|
Virtual Instrumentation
Virtual instrumentation is the use of customizable software and modular measurement hardware to create user-defined measurement systems. Overview Traditional hardware instrumentation systems are made up of fixed hardware components, such as digital multimeters and oscilloscopes that are completely specific to their stimulus, analysis, or measurement function. Because of their hard-coded function, these systems are more limited in their versatility than virtual instrumentation systems. The primary difference between hardware instrumentation and virtual instrumentation is that software is used to replace a large amount of hardware. The software enables complex and expensive hardware to be replaced by already purchased computer hardware; e. g. analog-to-digital converter can act as a hardware complement of a virtual oscilloscope, a potentiostat enables frequency response acquisition and analysis in electrochemical impedance spectroscopy with virtual instrumentation. The concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Multimeter
A multimeter (also known as a multi-tester, volt-ohm-milliammeter, volt-ohmmeter or VOM, avometer or ampere-volt-ohmmeter) is a measuring instrument that can measure multiple electrical properties. A typical multimeter can measure voltage, resistance, and current, in which case can be used as a voltmeter, ohmmeter, and ammeter. Some feature the measurement of additional properties such as temperature and capacitance. Analog multimeters use a microammeter with a moving pointer to display readings. Digital multimeters (DMMs) have numeric displays and are more precise than analog multimeters as a result. Meters will typically include probes that temporarily connect the instrument to the device or circuit under test, and offer some intrinsic safety features to protect the operator if the instrument is connected to high voltages that exceed its measurement capabilities. Multimeters vary in size, features, and price. They can be portable handheld devices or highly-precise bench inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing information on electrical signals for debugging, analysis, or characterization. The displayed waveform can then be analyzed for properties such as amplitude, frequency, rise time, time interval, distortion, and others. Originally, calculation of these values required manually measuring the waveform against the scales built into the screen of the instrument. Modern digital instruments may calculate and display these properties directly. Oscilloscopes are used in the sciences, engineering, biomedical, automotive and the telecommunications industry. General-purpose instruments are used for maintenance of electronic equipment and laboratory work. Special-purpose oscilloscopes may be used to analyze an automotive ignition system or to display th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog-to-digital Converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digital signal. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an analog input voltage or Electric current, current to a digital number representing the magnitude of the voltage or current. Typically the digital output is a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. There are several ADC hardware architecture, architectures. Due to the complexity and the need for precisely matched electronic component, components, all but the most specialized ADCs are implemented as integrated circuits (ICs). These typically take the form of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) mixed-signal integrated circuit chips that integrate both Analogue electronics, anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
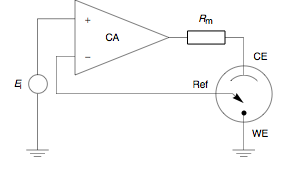
Potentiostat
A potentiostat is the electronic hardware required to control a three electrode cell and run most electroanalytical experiments. A ''Bipotentiostat'' and ''polypotentiostat'' are potentiostats capable of controlling two working electrodes and more than two working electrodes, respectively. The system functions by maintaining the potential of the working electrode at a constant level with respect to the reference electrode by adjusting the current at an auxiliary electrode. The heart of the different potentiostatic electronic circuits is an operational amplifier (op amp). It consists of an electric circuit which is usually described in terms of simple op amps. Primary use This equipment is fundamental to modern electrochemical studies using three electrode systems for investigations of reaction mechanisms related to redox chemistry and other chemical phenomena. The dimensions of the resulting data depend on the experiment. In voltammetry, electric current in amps is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and Phase (waves), phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and analysis of systems, such as audio system, audio and control systems, where they simplify mathematical analysis by converting governing differential equations into algebraic equations. In an audio system, it may be used to minimize audible distortion by designing components (such as microphones, Audio power amplifier, amplifiers and loudspeakers) so that the overall response is as flat (uniform) as possible across the system's Bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth. In control systems, such as a vehicle's cruise control, it may be used to assess system Stability theory, stability, often through the use of Bode plots. Systems with a specific frequency response can be designed using analog filter, analog and digital filters. The frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
Dielectric spectroscopy (which falls in a subcategory of the impedance spectroscopy) measures the dielectric properties of a medium as a function of frequency.Kremer F., Schonhals A., Luck W. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. – Springer-Verlag, 2002. It is based on the interaction of an external field with the electric dipole moment of the sample, often expressed by permittivity. It is also an experimental method of characterizing electrochemical systems. This technique measures the impedance of a system over a range of frequencies, and therefore the frequency response of the system, including the energy storage and dissipation properties, is revealed. Often, data obtained by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is expressed graphically in a Bode plot or a Nyquist plot. Impedance is the opposition to the flow of alternating current (AC) in a complex system. A passive complex electrical system comprises both energy dissipater (resistor) and energy storage (capacitor) e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Instrument
In metrology (test and measurement science), a synthetic instrument is software that performs a specific synthesis, analysis, or measurement function. A Synthetic Measurement System (SMS) is a common, general purpose, physical hardware platform that is intended to perform many kinds of synthesis, analysis, or measurement functions using synthetic instruments. Typically the generic SMS hardware is dual cascade of three subsystems: digital processing and control, analog-to-digital or digital-to-analog conversion (codec), and signal conditioning. One cascade is for stimulus, one for response. Sandwiched between them is the device under test (DUT) that is being measured. A synthetic instrument is the opposite of the retronym natural instrument. Although the word “synthetic” in the phrase synthetic instrument might seem to imply that synthetic instruments are synthesizers: that they only do synthesis; this is incorrect. The instrument itself is being synthesized; nothing is implie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Instruments
The National Instruments Corporation, doing business as NI, is an America, American multinational corporation, multinational company with international operations. Headquartered in Austin, Texas, Austin, Texas, it is a producer of automated test equipment, semiconductor production, and LabVIEW, virtual instrumentation software. Common applications include data acquisition (DAQ), instrument control, system management, and machine learning and machine vision, vision. Following its acquisition by Emerson Electric, the NI has operated the company’s test and measurement business unit since October 2023. In 2022, the company sold products to more than 35,000 companies worldwide with revenues of USD$1.66 billion. History Founding In the early 1970s, James Truchard, Jeff Kodosky, and Bill Nowlin were employed at the J. J. Pickle Research Campus#Campus, University of Texas at Austin Applied Research Laboratories. While working on a project for the U.S. Navy, they utilized early c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Programming
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instrument
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments, used for indicating, measuring, and recording physical quantities. It is also a field of study about the art and science about making measurement instruments, involving the related areas of metrology, automation, and control theory. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making. Instrumentation can refer to devices as simple as direct-reading thermometers, or as complex as multi- sensor components of industrial control systems. Instruments can be found in laboratories, refineries, factories and vehicles, as well as in everyday household use (e.g., smoke detectors and thermostats). Measurement parameters Instrumentation is used to measure many parameters (physical values), including: *Pressure, either differential or static * Flow *Temperature * Levels of liquids, etc. *Moisture or humidity *Density *Viscosity * ionising radiation * Frequency * Current *Voltage * Induct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow. Previously electrical engineering only used passive devices such as mechanical switches, resistors, inductors, and capacitors. It covers fields such as analog electronics, digital electronics, consumer electronics, embedded systems and power electronics. It is also involved in many related fields, for example solid-state physics, radio engineering, telecommunications, control systems, signal processing, systems engineering, computer engineering, instrumentation engineering, electric power control, photonics and robotics. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is one of the most important professional bodies for electronics engineers in the US; the equivalent body in the UK is the Institution of Engin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |