|
Volvo Sharpnose
The Volvo LV101-112, or the Sharpnose was a light truck produced by Swedish automaker Volvo between 1938 and 1950. History In 1938 Volvo presented its light LV101-series truck, affectionately known as the "Sharpnose". At the same time Volvo introduced the taxicab PV800. The two models series shared engine, radiator cover and bonnet. The smallest model LV101 was mechanically almost identical to the taxicab, while the larger LV102 was a “genuine” truck. In 1940 the program was supplemented with the heavier LV110/111/112, built on three different wheelbases. After the Second World War Volvo updated the truck series with the stronger ED engine, renaming it L201/202. Engines Gallery File:1939 Volvo LV103.jpg, 1939 Volvo LV103 File:Volvo LV 111 DS Fire Engine 1941.jpg, 1941 Volvo LV111 fire engine A fire engine (also known in some places as a fire truck or fire lorry) is a road vehicle (usually a truck) that functions as a firefighting apparatus. The primary purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo Trucks
Volvo Trucks ( sv, Volvo Lastvagnar) is a truck manufacturing division of Volvo based in Gothenburg, Sweden. Volvo Trucks was a separate company within Volvo. The Volvo Group was reorganised on 1 January 2012 and as a part of the process, Volvo Trucks ceased to be a separate company and was instead incorporated into Volvo Group Trucks along Volvo's other truck operations, as Renault Trucks and Mack Trucks.Volvo Group reorganizes global truck business FleetOwner, 4 October 2011. Retrieved 19 November 2022. The first Volvo truck rolled off the production lines in 1928, and in 2016 Volvo Trucks employed more than 52,000 people around the world. With global headquarters in Gothenburg, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy. Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Engine
A fire engine (also known in some places as a fire truck or fire lorry) is a road vehicle (usually a truck) that functions as a firefighting apparatus. The primary purposes of a fire engine include transporting firefighters and water to an incident as well as carrying equipment for firefighting operations. Some fire engines have specialized functions, such as wildfire suppression and aircraft rescue and firefighting, and may also carry equipment for technical rescue. Many fire engines are based on commercial vehicle chassis that are further upgraded and customised for firefighting requirements. They are normally fitted with sirens and emergency vehicle lighting, as well as communication equipment such as two-way radios and mobile computer technology. The terms ''fire engine'' and ''fire truck'' are often used interchangeably to a broad range of vehicles involved in firefighting; however, in some fire departments they refer to separate and specific types of vehicle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Gas
Wood gas is a fuel gas that can be used for furnaces, stoves, and vehicles. During the production process, biomass or related carbon-containing materials are gasified within the oxygen-limited environment of a wood gas generator to produce a combustible mixture. In some gasifiers this process is preceded by pyrolysis, where the biomass or coal is first converted to char, releasing methane and tar rich in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In stark contrast with synthesis gas, which is almost pure H2/CO mixture, wood gas ''also'' contains a variety of organic compound ("distillates") that require scrubbing for use in other applications. Depending on the kind of biomass, a variety of contaminants are produced that will condense out as the gas cools. When producer gas is used to power cars and boats or distributed to remote locations it is necessary to scrub the gas to remove the materials that can condense and clog carburetors and gas lines. Anthracite and coke are preferred for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrol Engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as ''E10'' and ''E85''). Most petrol engines use spark ignition, unlike diesel engines which typically use compression ignition. Another key difference to diesel engines is that petrol engines typically have a lower compression ratio. Design Thermodynamic cycle Most petrol engines use either the four-stroke Otto cycle or the two-stroke cycle. Petrol engines have also been produced using the Miller cycle and Atkinson cycle. Layout Most petrol-powered piston engines are straight engines or V engines. However, flat engines, W engines and other layouts are sometimes used. Wankel engines are classified by the number of rotors used. Compression ratio Cooling Petrol engines are either air-cooled or water-cooled. Ignitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Valve
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the engine block, instead of in the cylinder head, as in an overhead valve engine. Flatheads were widely used internationally by automobile manufacturers from the late 1890s until the mid-1950s but were replaced by more efficient overhead valve and overhead camshaft engines. They are currently experiencing a revival in low-revving aero-engines such as the D-Motor. The side-valve design The valve gear comprises a camshaft sited low in the cylinder block which operates the poppet valves via tappets and short pushrods (or sometimes with no pushrods at all). The flathead system obviates the need for further valvetrain components such as lengthy pushrods, rocker arms, overhead valves or overhead camshafts. The sidevalves are typically adjacent, sited on one side of the cylinder(s), though some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-six Engine
The straight-six engine (also referred to as an inline-six engine; abbreviated I6 or L6) is a piston engine with six cylinders arranged in a straight line along the crankshaft. A straight-six engine has perfect primary and secondary engine balance, resulting in fewer vibrations than other designs of six or less cylinders. Until the mid-20th century, the straight-six layout was the most common design for engines with six cylinders. However, V6 engines became more common from the 1960s and by the 2000s most straight-six engines had been replaced by V6 engines. An exception to this trend is BMW which has produced automotive straight-six engines from 1933 to the present day. Characteristics In terms of packaging, straight-six engines are almost always narrower than a V6 engine or V8 engine, but longer than straight-four engines, V6s, and most V8s. Straight-six engines are typically produced in displacements ranging from , however engines ranging in size from the Benelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
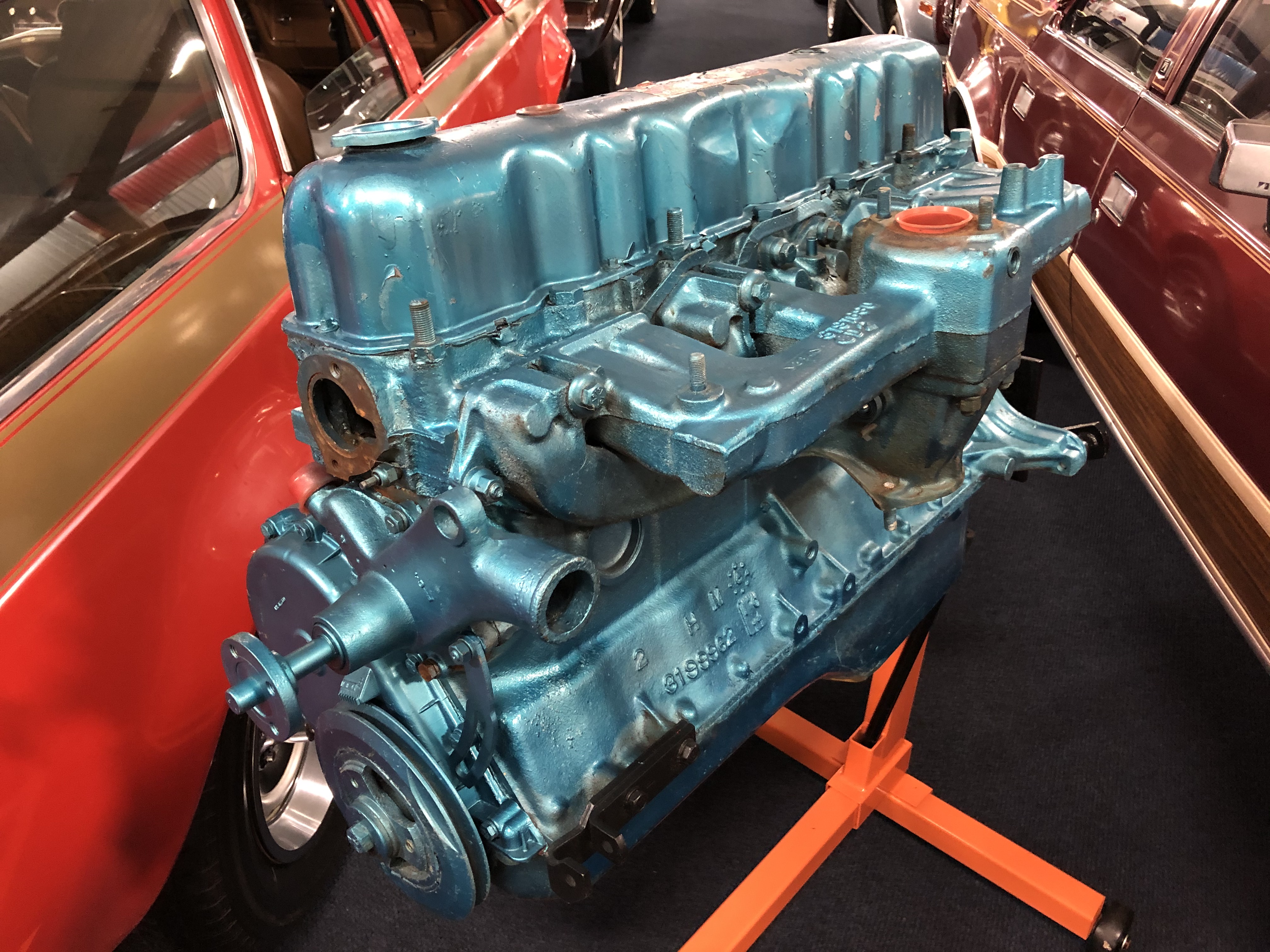
Volvo Sidevalve Straight-6 Engine ...
Penta DB was an engine model produced by AB Pentaverken. The 1929 introduced engine was a side-valve engine with a cast-iron block and seven main bearings, and the first straight-6 engine used in Volvos. Four other variants followed after. These engines powered all six-cylinder Volvo passenger cars and taxi cabs, as well as the company's small trucks between 1929 and 1958. Versions: See also * List of Volvo engines References * Volvo Personvagnar-från 20-tal till 80-tal av Björn-Eric Lindh, 1984. {{ISBN, 91-86442-06-6 Pentadb Volvo The Volvo Group ( sv, Volvokoncernen; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distributio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million Military personnel, personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Air warfare of World War II, Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
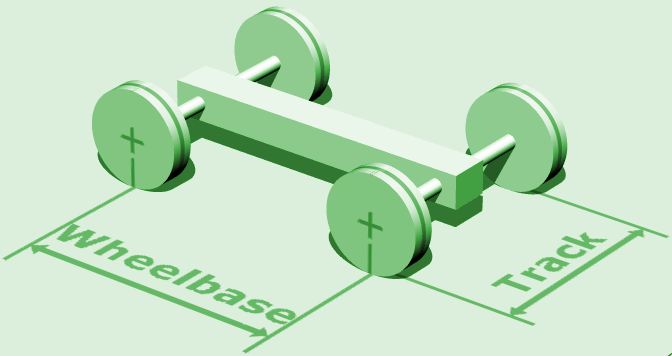
Wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles. Vehicles The wheelbase of a vehicle equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force on each pair of tires by the following formula: :F_f = mg :F_r = mg where F_f is the force on the front tires, F_r is the force on the rear tires, L is the wheelbase, d_r is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, d_f is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels (d_f + d_r = L), m is the mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hood (vehicle)
The hood (American English) or bonnet (Commonwealth English) is the hinged cover over the engine of motor vehicles. Hoods can open to allow access to the engine compartment, or trunk (boot in Commonwealth English) on rear-engine and some mid-engine vehicles) for maintenance and repair. Terminology In British terminology, ''hood'' refers to a fabric cover over the passenger compartment of the car (known as the 'roof' or 'top' in the US). In many motor vehicles built in the 1930s and 1940s, the resemblance to an actual hood or bonnet is clear when open and viewed head-on; in modern vehicles it continues to serve the same purpose but no longer resembles a head covering. Styles and materials On front-engined cars, the hood may be hinged at either the front or the rear edge, or in earlier models (e.g. the Ford Model T) it may be split into two sections, one each side, each hinged along the centre line. A further variant combines the bonnet and wheelarches into one section an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo PV800 Series
The Volvo PV800 Series (nicknamed the Volvo Sugga, literally the '' Sow'') is a taxicab manufactured by Volvo from 1938 until 1958. The Sow series dominated the Swedish taxicab market during the 1940s and 1950s. During World War II and in the 1950s, Volvo built a four-wheel drive off-road vehicle for the Swedish Armed Forces and Belgian Armed Forces, using the mechanical parts from Volvo’s small trucks, combined with much of the body from the PV-800 series Sow. __TOC__ PV800-810 The PV801 (with a glass division between the front and rear seat) and the PV802 (without the glass division) were introduced in 1938 and superseded the TR670 Series. The chassis and body were all new but the side-valve engine was the same as in the older cars. The front end was also used on Volvo’s smallest lorry, the LV100 Series. The PV802 could be used as a spare ambulance. After folding all seats on the car’s right side, a stretcher could be loaded through the bootlid. Volvo continued to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)