|
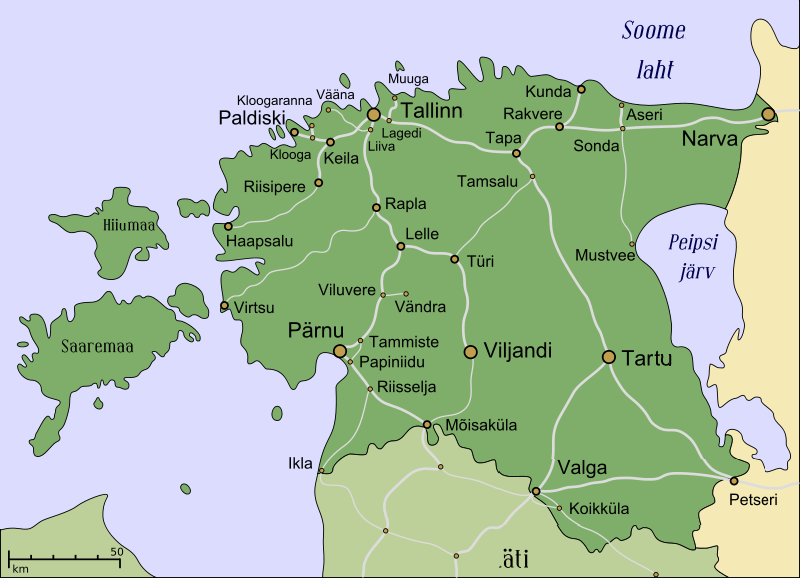
Viljandi Railway Station
Viljandi railway station () is a railway station serving the town of Viljandi in southern Estonia. The station is the southern terminus of the Tallinn–Viljandi railway line. The station opened in 1897 when a narrow-gauge railway line was opened connecting Mõisaküla with Vijandi, which was prolonged to Tallinn in 1901. The narrow-gauge railway between Mõisaküla and Viljandi was closed in 1973. Currently, the station is owned by the railway infrastructure company Edelaraudtee and served by trains operated by the government-owned passenger train operator Elron. See also * List of railway stations in Estonia * Rail transport in Estonia * History of rail transport in Estonia References External links Official websiteof Edelaraudtee – a railway infrastructure company which owns the railway lines from Tallinn to Rapla, Pärnu & Viljandi Official websiteof Elron – the national passenger train operating company of Estonia operating all domestic passenger train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Train Station
A train station, railroad station, or railway station is a railway facility where trains stop to load or unload passengers, freight, or both. It generally consists of at least one platform, one track, and a station building providing such ancillary services as ticket sales, waiting rooms, and baggage/freight service. Stations on a single-track line often have a passing loop to accommodate trains travelling in the opposite direction. Locations at which passengers only occasionally board or leave a train, sometimes consisting of a short platform and a waiting area but sometimes indicated by no more than a sign, are variously referred to as "stops", "flag stops", " halts", or "provisional stopping places". The stations themselves may be at ground level, underground, or elevated. Connections may be available to intersecting rail lines or other transport modes such as buses, trams, or other rapid transit systems. Terminology ''Train station'' is the terminology typically use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and administratively lies in the Harju County, Harju ''Counties of Estonia, maakond'' (county). Tallinn is the main governmental, financial, industrial, and cultural centre of Estonia. It is located northwest of the country's second largest city, Tartu, however, only south of Helsinki, Finland; it is also west of Saint Petersburg, Russia, north of Riga, Latvia, and east of Stockholm, Sweden. From the 13th century until the first half of the 20th century, Tallinn was known in most of the world by variants of its other historical Names of Tallinn in different languages, name Reval. “Reval” received Lübeck law, Lübeck city rights in 1248; however, the earliest evidence of human settlement in the area dates back nearly 5,000 years. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passenger Train
A passenger train is a train used to transport people along a railroad line, as opposed to a freight train that carries goods. These trains may consist of unpowered passenger railroad cars (also known as coaches or carriages) push-pull train, hauled by one or more locomotives, or may be self-propelled; self propelled passenger trains are known as multiple units or railcars. Passenger trains stop at Train station, stations or depots, where passengers may board and disembark. In most cases, passenger trains operate on a fixed Public transport timetable, schedule and have priority over freight trains. Car design and the general safety of passenger trains have dramatically evolved over time, making travel by rail remarkably safe. Some passenger trains, both long-distance and short-distance, use Bilevel car, bi-level (double-decker) cars to carry more passengers per train. Sleeper trains include sleeping cars with beds. Passenger trains hauled by locomotives are more expensive to op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Train Operating Company
In the railway system of Great Britain, a train operating company (TOC) is a railway undertaking operating passenger trains under the collective National Rail brand. TOCs have existed since the privatisation of the network under the Railways Act 1993. There are two types of TOC: most hold franchises let by the Department for Transport (DfT) through a tendering system, to operate services on certain routes for a specified duration, while a small number of open-access operators hold licences to provide supplementary services on chosen routes. These operators can run services for the duration of the licence validity. The franchised operators have changed considerably since privatisation: previous franchises have been divided, merged, re-let to new operators, or renamed. Some privately-operated franchises have been taken over by a government-owned operator of last resort, due either to failing expectations or to events on the rail system as a whole. The term is also sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Infrastructure Manager
A railway infrastructure manager is a rail transport company or body of other type, responsible for maintaining railway infrastructure. The European Union defines it as "any body or undertaking that is responsible in particular for establishing and maintaining railway infrastructure. This may also include the management of infrastructure control and safety systems. The functions of the infrastructure manager on a network or part of a network may be allocated to different bodies or undertakings" This includes mainly railway track and catenary, if the railway line is electrified, and respective command and control systems. It can also include the stations and power supply network. A significant proportion of these companies are state-owned monopolies, responsible for all or most of the railway infrastructure within a given country. Ownership and operation of these two components varies by location. In some places (notably, most of North America) private railway companies own and ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Rail Transport In Estonia
The history of rail transport in Estonia starts in 1870 when a railway line was opened connecting Paldiski, Tallinn, Tapa and Narva; the line extending all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia. Beginnings of Estonian railways in Imperial Russia The first railway line to be built in Estonia was the Paldiski – Tallinn – Narva – Gatchina line constructed in 1870; Baltic German nobility provided the impetus for the construction of the line, though because of the Russian influence the line was built to 1524mm (5 ft) gauge to connect with the line from Saint Petersburg to Warsaw . The construction project was controlled by the Russian Ministry of Roads. The port of Paldiski was chosen because its southerly position made it ice free all the year round. Soon after both Paldiski and Tallinn experienced an upswing in trade, notably exports of grain. In 1877 another line was complete, connecting Tapa and Tartu; later extended to Valga in 1887, which brought a connection to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Estonia
The rail transport system in Estonia consists of about of railway lines, of which are currently in public use. The infrastructure of the railway network is mostly owned by the state and is regulated and surveyed by the Estonian Technical Surveillance Authority (). All public railways in Estonia are (Russian gauge), the same as in Russia, Belarus, Latvia, and Lithuania. The gauge used in Estonia is also compatible with Finland's gauge. Sometimes it is defined to be (see Rail gauge in Estonia), for example when buying track maintenance or vehicles from Finland. Railways in Estonia today are used mostly for freight transport, but also for passenger traffic, with 8.3 million passengers reported in 2019. Passenger transport is most frequent near Tallinn, centred on the main Tallinn Baltic Station. The Tallinn to Tartu railway is due to be electrified by 2024, with electrification of the remaining network expected to be completed by 2028. 16 new electric trains manufactured b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Railway Stations In Estonia
A list is a Set (mathematics), set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of ''The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |