to 1972, as this information has been declassified due to its age. Some information about programs before that time is still classified information, and a small amount of information is available on subsequent missions. A few up-to-date reconnaissance satellite images have been declassifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voskhod Programme
The Voskhod programme (, , ''Ascent'' or ''Dawn'') was the second Soviet human spaceflight project. Two one-day crewed missions were flown using the Voskhod spacecraft and rocket, one in 1964 and one in 1965, and two dogs flew on a 22-day mission in 1966. Voskhod development was both a follow-on to the Vostok programme and a recycling of components left over from that programme's cancellation following its first six flights. The Voskhod programme was superseded by the Soyuz programme. Design The Voskhod spacecraft was basically a Vostok spacecraft that had a backup, solid-fueled retrorocket added to the top of the descent module. As it was much heavier, the launch vehicle would be the 11A57, a Molniya 8K78M with the Blok L stage removed and later the basis of the Soyuz booster. The ejection seat was removed and two or three crew couches were added to the interior at a 90-degree angle to that of the Vostok crew position. However, the position of the in-flight controls was not chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be telerobotic, remotely operated from ground stations on Earth, or Autonomous robot, autonomously, without any direct human involvement. People trained for spaceflight are called astronauts (American or other), ''cosmonauts'' (Russian), or ''taikonauts'' (Chinese); and non-professionals are referred to as spaceflight participants or ''spacefarers''. The first human in space was Soviet Union, Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, who launched as part of the Soviet Union's Vostok program on Cosmonautics Day, 12 April 1961 at the beginning of the Space Race. On 5 May 1961, Alan Shepard became the first American in space, as part of Project Mercury. Humans traveled to the Moon nine times between 1968 and 1972 as part of the United States' Apollo progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |