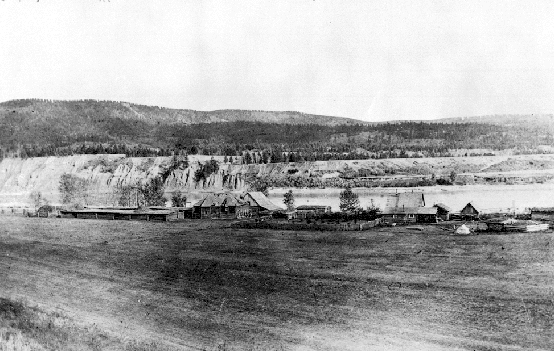|
Victoria (sternwheeler)
''Victoria'' was a passenger and freight sternwheeler that was built for service on the Soda Creek to Quesnel route on the upper Fraser River in British Columbia. She was built at Quesnel by pioneer shipbuilder James Trahey of Victoria for Gustavus Blin-Wright and Captain Thomas Wright and was put into service in the spring of 1869 to augment the service of also built by Trahey for the Wrights. Although the ''Victoria''s hull was new, her engines and boiler had originally been in the ''Prince of Wales'' from Lillooet Lake. The ''Victoria'' was the second of twelve sternwheelers that would work on this section of the Fraser River. She was larger than the ''Enterprise'' and more powerful. The two steamers worked together for only three years, when in 1871, the ''Enterprise'' was taken up to Takla Landing and abandoned on Trembleur Lake. The ''Victoria'' would work alone on the Soda Creek to Quesnel route for fifteen more years until 1886. The route The Fraser River was not con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Red Ensign 1868-1921
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Canadian''. Canada is a multilingual and multicultural society home to people of groups of many different ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. Following the initial period of French and then the much larger British colonization, different waves (or peaks) of immigration and settlement of non-indigenous peoples took place over the course of nearly two centuries and continue today. Elements of Indigenous, French, British, and more recent immigrant customs, languages, and religions have combined to form the culture of Canada, and thus a Canadian identity. Canada has also been strongly influenced by its linguistic, geographic, and eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trembleur Lake
Trembleur Lake is a lake in the Omineca Country of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, northwest of Fort St. James between Stuart Lake and the south end of Takla Lake Takla Lake is the fifth largest natural lake in British Columbia, Canada. It is a deep fjord-like lake with the Swannell Ranges to the east, the Driftwood River flowing into it from the north, and the Middle River draining it. It is the te .... It is part of the Nechako Lakes. Its name in the Dakelh language is Dzindlat Bun. It has also been known as Cross Lake. Trembleur Lake Provincial Park is on its north shore, above the Middle River. The reserve settlement of Middle River is at that river's mouth into Trembleur Lake. References {{authority control Lakes of British Columbia Omineca Country Range 5 Coast Land District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ships In British Columbia
The following is a list of vessels notable in the history of the Canadian province of British Columbia, including Spanish, Russian, American and other military vessels and all commercial vessels on inland waters as well as on saltwater routes up to the end of World War II (1945). A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Y See also *Steamboats of the Upper Fraser River in British Columbia * Steamboats of the Skeena River * Steamboats of the Arrow Lakes * Steamboats of Lake Okanagan * Vessels of the Lakes Route *Graveyard of the Pacific *Inside Passage * Puget Sound Mosquito Fleet * American Bay References *''British Columbia Chronicle: Adventurers by Sea and Land'', Helen B. Akrigg and G.P.V. Akrigg, Discovery Press, Vancouver, 1975. ISBN *''British Columbia Chronicle: Gold and Colonists'', Helen B. Akrigg and G.P.V. Akrigg, Discovery Press, Vancouver, 1977. ISBN *''The No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamboats Of The Upper Fraser River In British Columbia
Twelve paddlewheel steamboats plied the upper Fraser River in British Columbia from 1863 until 1921. They were used for a variety of purposes: working on railroad construction, delivering mail, promoting real estate in infant townsites and bringing settlers in to a new frontier. They served the towns of Quesnel, Barkerville and Fort George. Some only worked the Fraser from Soda Creek to Quesnel, while others went all the way to Tête Jaune Cache or took the Nechako River and served Fort Fraser and beyond. Pioneer sternwheelers - the Wright boats The first steamer used on the upper Fraser River was the ''Enterprise''. She was built in 1862 near Alexandria by James Trahey for her owners Captain Thomas Wright and Gustavus Blin Wright, who also were her operators. She ran between Soda Creek and Quesnel from 1863 until 1871 when the Wrights took her to Takla Landing for use in the Omineca Gold Rush. This voyage was to be her last and she was abandoned after she made the trip. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariboo Road
The Cariboo Road (also called the Cariboo Wagon Road, the Great North Road or the Queen's Highway) was a project initiated in 1860 by the Governor of the Colony of British Columbia, James Douglas. It involved a feat of engineering stretching from Fort Yale to Barkerville, B.C. through extremely hazardous canyon territory in the Interior of British Columbia. Between the 1860s and the 1880s the Cariboo Road existed in three versions as a surveyed and constructed wagon-road route. The first Cariboo Wagon Road surveyed in 1861 and built in 1862 followed the original Hudson's Bay Company's Harrison Trail (Port Douglas) route from Lillooet to Clinton, 70 Mile House, 100 Mile House, Lac La Hache, 150 Mile House to the contract end around Soda Creek and Alexandria at the doorstep of the Cariboo Gold Fields. The second Cariboo Wagon Road (or Yale Cariboo Road) operated during the period of the fast stage-coaches and freight-wagon companies headquartered in Yale: 1865 to 1885. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnard's Express
Barnard's Express, later known as the British Columbia Express Company or BX, was a pioneer transportation company that served the Cariboo and Fraser-Fort George regions in British Columbia, Canada from 1861 until 1921. The company's beginnings date back to the peak of the Cariboo Gold Rush when hordes of adventurers were descending on the Cariboo region. There was a great demand for the transportation of passengers to and from the goldfields, as well as the delivery of mining equipment, food supplies and mail between Victoria and Barkerville. The stage years The first express service offered on the Cariboo Road was operated by William Ballou in 1858. Others soon followed, usually one or two man operations where the proprietor himself packed the express goods, either on his back or with the help of a trusty mule. In December, 1861, Francis Jones Barnard established a pony express from Yale to Barkerville. The company had originally been owned by William Jeffray and W.H. Thain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barkerville
Barkerville was the main town of the Cariboo Gold Rush in British Columbia, Canada, and is preserved as a historic town. It is located on the north slope of the Cariboo Plateau near the Cariboo Mountains east of Quesnel. BC Highway 26, which follows the route of the Cariboo Wagon Road, the original access to Barkerville, goes through it. History Founding Barkerville is located on the western edge of the Cariboo Mountains in British Columbia. It was named after Billy Barker from Cambridgeshire, England, who was among those who first struck gold at the location in 1861. His claim was the richest and the most famous. Barkerville was built up almost overnight, and was a case of "growth via word of mouth". It grew as fast as the word of Barker's strike spread. His claim would eventually yield 37,500 ounces (1,065 kg/2,350 lb) of gold. Before the construction of the Cariboo Wagon Road, people hauled their own supplies to Barkerville, either on their backs or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soda Creek Canyon
Soda or SODA may refer to: Chemistry * Some chemical compounds containing sodium ** Sodium carbonate, washing soda or soda ash ** Sodium bicarbonate, baking soda ** Sodium hydroxide, caustic soda ** Sodium oxide, an alkali metal oxide * Soda glass, a common glass made with sodium carbonate or sodium oxide * Soda lake, an alternate generic name for a salt lake, with high concentration of sodium carbonates * Soda lime, a mixture of sodium, calcium, and potassium hydroxides * Soda pulping, a process for paper production using sodium compounds Computing * SODA (operating system) * Service-oriented development of applications * Service-oriented device architecture, to enable devices to be connected to a service-oriented architecture * Service-oriented distributed applications * Simple Object Database Access, an API for database queries * Soda PDF, a family of applications used on .pdf files * Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, an annual academic conference in computer science E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale, British Columbia
Yale is an unincorporated town in the Canadian province of British Columbia, which grew in importance during the gold rush era. Located on the Fraser River, it is generally considered to be on the dividing line between the Coast and the Interior regions of the British Columbia Mainland. Immediately north of the town, the Fraser Canyon begins and the river is generally considered unnavigable past this point. Rough water is common on the Fraser anywhere upstream from Chilliwack and even more so above Hope, about south of Yale. However, steamers could make it to Yale, good pilots and water conditions permitting, and the town had a busy dockside life as well as a variety of bars, restaurants, hotels, saloons and various services. Its maximum population during the gold rush era was in the 15,000 range. More generally, it housed 5,000-8,000. The higher figure was counted at the time of evacuation of the Canyon during the Fraser Canyon War of 1858. Most of today's population are membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lillooet Lake
Lillooet Lake is a lake in British Columbia, Canada about 25 km in length and about 33.5 square kilometres (22 mi²) in area. It is about 95 km downstream from the source of the Lillooet River, which resumes its course after leaving Little Lillooet Lake, aka Tenas Lake (''tenass'' in the Chinook Jargon means ''little''). Immediately adjacent to the mouth of the upper Lillooet River is the mouth of the Birkenhead River and just upstream along the Lillooet is the confluence of the Green River, which begins at Green Lake in the resort area of Whistler. The community of Pemberton is about 12 km upstream from the head of Lillooet Lake, while the eastern edge of the Mount Currie Indian Reserve of the Lil'wat branch of the St'at'imc people is the lakeshore itself. The eastern ramparts of the mountain ranges of Garibaldi Provincial Park overlook Lillooet Lake from the west, while to the east are the northern reaches of the Lillooet Ranges which lie between the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandria, British Columbia
Alexandria or Fort Alexandria is a National Historic Site of Canada on the Fraser River in British Columbia, and was the end of the Old Cariboo Road and the Cariboo Wagon Road. It is located on Highway 97, north of 100 Mile House and south of Quesnel. History On June 21, 1793, explorer Alexander MacKenzie reached the shores of the First Nations village at what would become Alexandria. He was told by the people of the village that the river was not safe for navigation beyond that point. Mackenzie heeded their advice and he and his party turned around and returned upriver to what would become the town of Quesnellemouth, (later Quesnel) and continued on to Bella Coola. In 1821, the North West Company erected a fort at Alexandria, the last the company would build before it was merged the same year with the Hudson's Bay Company. The fort was named Alexandria in honour of Alexander Mackenzie. They also built a granary and wintered their horses there. Alexandria became a key way st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hull (watercraft)
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as a funnel, derrick, or mast. The line where the hull meets the water surface is called the waterline. General features There is a wide variety of hull types that are chosen for suitability for different usages, the hull shape being dependent upon the needs of the design. Shapes range from a nearly perfect box in the case of scow barges to a needle-sharp surface of revolution in the case of a racing multihull sailboat. The shape is chosen to strike a balance between cost, hydrostatic considerations (accommodation, load carrying, and stability), hydrodynamics (speed, power requirements, and motion and behavior in a seaway) and special considerations for the ship's role, such as the rounded bow of an icebreaker or the flat bottom of a landing craft. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |