|
Viennensis
Viennensis or Gallia Viennensis was a Late Roman province that derived its name from its capital Vienna (modern day Vienne, Isère), a Roman city, first located in Gallia Narbonensis. Vienna was first given the rank of colonia by Julius Caesar, after his Gallic campaigns in 58 BCE and 52 BCE, as a colony of veterans (''Colonia Julia Viennensium''); Augustus reinstated the rights after the romanized Allobroges had revolted which led to a temporary loss of the title; Caligula eventually named it ''Colonia Julia Augusta Florentia Viennensium'' in 40 CE. During the reorganization of the provinces under the tetrachy of Diocletian in the early 4th century, Vienna then became the capital of the province of Viennensis with the tribes of the Allobrogi, Segovellauni, Helvii, Tricastini, Vocontii and Cavari. In the 5th century the province was further divided into Gallia Viennense I, with its capital Vienne, and Gallia Viennense II, with its capital Arles. References See also * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septem Provinciae
The Diocese of the Seven Provinces (), originally called the Diocese of Vienne () after the city of ''Vienna'' (modern Vienne), was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, under the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. It encompassed southern and western Gaul ( Aquitania and Gallia Narbonensis), that is, modern France south and west of the Loire, including Provence. The diocese comprised the following provinces: Aquitanica I, Aquitanica II, Novempopulana (Aquitanica III), Narbonensis I, Narbonensis II, Viennensis and Alpes Maritimae. History The diocese was established during the reforms of Diocletian who reigned from 284-305. It is attested early in the reign of Constantine I in the Verona List which has been dated to around 314. In 402 an annual provincial assembly, the '' Concilium septem provinciarum'', was established in Arles. In 407, the Vandals and their allies invaded Gaul, devastating the region until they departed for the Iberian peninsula in 409. The Visigoths were b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocontii
The Vocontii (Gaulish: *''Uocontioi''; Ancient Greek, Greek: Οὐοκόντιοι, Οὐοκοντίων) were a Gauls, Gallic people dwelling on the western foothills of the Alps during the La Tène culture, Iron Age and the Roman period. The Vocontii settled in the region in the 3rd century BC at the latest. Gnaeus Pompeius Trogus, Pompeius Trogus, a Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman Roman historiography, historian and citizen of Vasio during the 1st century BC, was a member of the Vocontii. During the Roman period, they were probably at the head of a confederation that included the Sogiontii, Avantici, Sebaginni and Vertamocorii (Narbonensis), Vertamocorii. Name They are mentioned as ''Vocontii'' (in the genitive plural ''Vocontiorum'') by Julius Caesar, Caesar (mid-1st c. BC), Livy (late 1st c. BC), Pliny the Elder, Pliny (1st c. AD) and Pomponius Mela (mid-1st c. AD), as ''Ouokóntioi'' (Οὐοκόντιοι, gen. pl. ''Ouokontíōn'' [Οὐοκοντίων]) by Strabo (ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienne, Isère
Vienne (; ) is a town in southeastern France, located south of Lyon, at the confluence of the Gère and the Rhône. It is the fourth-largest commune in the Isère department, of which it is a subprefecture alongside La Tour-du-Pin. Vienne was a major centre of the Roman Empire under the Latin name ''Vienna''. Vienne was the capital of the Allobroges, a Gallic people, before its conquest by the Romans. Transformed into a Roman colony in 47 BC under Julius Caesar, it became a major urban centre, ideally located along the Rhône, then a major axis of communication. Emperor Augustus banished Herod the Great's son, the ethnarch Herod Archelaus to Vienne in 6 AD. As Vienne was a Roman provincial capital, remains of Roman constructions are still widespread across it. The city was also an important early bishopric in Christian Gaul. Its most famous bishop was Avitus of Vienne. At the Council of Vienne, which was convened there in October 1311, Pope Clement V abolished the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in Occitania and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the first Roman province north of the Alps, and as Gallia Transalpina ("Transalpine Gaul"), distinguishing it from Cisalpine Gaul in Northern Italy. It became a Roman province in the late 2nd century BC. Gallia Narbonensis was bordered by the Pyrenees Mountains on the west, the Cévennes to the north, the Alps on the east, and the Gulf of Lion on the south; the province included the majority of the Rhone catchment. The western region of Gallia Narbonensis was known as Septimania. The province was a valuable part of the Roman Empire, owing to the Greek colony and later Roman Civitas of Massalia, its location between the Spanish provinces and Rome, and its financial output. Names The province of ''Gallia Transalpina'' ("Transalpine Gaul" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Roman Empire
The history of the Roman Empire covers the history of ancient Rome from the traditional end of the Roman Republic in 27 BC until the abdication of Romulus Augustulus in AD 476 in the West, and the Fall of Constantinople in the East in 1453. Ancient Rome became a territorial empire while still a republic, but was then ruled by Roman emperor, emperors beginning with Augustus, Octavian Augustus, the final victor of the Crisis of the Roman Republic, republican civil wars. Rome had begun expanding shortly after the founding of the Republic in the 6th century BC, though it did not expand outside the Italian Peninsula until the 3rd century BC, during the Punic Wars, after which the Republic expanded across the Mediterranean. Civil war engulfed Rome in the mid-1st century BC, first between Julius Caesar and Pompey, and finally between Augustus, Octavian (Caesar's grand-nephew) and Mark Antony. Antony was defeated at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, leading to the annexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Disestablished In The 5th Century
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * '' State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * '' Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century Disestablishments In The Roman Empire
The 5th century is the time period from AD 401 (represented by the Roman numerals CDI) through AD 500 (D) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to a formal end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century Establishments In The Roman Empire
The 4th century was the time period from 301 CE (represented by the Roman numerals CCCI) to 400 CE (CD) in accordance with the Julian calendar. In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two-emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
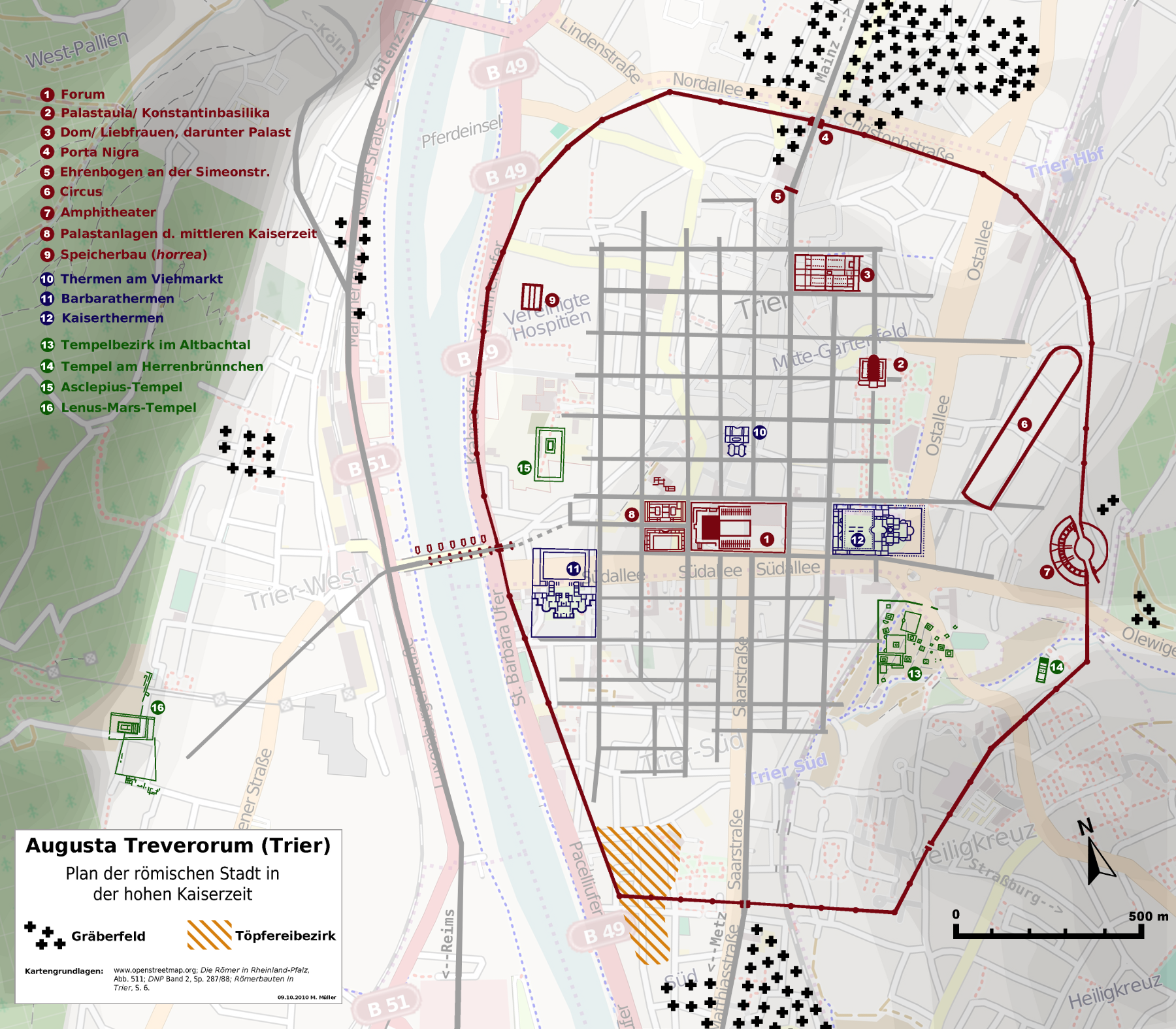
Augusta Treverorum
Augusta Treverorum (Latin for "City of Augustus in the Land of the Treveri") was a Ancient Rome, Roman city on the Moselle River, from which modern Trier emerged. The date of the city's founding is placed between the construction of the first Roman bridge, Roman bridge in Trier (18/17 BC) and the late reign of Augustus († 14 AD). In the Roman Empire, Trier formed the main town of the ''civitas'' of the Treverians, where several ten thousand people lived, and belonged to the province of Gallia Belgica. Roman Trier gained particular importance in late antiquity: between the late 3rd and late 4th centuries several rulers, including Constantine the Great, used the city as one of the western imperial residences, sponsoring monumental buildings such as the Trier Imperial Baths and the Aula Palatina, Basilica of Constantine. With a high five-digit population in 300, Augusta Treverorum, now sometimes called Treveris, was the largest city north of the Alps and thus had the status of a glo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugdunum
Lugdunum (also spelled Lugudunum, ; modern Lyon, France) was an important Colonia (Roman), Roman city in Gaul, established on the current site of Lyon, France, Lyon. The Roman city was founded in 43 BC by Lucius Munatius Plancus, but continued an existing Gallic settlement with a likely population of several thousands. It served as the capital of the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis and was an important city in the western half of the Roman Empire for centuries. Two emperors, Claudius and Caracalla, were born in Lugdunum. In the period 69–192 AD, the city's population may have numbered 50,000 to 100,000, and possibly up to 200,000 inhabitants. The original Roman city was situated west of the confluence of the Rhône River, Rhône and Saône, on the Fourvière heights. By the late centuries of the empire much of the population was located in the Saône River valley at the foot of Fourvière. Name The Roman city was founded as ''Colonia Copia Felix Munatia'', a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arles
Arles ( , , ; ; Classical ) is a coastal city and Communes of France, commune in the South of France, a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture in the Bouches-du-Rhône Departments of France, department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region, in the former Provinces of France, province of Provence. A large part of the Camargue, the largest wetlands in France, is located within the territory of the commune, which is the List of French communes by surface area, largest in Metropolitan France in terms of geographic territory. In non-metropolitan France, Maripasoula in French Guiana is the largest French commune in general. The commune's land area is roughly similar to that of Singapore. The city has a long history, and was of considerable importance in the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis. The Arles, Roman and Romanesque Monuments, Roman and Romanesque Monuments of Arles were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1981 for their testimony to the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |