|
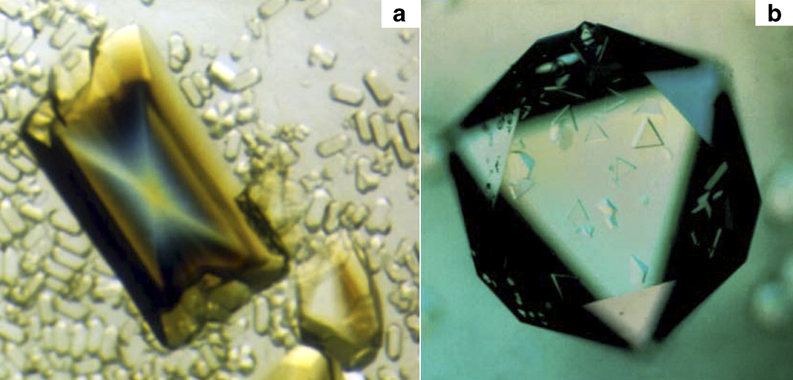
Virus Crystallisation
Virus crystallisation is the re-arrangement of Virus, viral components into solid crystal particles. The crystals are composed of thousands of inactive forms of a particular virus arranged in the shape of a Prism (geometry), prism. The inactive nature of virus crystals provide advantages for Immunology, immunologists to effectively analyze the structure and function behind viruses. Understanding of such characteristics have been enhanced thanks to the enhancement and diversity in crystallisation technologies. Virus crystals have a deep history of being widely applied in epidemiology and virology, and still to this day remains a catalyst for studying viral patterns to mitigate potential disease outbreaks. Historical background Pre-20th century Virus crystals originate back to the late 19th century where the first protein crystallization, protein crystallisation discoveries were made by German biologists Karl Heinrich Ritthausen, Ritthausen and Thomas Burr Osborne (chemist), Osb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology And Man (1944) (19762396143)
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell (biology), cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple biological organisation, levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including scientific method, observation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical microscope, optical, electron microscope, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection (physics), reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the Laboratory specimen, specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscope, transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological Dosage form, preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease, infectious or cancer, malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be prophylaxis, prophylactic (to prevent or alleviate the effects of a future infection by a natural or "wild" pathogen), or therapeutic vaccines, therapeutic (to fight a disease that has already occurred, such as cancer vaccine, cancer). Some vaccines offer full sterilizing immunity, in which infection is prevented. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to pharmacotherapy, treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, Herpesviridae, herpes viruses, the hepatitis B and Hepatitis C, C viruses, and Influenzavirus A, influenza A and Influenzavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm. Viral production / replication Viruses multiply only in living cells. The host cell must provide the energy and synthetic machinery and the low-molecular-weight precursors for the synthesis of viral proteins and nucleic acids. Virus replication occurs in seven stages: # Attachment # Entry (penetration) # Uncoating # Replication # Assembly # Maturation # Release (liberation stage). Attachment It is the first step of viral replication. Some viruses attach to the cell membrane of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Disease
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells. Examples include the common cold, gastroenteritis, COVID-19, the flu, and rabies. Structural characteristics Basic structural characteristics, such as genome type, virion shape and replication site, generally share the same features among virus species within the same family. * Double-stranded DNA families: three are non-enveloped (''Adenoviridae'', '' Papillomaviridae'' and '' Polyomaviridae'') and two are enveloped ('' Herpesviridae'' and '' Poxviridae''). All of the non-enveloped families have icosahedral capsids. * Partly double-stranded DNA viruses: '' Hepadnaviridae''. These viruses are enveloped. * One family of single-stranded DNA viruses infects humans: ''Parvoviridae''. These viruses are non-enveloped. * Positive single-stranded RNA families: three non-enveloped ('' Astroviridae'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the ) is a Positive-sense single stranded RNA virus, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the genus ''Enterovirus'' in the family ''Picornaviridae''. Rhinovirus is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. The three species of rhinovirus (A, B, and C) include at least 165 recognized types that differ according to their surface antigens or genetics. They are among the smallest viruses, with diameters of about 30 nanometers. By comparison, other viruses, such as smallpox and vaccinia, are around ten times larger at about 300 nanometers, while Orthomyxoviridae, influenza viruses are around 80–120 nm. Rhinoviruses are transmitted through aerosols, respiratory droplets, fomites, and direct person-to-person contact. They primarily infect nasal epithelial cells in the airway and cause mild symptoms such as sore throat, cough, and nasal con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poliovirus
Poliovirus, the causative agent of polio (also known as poliomyelitis), is a serotype of the species '' Enterovirus C'', in the family of '' Picornaviridae''. There are three poliovirus serotypes, numbered 1, 2, and 3. Poliovirus is composed of an RNA genome and a protein capsid. The genome is a single-stranded positive-sense RNA (+ssRNA) genome that is about 7500 nucleotides long. The viral particle is about 30 nm in diameter with icosahedral symmetry. Because of its short genome and its simple composition—only a strand of RNA and a nonenveloped icosahedral protein coat encapsulating it—poliovirus is widely regarded as the simplest significant virus. Poliovirus is one of the most well-characterized viruses, and has become a useful model system for understanding the biology of RNA viruses. Replication cycle Poliovirus infects human cells by binding to an immunoglobulin-like receptor, CD155 (also known as the poliovirus receptor or PVR) on the cell surface. Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Structure
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long molecules of DNA or RNA that encode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorothy Hodgkin
Dorothy Mary Crowfoot Hodgkin (née Crowfoot; 12 May 1910 – 29 July 1994) was a Nobel Prize-winning English chemist who advanced the technique of X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of biomolecules, which became essential for structural biology. Among her most influential discoveries are the confirmation of the structure of penicillin as previously surmised by Edward Abraham and Ernst Boris Chain; and mapping the structure of vitamin B12, vitamin B12, for which in 1964 she became the third woman to win the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Hodgkin also elucidated the structure of insulin in 1969 after 35 years of work. Hodgkin used the name "Dorothy Crowfoot" until twelve years after marrying Thomas Lionel Hodgkin, when she began using "Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin". Hodgkin is referred to as "Dorothy Hodgkin" by the Royal Society (when referring to its sponsorship of the Dorothy Hodgkin fellowship), and by Somerville College. The National Archives (United Kingdom), The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Tobacco Mosaic Virus Crystal
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation (GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellations. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |