|
Victor Démé
Victor Démé (1962 – 21 September 2015) was a Burkinabé musician and singer-songwriter originating from a Mandinka family. His death was caused by a bout of malaria. Biography Victor Démé was born in Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso. His mother was a popular singer in social occasions in her hometown in the 1960s. His father was a tailor and stylist and with his uncles and aunts promoted a line of clothing unique to Marka ethnics, part of West Africa's Mandinka people. Démé worked in his father's business established in Abidjan, Ivory Coast since his youth. During the nights, he used to perform at various clubs of Abidjan with musicians, most notably the famous band Super Mandé and its star artist Abdoulaye Diabaté. Démé returned to Burkina Faso in 1988 benefiting from a renewed artistic freedom in the country and at age 26 gained fame. His appearance in a special contest by the Bobo-Dioulasso French Cultural Centre rebroadcast by Radio France International in 1989 and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,878 sq mi). In 2024, the country had an estimated population of approximately 23,286,000. Previously called the Republic of Upper Volta (1958–1984), it was Geographical renaming, renamed Burkina Faso by then-List of heads of state of Burkina Faso, president Thomas Sankara. Its citizens are known as Burkinabes, and its Capital city, capital and largest city is Ouagadougou. The largest ethnic group in Burkina Faso is the Mossi people, who settled the area in the 11th and 13th centuries. They established powerful Mossi Kingdoms, kingdoms such as Ouagadougou, Tenkodogo, and Yatenga. In 1896, it was Colonization, colonized by the French colonial empire, French as part of French West Africa; in 1958, Upper Volta became a self-governing colony wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
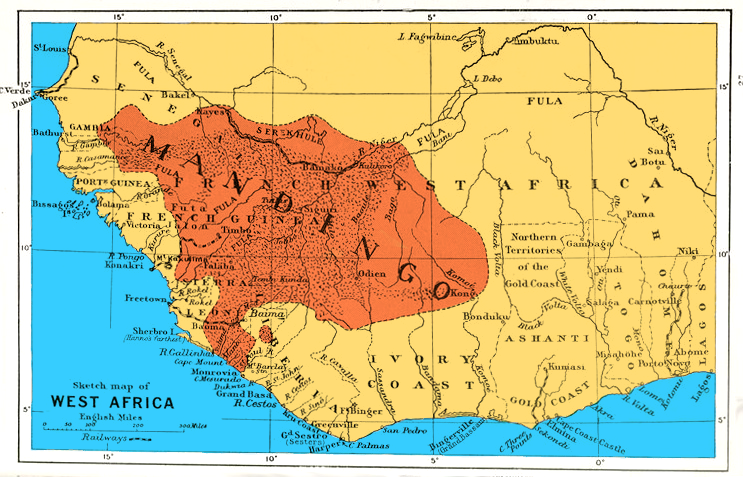
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bobo-Dioulasso
Bobo-Dioulasso ( , ) is a city in Burkina Faso with a population of 1,129,000 (); it is the second-largest city in the country, after Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso's capital. The name means "home of the Bobo- Dioula". The local Bobo-speaking population (related to the Mande) refers to the city simply as ''Sia''. There are two distinct dialects of Jula spoken, based on the origins of different groups of speakers. The city is situated in the southwest of the country, in the Houet Province, some 350 km (220 mi) from Ouagadougou. Bobo-Dioulasso is significant both economically (agricultural trade, textile industry) and culturally, as it is a major center of culture and music. History Early History According to local tradition, Bobo-Dioulasso was founded as Sia in the 15th century. Populated by the Oule and Dioula subgroups of the Bobo people, it became an important market center, particularly in the export of horses southwards. Sia was therefore an important link i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio France International
Radio France Internationale, usually referred to as RFI, is the State media, state-owned international radio news network of France. With 59.5 million listeners in 2022, it is one of the most-listened-to international radio stations in the world, along with Deutsche Welle, the BBC World Service and Voice of America. RFI broadcasts 24 hours per day around the world in French and in 16 other languages in FM, shortwave, medium wave, satellite and on its website. It is a channel of the state company France Médias Monde. The majority of shortwave transmissions are in French and Hausa language, Hausa but also includes some hours of Swahili language, Swahili, Fulfulde language, Fulfulde and Mandinka language, Mandinka. RFI broadcasts to over 150 countries on 5 continents. Africa is the largest part of radio listeners, representing 60% of the total audience in 2010. In the Île-de-France, Paris region, RFI comprises between 150,000 and 200,000 listeners. Its digital platforms attract an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salif Keita
Salif Keïta () (born 25 August 1949) is a Malian singer-songwriter, referred to as the "Golden Voice of Africa". He is a member of the Keita royal family of Mali. Early life Salif Keita was born a traditional prince in the village of Djoliba. He was born to the Keita royal family, who trace their lineage to Sundiata Keita, founder of the Mali Empire. He was cast out by his family and ostracized by the community because of his albinism, a sign of bad luck in Mandinka culture. Raised in a Muslim family, he went to an Islamic school where he was influenced by his Qur'an teacher's singing. He decided to pursue music in his teenage years, further distancing him from his family as that was against occupational prohibitions of his noble status. In 1967, he left Djoliba for Bamako, where he joined the government-sponsored Super Rail Band de Bamako. In 1973, Keita joined the group ''Les Ambassadeurs (du Motel de Bamako)''. Keita and Les Ambassadeurs fled political unrest in Mali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mory Kanté
Mory Kanté (29 March 195022 May 2020) was a Guinean vocalist and player of the kora harp. He was best known internationally for his 1987 hit song " Yé ké yé ké", which reached number-one in Belgium, Finland, the Netherlands, and Spain. The album it came from, ''Akwaba Beach'', was the best-selling African record of its time. Early life Kanté was born in Albadaria, French Guinea (a part of French West Africa at the time) on 29 March 1950. His father was El Hadj Djeli Fodé Kanté and his mother, Fatouma Kamissoko, was a singer. They were one of Guinea's best known families of griot (hereditary) musicians. He was of mixed Malian and Guinean descent. After being brought up in the Mandinka griot tradition in Guinea, he was sent to Mali at the age of seven years – where he learned to play the kora, as well as important voice traditions, some of which are necessary to become a griot. As a Muslim, he integrated aspects of Islamic music in his work. Career In 1971 Kan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyula Language
Dyula (or Jula, Dioula, ''Julakan'' ߖߎ߬ߟߊ߬ߞߊ߲) is a language of the Mande language family spoken mainly in Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast and Mali, and also in some other countries, including Ghana, Guinea and Guinea-Bissau. It is one of the Manding languages and is most closely related to Bambara, being mutually intelligible with Bambara as well as Malinke. It is a trade language in West Africa and is spoken by millions of people, either as a first or second language. Similar to the other Mande languages, it uses tones. It may be written in the Latin, Arabic or N'Ko scripts. History Historically, Dyula ("jula" in the language) was not an ethonym, but rather a Manding language label literally meaning 'trader'. The term used to distinguish Muslim traders from the non-Muslim population living in the same area, mainly Senufo agricultors. It then became an exonym for Manding-speaking traders such as the Bambara or the Mandinka and their languages. At the same time, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mande Languages
The Mande languages are a family of languages spoken in several countries in West Africa by the Mandé peoples. They include Maninka (Malinke), Mandinka, Soninke, Bambara, Kpelle, Jula (Dioula), Bozo, Mende, Susu, and Vai. There are around 60 to 75 languages spoken by 30 to 40 million people, chiefly in Burkina Faso, Mali, Senegal, The Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast (Côte d'Ivoire) and also in southern Mauritania, northern Ghana, northwestern Nigeria and northern Benin. The Mande languages show a few lexical similarities with the Atlantic–Congo language family, so together they have been proposed as parts of a larger Niger–Congo language family since the 1950s. However, the Mande languages lack the noun-class morphology that is the primary identifying feature of the Atlantic–Congo languages. Accordingly, linguists increasingly treat Mande and Atlantic–Congo as independent language families. History Various opinions exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djôn'maya
"Djôn'maya (sometimes simplified as "Djon maya") is a song composed and recorded by Burkinabé singer-songwriter and musician Victor Démé and is considered his signature tune. After years of interpreting the song live, he recorded a studio version in his self-titled debut album ''Victor Démé'' in 2008 on the independent Chapa Blues Records in France. Djon maya maï In 2014, the Electro, Nu-Disco and Deep House DJ record producers Synapson recorded a remake of the song featuring Victor Démé. The single renamed "Djon maya maï" charted in France and Belgium reaching number 12 in SNEP SNEP (, in English National Syndicate of Phonographic Publishing) is the inter-professional organisation that protects the interests of the French record industry. Originally known under the acronym SNICOP, the organisation was established in ... French Singles Chart. Track list #"Djon maya maï" (radio edit) (3:04) #"Djon maya maï" (original) (3:14) #"Djon maya maï" (extended) (4:49 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNEP
SNEP (, in English National Syndicate of Phonographic Publishing) is the inter-professional organisation that protects the interests of the French record industry. Originally known under the acronym SNICOP, the organisation was established in 1922 and has 48 member companies. SNEP's responsibilities include collecting and distributing royalty payments for broadcast and performance, preventing copyright infringement of its members' works (including music piracy), and sales certification of silver, gold, platinum and diamond records and videos. SNEP also compiles weekly official charts of France's top-selling music, including singles and albums. Official charts History The first attempt at a French national chart of best-selling records originated from a request by the American music industry magazine '' Billboard''. The magazine's French correspondent, Eddie Adamis, compiled a top 10 list of the country's preferred format, the extended play (EP), for ''Billboard''s "Hits of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkinabe Male Singers
Burkinabe (Fulfulde: ''Burkinabè'', French: ''burkinabè'' or ''burkinabé'') may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Burkina Faso, a nation in West Africa * A person from Burkina Faso, or of Burkinabe descent. For information about the Burkinabe people, see: ** Demographics of Burkina Faso ** Culture of Burkina Faso ** List of Burkinabes * Burkinabe cuisine Burkinabe cuisine, the cuisine of Burkina Faso, is similar to the cuisines in many parts of West Africa, and is based on staple foods of sorghum, millet, rice, fonio, maize, peanuts, potatoes, beans, yams and okra. Rice, maize and millet are the ... * See also * {{DEFAULTSORT:Burkinabe Language and nationality disambiguation pages Demonyms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |