|
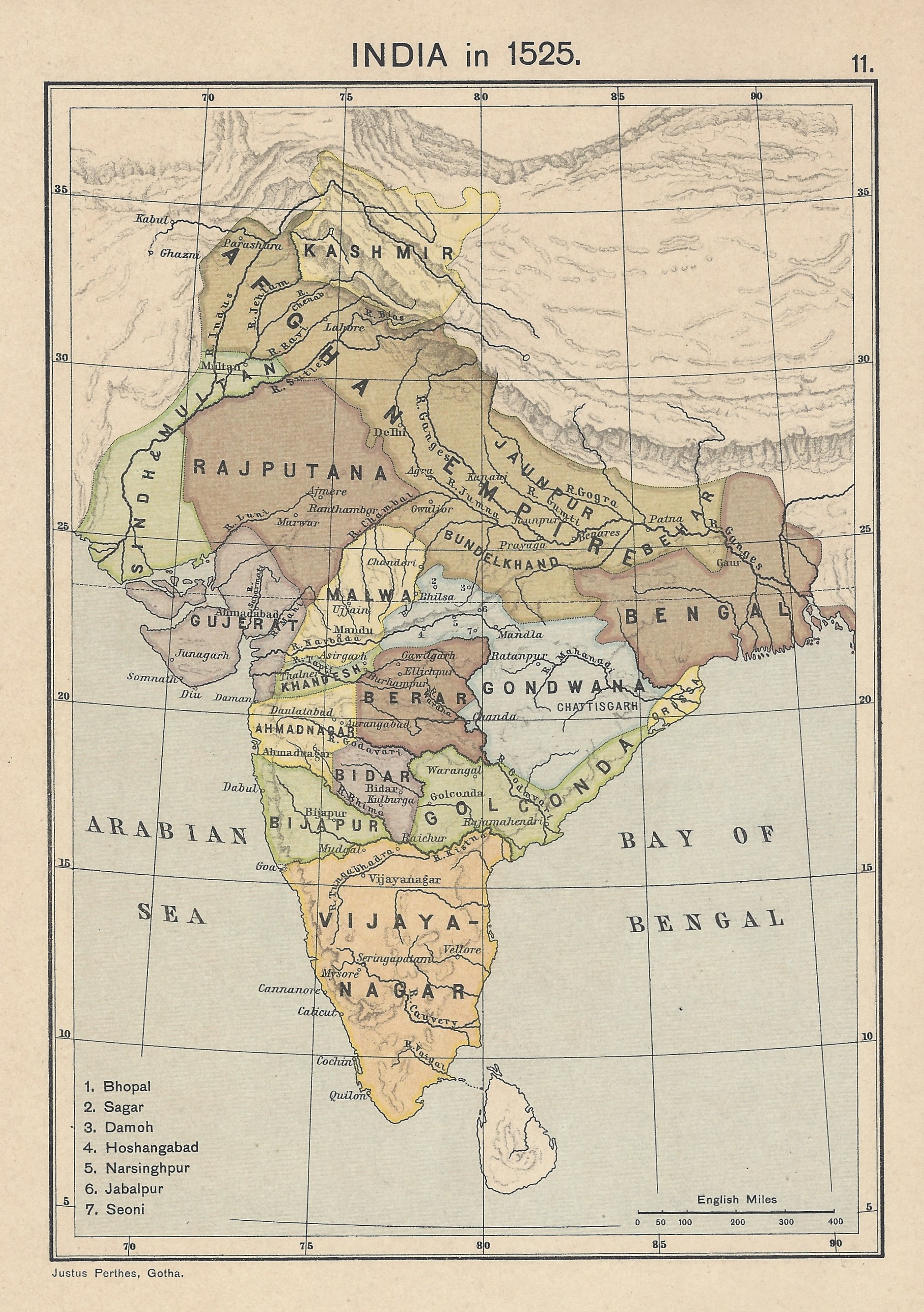
Viceroy Of The Deccan
Viceroy of the Deccan was the representative of the Mughal emperors in Deccan, Deccan consisted of six Mughal governorates ( Subah): Khandesh, Bijapur, Berar, Aurangabad, Hyderabad and Bidar. Carnatic region was a subdivision which was partly administered by the governor of Bijapur and Hyderabad. The domain of Viceroy of the Deccan extends from the Narmada River in the North to Trichinopoly in the South and Masulipatnam in the east to Bijapur in the west. The Aurangabad city was selected as the viceregal capital of Deccan where Aurangzeb resided until his death in 1707 AD, and the Asaf Jah I ruled from the very place until 1750 AD, when his capital was shifted to Hyderabad city and the domain of Viceroy of Deccan was renamed as Hyderabad Deccan. History In 1636, Shah Jahan appointed Aurangzeb Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Division
Administrative divisions (also administrative units, administrative regions, subnational entities, or constituent states, as well as many similar generic terms) are geographical areas into which a particular independent sovereign state is divided. Such a unit usually has an administrative authority with the power to take administrative or policy decisions for its area. Administrative divisions are often used as polygons in geospatial analysis. Description Usually, sovereign states have several levels of administrative division. Common names for the principal (largest) administrative divisions include: Federated state, states (subnational states, rather than sovereign states), provinces, States of Germany#States, lands, oblasts and Region#Administrative regions, regions. These in turn are often subdivided into smaller administrative units known by names such as comarcas, raions or districts, which are further subdivided into municipality, municipalities, Commune (administrativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berar Subah
The Berar Subah () was one of the Subahs (provinces) of the Mughal Empire, in Central India from 1596 to 1724. It bordered Golconda, Ahmandagar (both conquered in 1601), Kandesh and Malwa provinces as well as the independent and tributary kingdoms to the east. Origin of name According to the ''Ain-i-Akbari'', the original name of Berar was ''Waradatat'' (the banks of Varada River). History Before the Mughal occupation, Berar was part of the Nizam Shahi sultanate of Ahmadnagar. It was ceded to the emperor Akbar by Chand Bibi in 1596, unable to stand against the imperial forces led by prince Murad. After this initial victory Prince Murad settled in Berar with Balapur as his headquarters. Near Balapur he founded a new city named Shahpur and constructed a beautiful palace for himself. As his relationship was deteriorating with Abdul Rahim Khan-i-Khanan, the commander of the army, Akbar recalled Khan-i-Khanan and sent his trusted friend Abul Fazl to help him. Murad died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becoming the second longest-ruling emperor of Hindustan (48 years and 7 months). Under his reign, the Mughal Empire reached its greatest extent, with territory spanning nearly the entirety of the Indian subcontinent. Aurangzeb and the Mughals belonged to a branch of the Timurid dynasty. He held administrative and military posts under his father Shah Jahan () and gained recognition as an accomplished military commander. Aurangzeb served as the viceroy of the Viceroy of the Deccan, Deccan in 1636–1637 and the governor of Gujarat under Mughal Empire, Gujarat in 1645–1647. He jointly administered the provinces of Subah of Multan, Multan and Sind State, Sindh in 1648–1652 and continued expeditions into the neighboring Safavid Iran, Safavid ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurangabad, Maharashtra
Aurangabad (), officially renamed as Chhatrapati Sambhajinagar in 2023, is a city in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarters of Aurangabad district and is the largest city in the Marathwada region. Located on a hilly upland terrain in the Deccan Traps, Aurangabad is the fifth-most populous urban area in Maharashtra, after Mumbai, Pune, Nagpur and Nashik, with a population of 1,175,116. The city is a major production center of cotton textile and artistic silk fabrics. Several prominent educational institutions, including Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, are located in the city. The city is also a popular tourism hub, with attractions like the Ajanta and Ellora caves lying on its outskirts, both of which have been designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 1983, the Aurangabad Caves, Devagiri Fort, Grishneshwar Temple, Jama Mosque, Bibi Ka Maqbara, Himayat Bagh, Panchakki and Salim Ali Lake. Historically, there wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Deccan Chronicle
''Deccan Chronicle'' is an English-language daily newspaper based in Hyderabad, India. Founded in 1938, it was initially launched as a weekly and later converted into a daily. The newspaper's name reflects its origins in the Deccan region of India. ''Deccan Chronicle'' is owned by Samagrah Commercial Pvt Limited and published by Deccan Chronicle Holdings Limited (DCHL). ''Deccan Chronicle'' has historically been one of the largest and most influential English dailies in the region, with editions in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Chennai, and Bengaluru. The newspaper's circulation peaked in the mid-2000s, making it one of India's top English newspapers. Despite facing financial challenges, including significant debt and the impact of digital media, ''Deccan Chronicle'' remains an important publication, primarily serving readers in the southern states of India. In addition to ''Deccan Chronicle'', DCHL also publishes '' Financial Chronicle'', a financial newspaper, and '' The Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bijapur Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a '' taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 and before the kingdom's political decline in the last quarter of the 15th century. It was one of the Deccan sultanates, the collective name of the kingdom's five successor states. The Sultanate of Bijapur was one of the most powerful states on the Indian Subcontinent at its peak, second to the Mughal Empire which conquered it in 1686 under Aurangzeb. After emigrating to the Bahmani Sultanate, Yusuf Adil Shah rose through the ranks to be appointed governor of the province of Bijapur. In 1490, he created a ''de facto'' independent Bijapur state which became formally independent with the Bahmani collapse in 1518. The Bijapur Sultanate's borders changed considerably throughout its history. Its northern boundary remained relatively stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masulipatnam
Machilipatnam (), also known as Masulipatnam and Bandar (), is a city in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a municipal corporation and the administrative headquarters of Krishna district. It is also the mandal headquarters of Machilipatnam mandal in Machilipatnam revenue division of the district. The ancient port town served as the settlement of European traders from the 16th century, and it was a major trading port for the Portuguese, British, Dutch and French in the 17th century. Etymology During the 17th century, it was known by the names ''Masulipatnam'', ''Masulipatam,'' ''Masula'' and ''Bandar'' (Bandar translates to 'port' in Persian language). The port town in the ancient times was also referred with the name ''Maesolia''. History The town has existed since at least the 3rd century BCE ( Satavahana period) when, according to Ptolemy, it was known as Maisolos. The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' calls it Masalia in the 1st-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichinopoly
Tiruchirappalli (), also known as Trichy, is a major tier II city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Tiruchirappalli district. The city is credited with being the best livable and the cleanest city of Tamil Nadu, as well as the fifth safest city for women in India. It is the fourth largest city as well as the fourth largest urban agglomeration in the state. Located south of Chennai and north of Kanyakumari, Tiruchirappalli sits almost at the geographic centre of Tamil Nadu. The Cauvery Delta begins west of the city where the Kaveri river splits into two, forming the island of Srirangam which is now incorporated into the Tiruchirappalli City Municipal Corporation. The city occupies an area of and had a population of 916,857 in 2011. Tiruchirappalli's recorded history begins under Chola rule in the 3rd century BC. The city has also been ruled by the Pallavas, Pandyas, Vijayanagar Empire, Nayak Dynasty, the Carnatic state and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narmada River
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Pradesh. This river flows through the states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat in India. It is also known as the "Lifeline of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat" due to its huge contribution to the two states in many ways. The Narmada River rises from the Amarkantak, Amarkantak Plateau in Anuppur district in Madhya Pradesh. It forms the traditional boundary between North India, North and South India and flows westwards for before draining through the Gulf of Khambhat into the Arabian Sea, west of Bharuch city of Gujarat. It is one of only two major rivers in peninsular India that runs from east to west (longest west flowing river), along with the Tapti River. It is one of the rivers in India that flows in a rift valley, bordered by the Satpura and Vindhy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University Press
Columbia University Press is a university press based in New York City New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ..., and affiliated with Columbia University. Founded in 1893, it is currently directed by Jennifer Crewe (2014–present) and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fields of literary and cultural studies, history, social work, sociology, religion, film, and international studies. History Columbia University Press was founded in May 1893. In 1933, the first four volumes of the ''History of the State of New York'' were published. In the early 1940s, the Press' revenues rose, partially thanks to the ''Encyclopedia'' and the government's purchase of 12,500 copies for use by the military. Columbia University Press is notable for publishing r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterling Publishing
Sterling Publishing Company, Inc. is a publisher of a broad range of subject areas, with multiple imprints and more than 5,000 titles in print. Founded in 1949 by David A. Boehm, Sterling also publishes books for a number of brands, including AARP, Hasbro, Hearst Magazines, and ''USA TODAY'', as well as serves as the North American distributor for domestic and international publishers including: Anova, the Brooklyn Botanic Garden, Carlton Books, Duncan Baird, Guild of Master Craftsmen, the Orion Publishing Group, and Sixth & Spring Books. Sterling Publishing became a wholly owned subsidiary of Barnes & Noble, when the book retailer acquired it in 2003. On January 5, 2012, ''The Wall Street Journal'' reported that Barnes & Noble had put its Sterling Publishing business up for sale. Negotiations failed to produce a buyer, however, and as of March 2012 Sterling was reportedly no longer for sale. In January 2022, Sterling rebranded as Union Square & Co. In March 2022, the compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnatic Region
The Carnatic region is the peninsular South Indian region between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal, in the erstwhile Madras Presidency and in the modern Indian states of Tamil Nadu and southern coastal Andhra Pradesh. During the British era, demarcation was different and the region included current-day Karnataka and the whole region south of the Deccan. Etymology A number of theories exist as to the derivation of the term ''Carnatic'' or ''Karnatic''. According to Bishop Robert Caldwell, in his ''Comparative Grammar of the Dravidian Languages'', the term is derived from ''Kar'', "black", and ''nadu,'' "country", i.e. "the black country", which refers to the black soil prevalent on the plateau of the Southern Deccan. When the English settled on the East Coast, all South India, from the river Krishna to Cape Comorin, was under the rule of a Kanarese dynasty, reigning at Vijayanagar, and was known as the Karnataka Realm. Hence the name "Carnatic" has come to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |