|
Vicke Schorler
Vicke Schorler (–1625) was a grocer in the German Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city of Rostock. He created two historically significant works about the city: the "Vicke Schorler scroll", a monumental drawing with the title ''Wahrhaftige Abcontrafactur der hochloblichen und weitberuhmten alten See- und Hensestadt Rostock'' (approximately ''True depiction of the highly praiseworthy and widely famous old sea port and Hanseatic city of Rostock'') (1578–1586), and the ''Rostock Chronicle'' (1583–1625). Sources Despite the extensive historical record, Vicke Schorler preserved of Rostock during his time, little is known about his life. For example, his authorship of the anonymous Rostock Chronicle was discovered by chance. He left his name only on the Vicke Schorler Scroll, which was later named after him. No evidence suggests that he created the Rostock Chronicle or the scroll as commissioned works. His work was therefore likely based on a personal interest in his hometown. Lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow. The name Mecklenburg derives from a castle named '' Mikilenburg'' (Old Saxon for "big castle", hence its translation into Neo-Latin and Greek as ), located between the cities of Schwerin and Wismar. In Slavic languages it was known as ''Veligrad'', which also means "big castle". It was the ancestral seat of the House of Mecklenburg; for a time the area was divided into Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz among the same dynasty. Linguistically Mecklenburgers retain and use many features of Low German vocabulary or phonology. The adjective for the region is ''Mecklenburgian'' or ''Mecklenburgish'' (); inhabitants are called Mecklenburgians or Mecklenburgers (). Geography Mecklenburg is known for its mostly flat countryside. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Chytraeus
David Chytraeus or Chyträus (26 February 1530 – 25 June 1600) was a German Lutheran theologian, reformer and historian. He was a disciple of Philip Melancthon. He was born at Ingelfingen. His real surname was Kochhafe, which in Classical Greek is χύτρα, from where he derived the Latinized pseudonym "Chyträus". Chytraeus was professor of the University of Rostock and one of the co-authors of the Formula of Concord. He is known for his work as the author of a Protestant catechism. His original Latin text was published in 1554, then reprinted in 1599. Now it has been translated for the first time in German. It has been published, together with editorial notes and commentary by Michael. The Protestant estates of Lower Austria, in the person of Leopold Grabner zu Rosenburg, Rüdiger von Starhemberg and Wolf Christoph von Enzersdorf, invited Chytraeus in 1568 at the instigation of Emperor Maximilian II so that he could work out a church order and an agenda for them. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High German Languages
The High German languages (, i.e. ''High German dialects''), or simply High German ( ) – not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called "High German" – comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and Uerdingen isoglosses, i.e., in central and southern Germany, Austria, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Luxembourg, and eastern Belgium, as well as in neighbouring portions of France (Alsace and northern Lorraine), Italy (South Tyrol), the Czech Republic (Bohemia), and Poland ( Upper Silesia). They are also spoken in diasporas in Romania, Russia, Canada, the United States, Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, Chile, and Namibia. High German is marked by the High German consonant shift, separating it from Low German (Low Saxon) and Low Franconian (including Dutch) within the continental West Germanic dialect continuum. "Low" and "high" refer to the lowland and highland geographies typically found in the two areas. Classification As a technica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
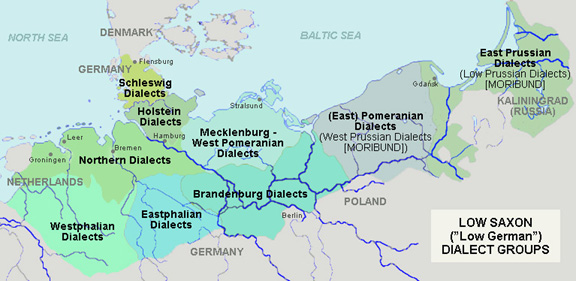
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Size
The size of a book is generally measured by the height against the width of a leaf, or sometimes the height and width of its cover. A series of terms is commonly used by libraries and publishers for the general sizes of modern books, ranging from ''folio'' (the largest), to ''quarto'' (smaller) and ''octavo'' (still smaller). Historically, these terms referred to the format of the book, a technical term used by printers and Bibliography, bibliographers to indicate the size of a leaf in terms of the size of the original sheet. For example, a quarto (from Latin ''quartō'', ablative form of ''quartus'', fourth) historically was a book printed on sheets of paper folded in half twice, with the first fold at right angles to the second, to produce 4 leaves (or 8 pages), each leaf one fourth the size of the original sheet printed – note that a ''leaf'' refers to the single piece of paper, whereas a ''page'' is one side of a leaf. Because the actual format of many modern books cannot be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binder (material)
A binder or binding agent is any material or substance that holds or draws other materials together to form a cohesive whole mechanically, chemically, by adhesion or cohesion. More narrowly, binders are liquid or dough-like substances that harden by a chemical or physical process and bind fibres, filler powder and other particles added into it. Examples include glue, adhesive and thickening. Examples of mechanical binders are bond stones in masonry and tie beams in timber framing. Classification Binders are loosely classified as organic ( bitums, animal and plant glues, polymers) and inorganic ( lime, cement, gypsum, liquid glass, etc.). These can be either metallic or ceramic as well as polymeric depending on the nature of the main material. For example, in the compound WC-Co (Tungsten Carbide used in cutting tools) Co constitutes the binding agent for the WC particles. Based on their chemical resistance, binders are classified by the field of use: non-hydrau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varnish
Varnish is a clear Transparency (optics), transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not to be confused with wood stain. It usually has a yellowish shade due to the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmented as desired. It is sold commercially in various shades. Varnish is primarily used as a wood finishing, wood finish where, stained or not, the distinctive tones and grains in the wood are intended to be visible. Varnish finishes are naturally Gloss (material appearance), glossy, but satin/semi-gloss and flat sheens are available. History The word "varnish" comes from Mediaeval Latin ''vernix'', meaning odorous resin, perhaps derived from Middle Greek ''berōnikón'' or ''beroníkē'', meaning amber or amber-colored glass. A false etymology traces the word to the Greek ''Berenice'', the ancient name of modern Benghazi in Libya, where the first varnishes in the Mediterranean area were supposedly used and where resins from the trees of now-v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several species of bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primarily floral nectar) or the secretions of other insects, like the honeydew of aphids. This refinement takes place both within individual bees, through regurgitation and enzymatic activity, and during storage in the hive, through water evaporation that concentrates the honey's sugars until it is thick and viscous. Honey bees stockpile honey in the hive. Within the hive is a structure made from wax called honeycomb. The honeycomb is made up of hundreds or thousands of hexagonal cells, into which the bees regurgitate honey for storage. Other honey-producing species of bee store the substance in different structures, such as the pots made of wax and resin used by the stingless bee. Honey for human consumption is collected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Black
Carbon black (with subtypes acetylene black, channel black, furnace black, lamp black and thermal black) is a material produced by the incomplete combustion of coal tar, vegetable matter, or petroleum products, including fuel oil, fluid catalytic cracking tar, and ethylene cracking in a limited supply of air. Carbon black is a form of paracrystalline carbon that has a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, albeit lower than that of activated carbon. It is dissimilar to soot in its much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio and significantly lower (negligible and non-bioavailable) polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) content. Carbon black is used as a colorant and reinforcing filler in tires and other rubber products and as a pigment and wear protection additive in plastics, paints, and ink pigment. It is used in the EU as a food colorant when produced from vegetable matter (E153). The current International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) evaluation is that, "Carbon black i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clays develop plasticity (physics), plasticity when wet but can be hardened through Pottery#Firing, firing. Clay is the longest-known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been radiocarbon dating, dated to around 14,000 BCE, and Clay tablet, clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtration, filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, often baked into brick, as an essenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |