|
Violent Threat
Intimidation is a behaviour and legal wrong which usually involves deterring or coercing an individual by threat of violence. It is in various jurisdictions a crime and a civil wrong (tort). Intimidation is similar to menacing, coercion, terrorizing and assault in the traditional sense. This includes intentional behaviors of forcing another person to experience general discomfort such as humiliation, embarrassment, inferiority, limited freedom, etc and the victim might be targeted based on multiple factors like gender, race, class, skin color, competency, knowledge, wealth, temperament, etc. Intimidation is done for making the other person submissive (also known as cowing), to destabilize/undermine the other, to force compliance, to hide one's insecurities, to socially valorize oneself, etc. There are active and passive coping mechanisms against intimidation that include, but are not limited to, not letting the intimidator invade your personal dignity and space, addressing their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HHH Stares Down Punk
HHH may refer to: People * H. H. Holmes, one of America's first modern-day serial killers * Hans-Hermann Hoppe (born 1949), Austrian school economist * Hubert H. Humphrey (1911–1978), the 38th Vice President of the United States * Haela Hunt-Hendrix, musician * Hunter Hearst Helmsley (Triple H), stage name of professional wrestler Paul Levesque Places * Haven of Hope Hospital, a public hospital in Hong Kong * Hilton Head Airport, in South Carolina, United States * Hilton Head Island High School, in South Carolina, United States * Holland Heineken House Groups, organizations, companies * Hash House Harriers, an international group of running clubs * Hog Hoggidy Hog, a South African band * Hot Hot Heat, a Canadian band Other uses * Hugo's House of Horrors, a 1990 computer game * ''Hungry Hungry Hippos Hungry Hungry Hippos (or Hungry Hippos in some UK editions) is a tabletop game made for 2–4 players, produced by Hasbro, under the brand of its subsidiary, Milton Brad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Manipulation
In psychology, manipulation is defined as an action designed to influence or control another person, usually in an underhanded or subtle manner which facilitates one's personal aims. Methods someone may use to manipulate another person may include seduction, suggestion, coercion, and blackmail. Manipulation is generally considered a dishonest form of social influence as it is used at the expense of others. Humans are inherently capable of manipulative and deceptive behavior, with the main differences being that of specific personality characteristics or disorders. Etymology By 1730, the word ''manipulation'' was used to refer to a method of digging ore. The term derives from the French manipulation, which in turn comes from manipule, meaning "handful", a unit of measure used by pharmacists, later having a sense by 1828 of handling or managing people for one's own purposes. The word ''manipulate'' originated in 1827 as a back-formation from manipulation, initially meaning "to handl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, and the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fourth-largest state by area, but the List of U.S. states and territories by population, eighth-least populous state and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, third-least densely populated state. Its List of capitals in the United States, capital is Helena, Montana, Helena, while the List of municipalities in Montana, most populous city is Billings, Montana, Billings. The western half of the state contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh Penal Code
The Penal Code of Bangladesh, formally titled the Penal Code, 1860, is the general criminal law of the country. It is based on the Indian Penal Code, which was enacted in 1860 by the Governor General-in-Council. The Code bears strong similarities to the penal laws of countries that were formerly part of the British Empire in South and Southeast Asia, including Singapore, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Malaysia. The Parliament of Bangladesh has amended the Penal Code on several occasions, the most recent amendment occurring in 2004. The Code is a legacy of the Victorian era. While its objective is to provide a general penal framework for Bangladesh, the Parliament has also enacted various penal statutes to address specific areas of criminal law. History The Code was drafted based on the recommendations of the First Law Commission of British India and was presented to the Governor of Bengal in 1837. Although primarily based on Victorian English law, it also incorporated element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Code (Malaysia)
The Penal Code () is a law that codifies most criminal offences and procedures in Malaysia. Its official long title is "An Act relating to criminal offences" hroughout Malaysia—31 March 1976, Act A327; P.U. (B) 139/1976 The sole jurisdiction of Parliament of Malaysia is established over criminal law in Malaysia. Structure Penal Code of Malaysia, in its current form (4 June 2015), sub-divided into twenty three chapters, comprises five hundred and eleven sections (including 37 amendments). The code starts with an introduction, provides explanations and exceptions used in the code, and covers a wide range of offences. Chapter I: Preliminary :1. Short title :2. Punishment of offences committed within Malaysia :3. Punishment of offences committed beyond, but which by law may be tried within Malaysia :4. Extension of Code to extraterritorial offences :5. Certain laws not to be affected by this Code Chapter II: General Explanations :6. Definitions in the Code to be understood subje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore Penal Code
The Penal Code 1871 sets out general principles of the criminal law of Singapore, as well as the elements and penalties of general criminal offences such as assault, criminal intimidation, mischief, grievous hurt, theft, extortion, sex crimes and cheating (law), cheating. The Penal Code does not define and list exhaustively all the criminal offences applicable in Singapore – a large number of these are created by other statutes such as the Arms Offences Act (Singapore), Arms Offences Act, Kidnapping Act (Singapore), Kidnapping Act, Misuse of Drugs Act (Singapore), Misuse of Drugs Act and Vandalism Act (Singapore), Vandalism Act. History For most of the 19th century the criminal law which applied in the Straits Settlements (comprising Prince of Wales' Island (Penang), Singapore Island, Singapore and Malacca) was that of the United Kingdom, insofar as local circumstances permitted. There was little doubt that at the time English common law crimes were recognized in these territor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Penal Code
The Indian Penal Code (IPC) was the official criminal code of the Republic of India, inherited from British India after independence. It remained in force until it was repealed and replaced by the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) in December 2023, which came into effect on July 1, 2024. It was a comprehensive code intended to cover all substantive aspects of criminal law. The Code was drafted on the recommendations of the first Law Commission of India established in 1834 under the Charter Act 1833 under the chairmanship of Thomas Babington Macaulay. It came into force in the subcontinent during the British rule in 1862. However, it did not apply automatically in the Princely states, which had their own courts and legal systems until the 1940s. While in force, the IPC was amended several times and was supplemented by other criminal provisions. Despite promulgation of the BNS, litigation for all relevant offences committed before 1 July 2024 will continue to be registered under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Use Of Force
The use of force, in the context of law enforcement, may be defined as "the amount of effort required by police to compel compliance by an unwilling subject." Multiple definitions exist according to context and purpose. In practical terms, use of force amounts to any combination of threatened or actual force used for a lawful purpose, e.g. to effect arrest; defend oneself or another person; or to interrupt a crime in progress or prevent an imminent crime. Depending on the jurisdiction, legal rights of this nature might be recognized to varying degrees for both police officers and non-sworn individuals; and may be accessible regardless of citizenship. Canada's Criminal Code, for example, provides in section 494 for arrest in certain circumstances by "any one." Use of force doctrines can be employed by law enforcement officers and military personnel, who are on guard duty. The aim of such doctrines is to balance the needs of security with ethical concerns for the rights and well-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teacher
A teacher, also called a schoolteacher or formally an educator, is a person who helps students to acquire knowledge, competence, or virtue, via the practice of teaching. ''Informally'' the role of teacher may be taken on by anyone (e.g. when showing a colleague how to perform a specific task). In some countries, teaching young people of school age may be carried out in an informal setting, such as within the family (homeschooling), rather than in a formal setting such as a school or college. Some other professions may involve a significant amount of teaching (e.g. youth worker, pastor). In most countries, ''formal'' teaching of students is usually carried out by paid professional teachers. This article focuses on those who are ''employed'', as their main role, to teach others in a ''formal'' education context, such as at a school or other place of ''initial'' formal education or training. Duties and functions A teacher's role may vary among cultures. Teachers may provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
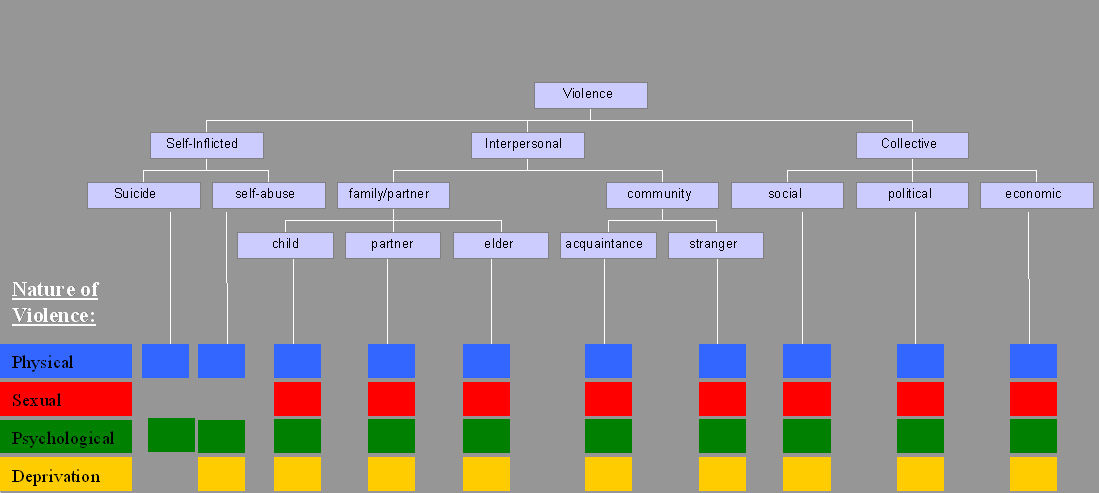
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (ethology)
In the zoological field of ethology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social groups interact, creating a ranking system. Different types of interactions can result in dominance depending on the species, including ritualized displays of aggression or direct physical violence. In social living groups, members are likely to compete for access to limited resources and mating opportunities. Rather than fighting each time they meet, individuals of the same sex establish a relative rank, with higher-ranking individuals often gaining more access to resources and mates. Based on repetitive interactions, a social order is created that is subject to change each time a dominant animal is challenged by a subordinate one. Definitions Dominance is an individual's preferential access to resources over another based on coercive capacity based on strength, threat, and intimidation, comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |