|
Victoria (mythology)
In ancient Roman religion Victoria was the deified personification of victory. She first appeared during the first Punic War, seemingly as a Romanised re-naming of Nike, the goddess of victory associated with Rome's Greek allies in the Greek mainland and in Magna Graecia. Thereafter she comes to symbolise Rome's eventual hegemony and right to rule. She is a deified abstraction, entitled to a cult. But unlike Nike, she has virtually no mythology of her own. History and iconography Victoria first appears during the first Punic War, as a translation or renaming of Nike, the Greek goddess of victory in peace or war. Nike would have become familiar to the Roman military as a goddess of Rome's Greek allies in the Punic Wars. She was worshipped in Magna Graecia and mainland Greece, and was a subject of Greek myth. Around this time, various Roman war-deities begin to receive the epithet ''victor'' (conqueror) or ''invictus'' (unconquered). By the late republican and early imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
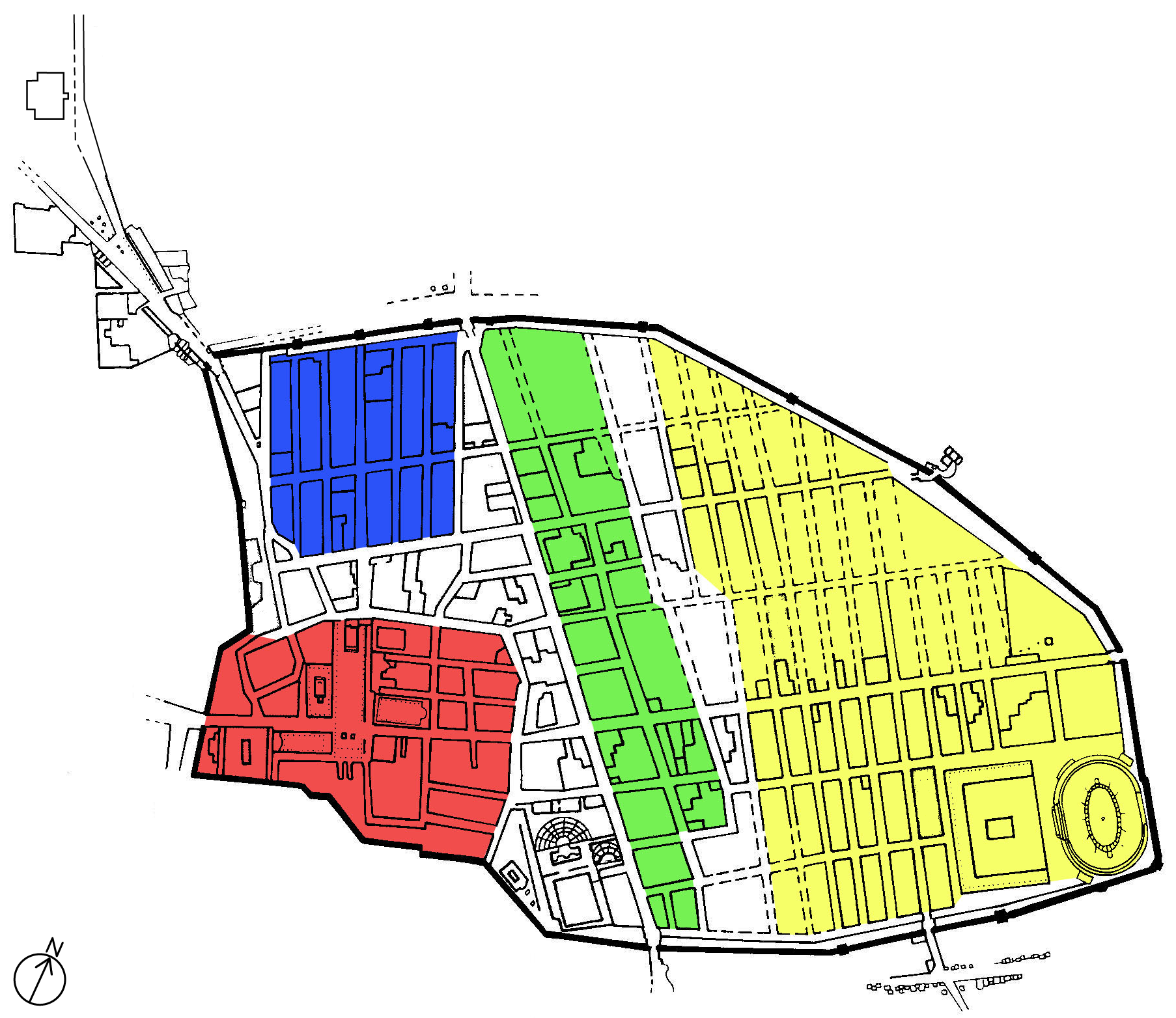
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cult Image
In the practice of religion, a cult image is a Cultural artifact, human-made object that is venerated or worshipped for the deity, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirit or Daimon, daemon that it embodies or represents. In several traditions, including the ancient religions of Ancient Egypt, Egypt, Ancient Greece, Greece and Rome, and Hinduism, cult images in a temple may undergo a daily routine of being washed, dressed, and having food left for them. Processions outside the temple on special feast days are often a feature. Religious images cover a wider range of all types of images made with a religious purpose, subject, or connection. In many contexts "cult image" specifically means the most important image in a temple, kept in an inner space, as opposed to what may be many other images decorating the temple. The term idol is an image or representation of a god used as an object of worship, while idolatry is the worship of an "idol" as though it were God. Ancient Near East and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of The Roman Empire
The growth of early Christianity from its obscure origin AD 40, with fewer than 1,000 followers, to being the majority religion of the entire Roman Empire by AD 400, has been examined through a wide variety of Historiography, historiographical approaches. Until the last decades of the 20th century, the primary theory was provided by Edward Gibbon in ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in 1776. Gibbon theorized that paganism declined from the second century BC and was finally eliminated by the top-down imposition of Christianity by Constantine the Great, Constantine, the first Christian emperor, and his successors in the fourth century AD. For over 200 years, Gibbon's model and its expanded explanatory versions—the conflict model and the legislative model—have provided the major narrative. The conflict model asserts that Christianity rose in conflict with paganism, defeating it only after emperors became Christian and were willing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
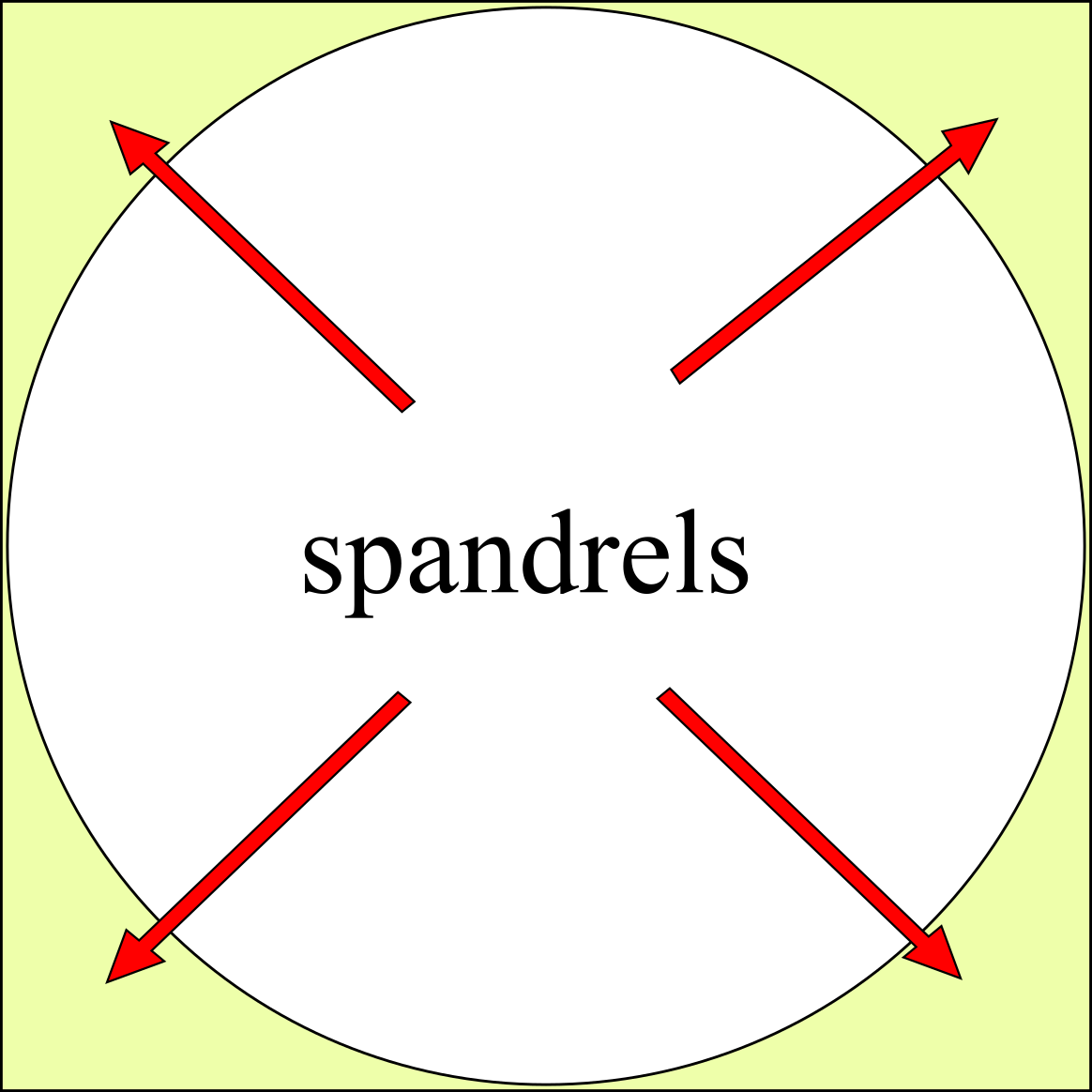
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame, between the tops of two adjacent arches, or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architecture, architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantius II
Constantius II (; ; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic peoples, while internally the Roman Empire went through repeated civil wars, court intrigues, and usurpations. His religious policies inflamed domestic conflicts that would continue after his death. Constantius was a son of Constantine the Great, who elevated him to the imperial rank of '' Caesar'' on 8 November 324 and after whose death Constantius became ''Augustus'' together with his brothers, Constantine II and Constans on 9 September 337. He promptly oversaw the massacre of his father-in-law, an uncle, and several cousins, consolidating his hold on power. The brothers divided the empire among themselves, with Constantius receiving Greece, Thrace, the Asian provinces, and Egypt in the east. For the following decade a costly and inconclusive war against Persia took most of Constantius's time and at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curia Julia
The Curia Julia () is the third named ''curia'', or senate house, in the ancient city of Rome. It was built in 44 BC, when Julius Caesar replaced Faustus Cornelius Sulla's reconstructed Curia Cornelia, which itself had replaced the Curia Hostilia. Caesar did so to redesign both spaces within the Comitium and the Roman Forum. The alterations within the Comitium reduced the prominence of the Senate and cleared the original space. The work, however, was interrupted by Caesar's assassination at the Curia of Pompey of the Theatre of Pompey, where the Senate had been meeting temporarily while the work was completed. The project was eventually finished by Caesar's heir and successor, Augustus Caesar, in 29 BC. The Curia Julia is one of a handful of Roman structures that survive mostly intact. This is due to its conversion into the basilica of Sant'Adriano al Foro in the 7th century and several later restorations. However, the roof, the upper elevations of the side walls and the rear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratian
Gratian (; ; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian was raised to the rank of ''Augustus'' as a child and inherited the West after his father's death in 375. He nominally shared the government with his infant half-brother Valentinian II, who was also acclaimed emperor in Pannonia on Valentinian's death. The East was ruled by his uncle Valens, who was later succeeded by Theodosius I. Gratian subsequently led a campaign across the Rhine, attacked the Lentienses, and forced the tribe to surrender. That same year, the eastern emperor Valens was killed fighting the Goths at the Battle of Adrianople, which led to Gratian elevating Theodosius to replace him in 379. Gratian favoured Nicene Christianity over traditional Roman religion, issuing the Edict of Thessalonica, refusing the office of '' pontifex maximus'', and removing the Altar of Victory from the Roman Senate's Curia Julia. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuna
Vacuna was an ancient Sabine goddess, identified by ancient Roman sources and later scholars with numerous other goddesses, including Ceres, Diana, Nike, Minerva, Bellona, Venus and Victoria. She was mainly worshipped at a sanctuary near Horace's villa (now in the commune of Licenza), in sacred woods at Reate, and at Rome. The protection she was asked to provide remains obscure. Pomponius Porphyrion calls her ''incerta specie'' (of an uncertain kind) in his commentaries on Horace. Renaissance authors and Leonhard Schmitz state that she was a divinity to whom the country people offered sacrifices when the labours of the field were over, that is, when they were at leisure, ''vacui''. The etymology of her name is linked to lack and privation, and Horace appears to call upon her in favour of a friend to whom one of his epistles is addressed. From this, it has been conjectured that she was prayed to in favour of absent people, family members or friends.G. Dumézil, ''La r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vica Pota
In ancient Roman religion, Vica Pota was a goddess whose shrine ''(aedes)'' was located at the foot of the Velian Hill, on the site of the ''domus'' of Publius Valerius Publicola. This location would place the temple on the same side of the Velia as the Forum and perhaps not far from the Regia. Cicero explains her name as deriving from ''vincendi atque potiundi'', "conquering and gaining mastery." In the '' Apocolocyntosis'', Vica Pota is the mother of Diespiter; although usually identified with Jupiter, Diespiter is here treated as a separate deity, and in the view of Arthur Bernard Cook should perhaps be regarded as the chthonic Dispater. The festival of Vica Pota was January 5. Asconius identifies her with Victoria, but she is probably an earlier Roman or Italic form of victory goddess that predated Victoria and the influence of Greek Nike; Vica Pota was thus the older equivalent of Victoria but probably not a personification of victory as such. In a conjecture not widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roma (personification)
In Religion in ancient Rome, ancient Roman religion, Roma was a female deity who National personification, personified the city of Rome and, more broadly, the Roman state. She was created and promoted to represent and propagate certain of Rome's ideas about itself, and to justify its rule. She was portrayed on coins, sculptures, architectural designs, and at official games and festivals. Images of Roma had elements in common with other goddesses, such as Rome's Minerva, her Greek equivalent Athena and various manifestations of Greek Tyche, who protected Greek city-states; among these, Roma stands dominant, over piled weapons that represent her conquests, and promising protection to the obedient. Her Amazons, "Amazonian" iconography shows her "manly virtue" (virtus) as fierce mother of a warrior race, augmenting rather than replacing local goddesses. On some coinage of the Roman Imperial era, she is shown as a serene advisor, partner and protector of ruling emperors. In Rome, the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |