|
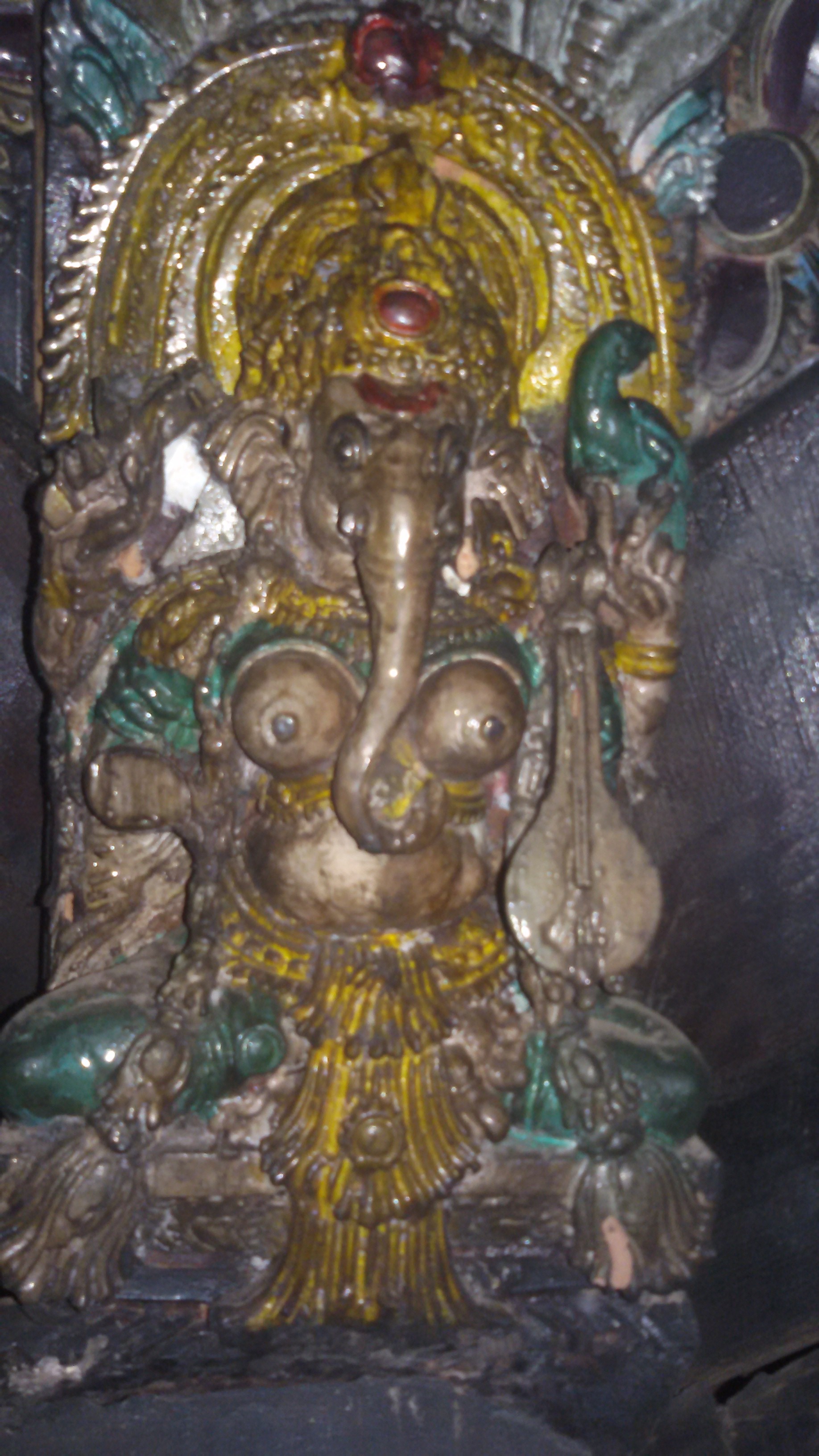
Vinayaki
Vinayaki (Vināyakī) is an elephant-headed Hinduism, Hindu goddess. Her mythology and iconography are not clearly defined. Little is told about her in Hindu scriptures and very few images of this deity exist.Mundkur p. 291 Due to her elephantine features, the goddess is generally associated with the elephant-headed god of wisdom, Ganesha. She does not have a consistent name and is known by various names, Stri Ganesha ("female Ganesha"), Vainayaki, Gajananā ("elephant-faced"), Vighneshvari ("Mistress of the remover of obstacles") and Ganeshani, all of them being feminine forms of Ganesha's epithets Vinayaka, Gajanana, Vighneshvara and Ganesha itself. These identifications have resulted in her being assumed as the shakti – feminine form of Ganesha.Mundkur p. 291 Vinayaki is sometimes also seen as the part of the sixty-four yoginis or the matrika goddesses. However, scholar Krishan believes that Vinayaki is an early elephant-headed matrikas, the Brahmanical ''shakti'' of Ganesha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
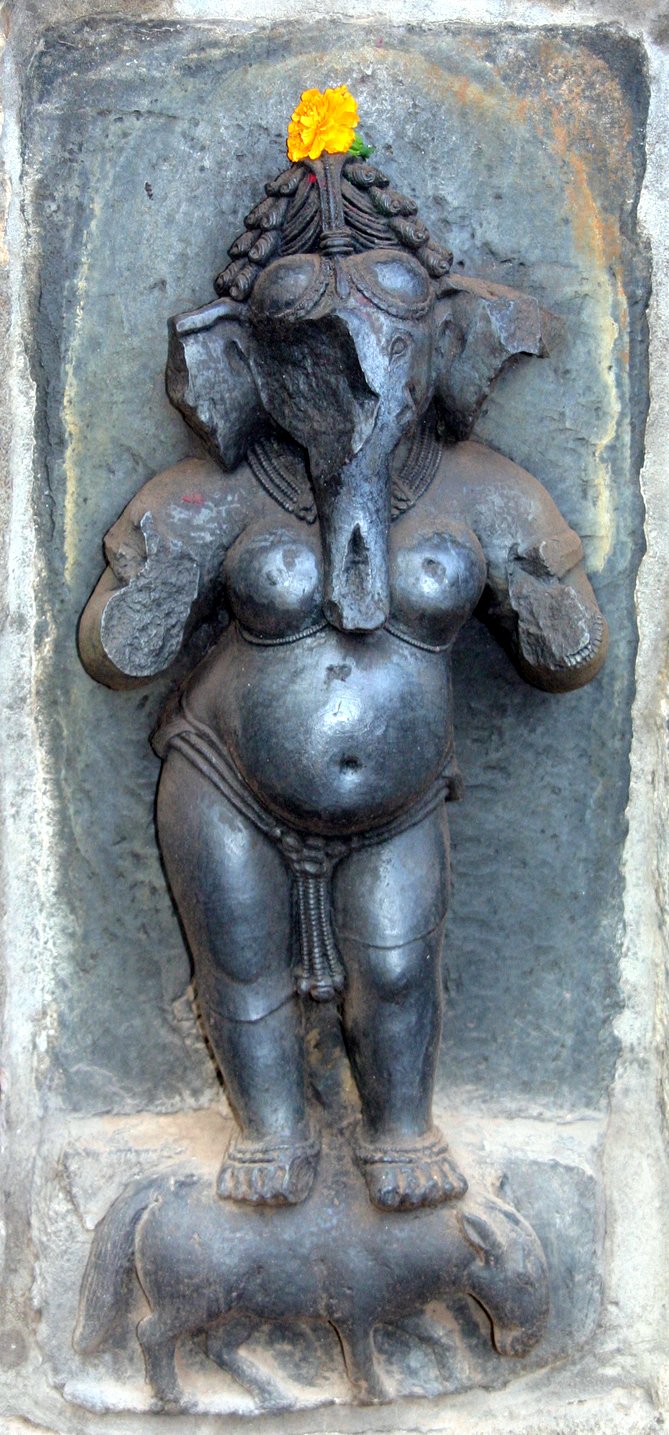
Vinayaki At Cheriyanad Temple
Vinayaki (Vināyakī) is an elephant-headed Hindu goddess. Her mythology and iconography are not clearly defined. Little is told about her in Hindu scriptures and very few images of this deity exist.Mundkur p. 291 Due to her elephantine features, the goddess is generally associated with the elephant-headed god of wisdom, Ganesha. She does not have a consistent name and is known by various names, Stri Ganesha ("female Ganesha"), Vainayaki, Gajananā ("elephant-faced"), Vighneshvari ("Mistress of the remover of obstacles") and Ganeshani, all of them being feminine forms of Ganesha's epithets Vinayaka, Gajanana, Vighneshvara and Ganesha itself. These identifications have resulted in her being assumed as the shakti – feminine form of Ganesha.Mundkur p. 291 Vinayaki is sometimes also seen as the part of the sixty-four yoginis or the matrika goddesses. However, scholar Krishan believes that Vinayaki is an early elephant-headed matrikas, the Brahmanical ''shakti'' of Ganesha, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
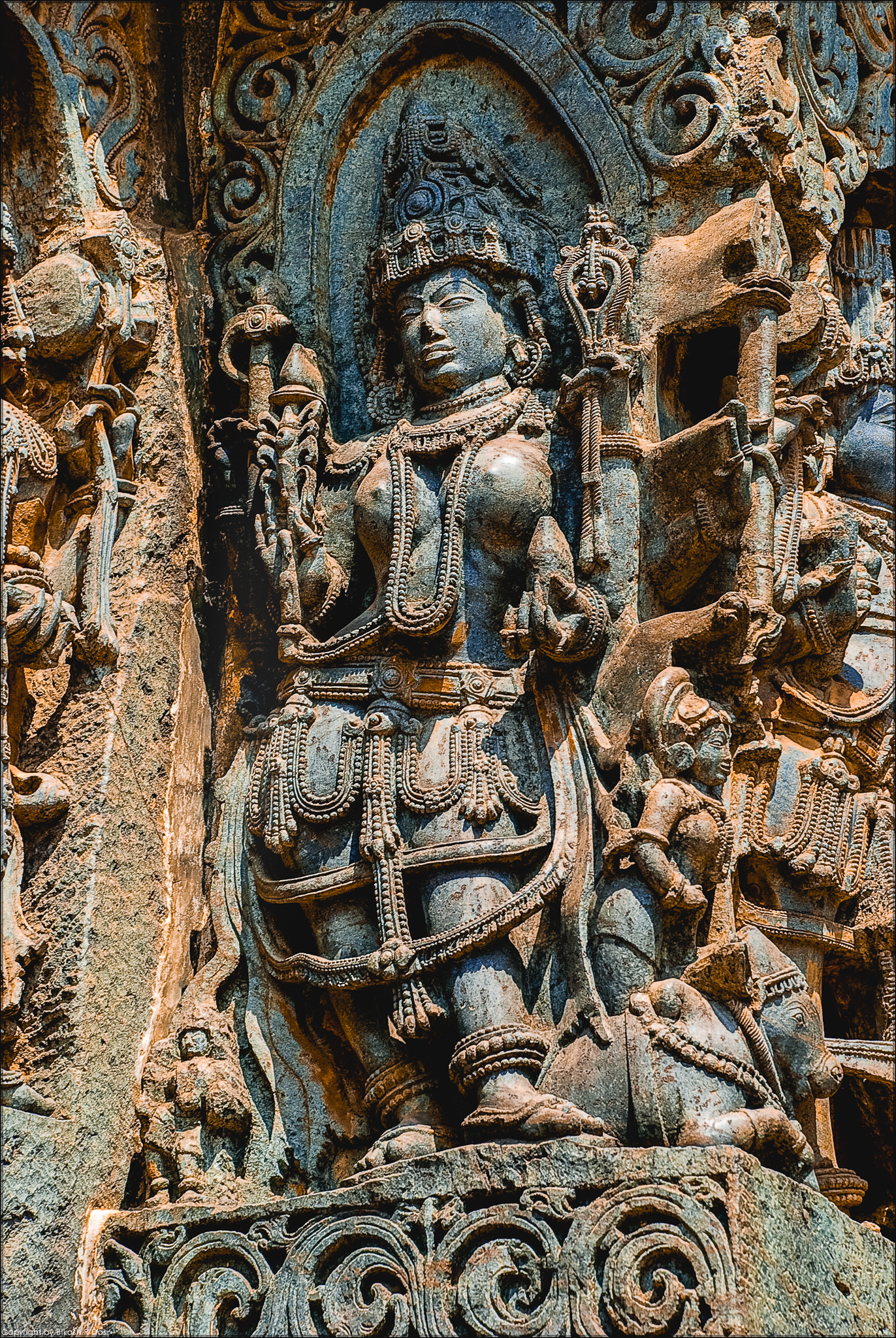
Matrika
Matrikas (Sanskrit: मातृका (singular), IAST: mātṛkā, lit. "mothers") also called Mataras or Matri, are a group of mother goddesses in Hinduism. The Matrikas are often depicted in a group of seven, the Saptamatrika(s) (Seven Mothers). However, they are also depicted as a group of eight, the Ashtamatrika(s). In the '' Brihat Samhita'', Varahamihira says that "Matrikas are forms of Parvati taken by her with cognizance of (different major Hindu) gods corresponding to their names." They are associated with these gods as their energies (''Shaktis''). Brahmani emerged from Brahma, Vaishnavi from Vishnu, Maheshvari from Shiva, Indrani from Indra, Kaumari from Kartikeya, Varahi from Varaha and Chamunda from Chandi. And additionals are Narasimhi from Narasimha and Vinayaki from Ganesha. Originally the seven goddesses of the seven stars of the star cluster of the Pleiades, they became quite popular by the seventh century CE and a standard feature of the Hindu goddes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakti
Shakti (Devanagari: शक्ति, IAST: Śakti; 'energy, ability, strength, effort, power, might, capability') in Hinduism, is the "Universal Power" that underlies and sustains all existence. Conceived as feminine in essence, Shakti refers to the personified energy or power of a Deva (Hinduism), male deity, often personified as the female consort of the given Hindu god. In Tantric Shaktism, Shakti is the foremost deity, akin to Brahman. In Puranic Hinduism, Shiva and Shakti are the masculine and feminine principles that are complementary to each other. The male deity is ''purusha'', pure consciousness, which creates the universe through the female creative energy of Shakti, which is ''Prakṛti, prakriti'', 'nature'. The term ''Shakta'' is used for the description of people associated with Shakti worship. The Shakta pithas are shrines, which are believed to be the sacred seats of Shakti. Etymology and overview According to the Monier Monier-Williams, Monier-Williams dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abhayamudra
The abhayamudra () is a mudra (gesture) that is the gesture of reassurance and safety, which dispels fear and accords divine protection and bliss in Hinduism, Buddhism, and other Indian religions. The right hand is raised to shoulder height, with the palm is facing outward and the fingers pointing upwards This is one of the earliest mudras found depicted on a number of Hindu, Buddhist, Jain, and Sikh images. Description The abhayamudra represents protection, peace, benevolence and the dispelling of fear. A form of the Hindu god Shiva, Nataraja, is depicted with the second right hand making the abhayamudra, bestowing protection from both evil and ignorance to those who follow the righteousness of dharma. In Theravada Buddhism, it is usually made with the right hand raised to shoulder height, the arm bent and the palm facing outward with the fingers upright and joined and the left hand hanging down while standing. In Thailand and Laos, this mudra is associated with the Walkin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varadamudra
The Varadamudra () or Abheeshta Mudra is a ''mudra'', a symbolic gesture featured in the iconography of Indian religions. It indicates a gesture by the hand and symbolises dispensing of boons. It is represented by the palm held outward, with the fingers outstretched and pointing downwards. Sometimes, the thumb and the index finger meet, forming a circle. The Varadamudra and the Abhayamudra are the most common of several other mudras seen on divine figures in the art of Indian religions Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification o .... References * ''Dictionary of Hindu Lore and Legend'' () by Anna Dallapiccola External links * Hand gestures Hindu iconography Hindu philosophical concepts Mudras {{Buddhism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudra
A mudra (; , , "seal", "mark", or "gesture"; ) is a symbolic or ritual gesture or pose in Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. While some mudras involve the entire body, most are performed with the hands and fingers. As well as being spiritual gestures employed in the iconography and spiritual practice of Indian religions, mudras have meaning in many forms of Indian dance, and yoga. The range of mudras used in each field (and religion) differs, but with some overlap. In addition, many of the Buddhist mudras are used outside South Asia, and have developed different local forms elsewhere. In hatha yoga, mudras are used in conjunction with pranayama (yogic breathing exercises), generally while in a seated posture, to stimulate different parts of the body involved with breathing and to affect the flow of prana. It is also associated with bindu, bodhicitta, amrita, or consciousness in the body. Unlike older tantric mudras, hatha yogic mudras are generally internal actions, involvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories of India by area, fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the List of states and union territories of India by population, ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million in 2011. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujarati people, Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state List of Indus Valley civilisation sites#List of Indus Valley sites discovered, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganapatya
Ganapatya is a denomination of Hinduism that worships Ganesha (also called Ganapati) as the Parabrahman, Saguna Brahman.Ganapatyas Article from PHILTAR, Division of Religion and Philosophy, St Martin's College Beliefs The worship of is considered complementary with the worship of other deities. Hindus of all sects begin prayers, important undertakings, and religious ceremonies with an invocation of Ganesha, because of Ganesha's role as the god of beginnings. But although most Hindu sects do revere Ganesha, the Ganapatya sect goes further than that, and declares Ganesha to be the supreme being. Ganapatya is one of the five principal Hindu sects which focus on a particular deity, along ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantra
Tantra (; ) is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the India, Indian subcontinent beginning in the middle of the 1st millennium CE, first within Shaivism and later in Buddhism. The term ''tantra'', in the Greater India, Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on Indian Tantras (Buddhism), Buddhist Tantras. They include Tibetan Buddhism, Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Japanese Shingon Buddhism and Nepalese Newar Buddhism. Although Southern Esoteric Buddhism does not directly reference the tantras, its practices and ideas parallel them. In Bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirali
Shirali is a village in Bhatkal taluk of Uttara Kannada district in Karnataka. Shirali is home to two prominent temples: the Chitrapur Math and the Maha Ganapathi Mahammaya Temple. The Chitrapur Math is the holiest temple of the Chitrapur Saraswat Brahmin community, and the Maha Ganapathi Mahammaya temple is the Kuladev to the Kamaths, Bhats, Puraniks, Prabhus, Joishys, Mallyas, Kudvas and Nayak families from the Goud Saraswat Brahmin community. Etymology The name ''Shirali'' is derived from Sanskrit ''Shrivalli'', which means ''wealthy''. The shrine of Goddess Shrivalli Bhuvaneshwari inside the premises of Chitrapur Math signifies the origin of the name '' Shirali''. Geography Shirali is located at . It has an average elevation of 12 meters (42 ft). Nearest towns- On the South is Bhatkal and Baindur. On the North is another temple town, Murudeshwar . Transportation Road Shirali is on the National Highway No. 66 (the highway that runs from Mumbai to Thiruvan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vamachara
''Vāmācāra'' (, ) is a tantric term meaning 'left-hand path' and is synonymous with the Sanskrit term ''vāmamārga''. It is used to describe a particular mode of worship or '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) that uses heterodox things to sublimate for spiritual growth. These practices are often generally considered to be tantric in orientation. The converse term is '' dakṣiṇācāra'' "right-hand path", which is used to refer not only to orthodox sects but to modes of spirituality that engage in spiritual practices that accord with Vedic injunction and are generally agreeable to the status quo. Left-handed and right-handed modes of practice may be evident in both orthodox and heterodox practices of Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and Buddhism and are a matter of taste, culture, proclivity, initiation, ''sadhana'' and lineage ('' parampara''). Nomenclature and etymology N. N. Bhattacharyya explains the Sanskrit technical term '' '' as follows: e me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |