|
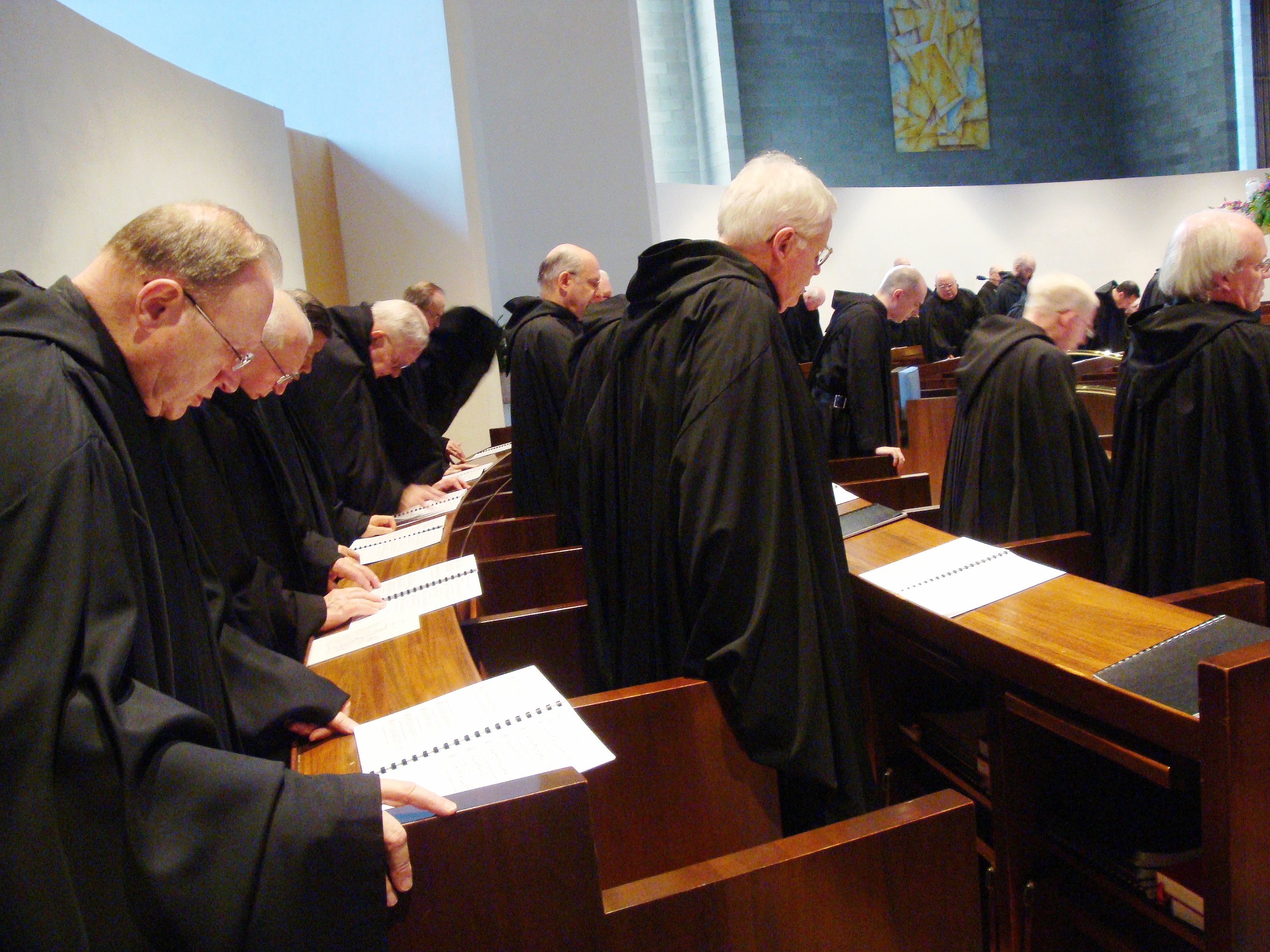
Vespers
Vespers /ˈvɛspərz/ () is a liturgy of evening prayer, one of the canonical hours in Catholic (both Latin and Eastern Catholic liturgical rites), Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Anglican, and Lutheran liturgies. The word for this prayer time comes from the Latin ''vesper'', meaning "evening". Vespers typically follows a set order that focuses on the performance of psalms and other biblical canticles. Eastern Orthodox liturgies recognised as vespers (, ) often conclude with compline, especially the all-night vigil. Performing these liturgies together without break was also a common practice in medieval Europe, especially outside of monastic and religious communities. Old English speakers translated the Latin word as , which became evensong in modern English. The term is now usually applied to the Anglican variant of the liturgy that combines vespers with compline, following the conception of early sixteenth-century worshippers that conceived these as a single unit. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direction Of Prayer
Prayer in a certain direction is characteristic of many world religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Bahá'í Faith. Judaism Jews traditionally pray in the direction of Jerusalem, where the presence of the transcendent God () esidedin the Holy of Holies of the Temple. Within the Holy of Holies lay the Ark of the Covenant that contained the Ten Commandments tablets given to the prophet Moses by God; this is the reason that the Temple of Solomon became the focal point for Jewish prayer. In the Bible, it is written that when the prophet Daniel was in Babylon, he "went to his house where he had windows in his upper chamber open to Jerusalem; and he got down upon his knees three times a day and prayed and gave thanks before his God, as he had done previously" (cf. Daniel 6:10). After the destruction of the Temple of Solomon, Jews continue to pray facing Jerusalem in hope for the coming of the Messiah whom they await. The Talmud ( 30a) instructs Jews outside th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Psalters
There exist a number of translations of the Book of Psalms into the Latin language. They are a resource used in the Liturgy of the Hours and other forms of the canonical hours in the Latin liturgical rites of the Catholic Church. These translations are typically placed in a separate volume or a section of the breviary called the psalter, in which the psalms are arranged to be prayed at the canonical hours of the day. In the Middle Ages, psalters were often lavish illuminated manuscripts, and in the Romanesque and early Gothic period were the type of book most often chosen to be richly illuminated. Versions The Latin Church has a number of more or less different full translations of the psalms into Latin. Three of these translations, the ''Romana'', ''Gallicana'', and ''juxta Hebraicum'', have been traditionally ascribed to Jerome, the author of most of the Latin Vulgate; however, the ''Romana'' was not produced by Jerome. Two other translations, the Pian and ''Nova Vulgata'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
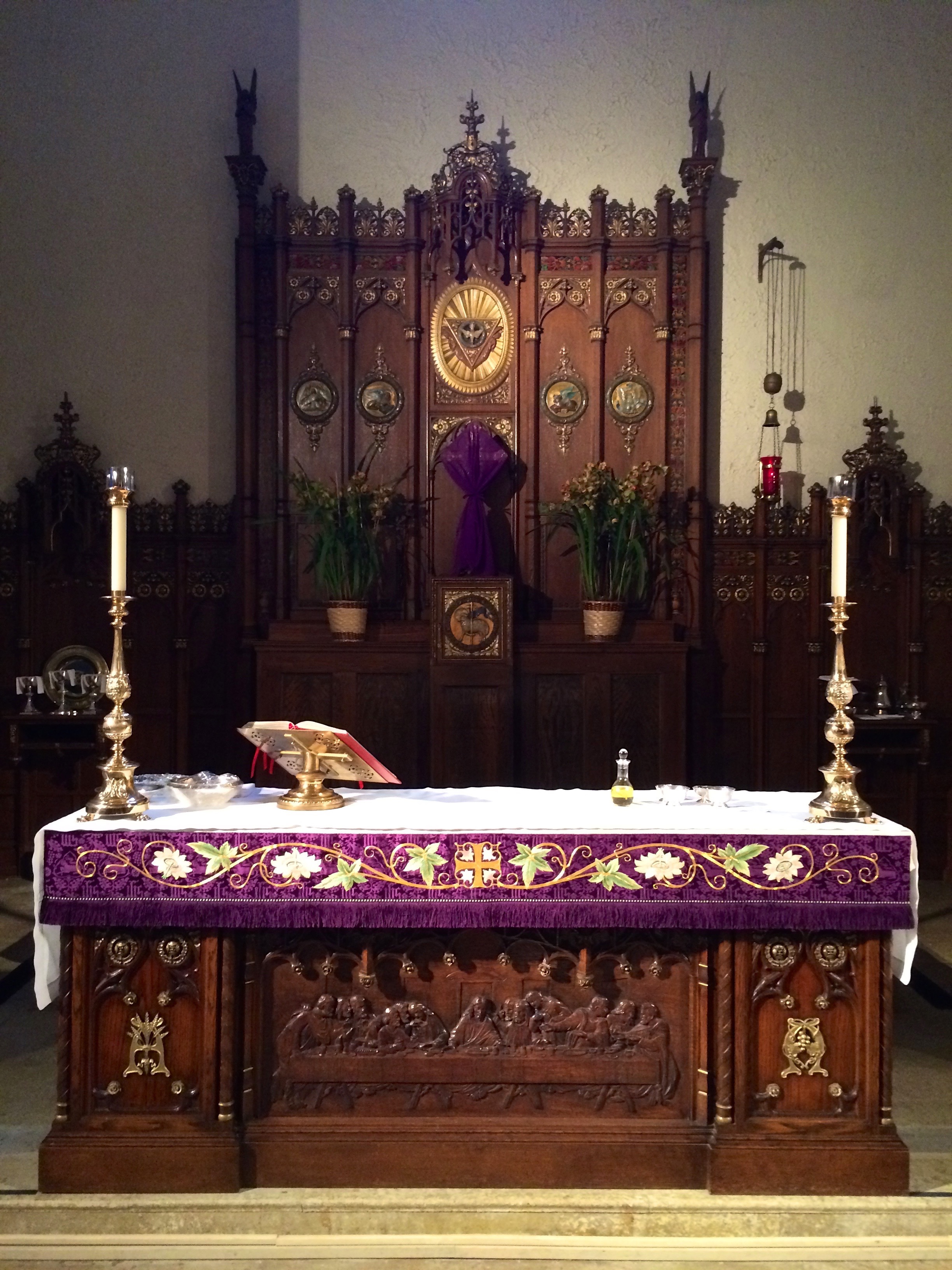
Liturgical Books Of The Roman Rite
Within the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church, a variety of liturgical books have been officially approved to contain the words to be recited and the actions to be performed in the celebration of Catholic liturgy. The Roman Rite of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church is the most widely used liturgical rite. The titles of some of these books contain the adjective "Roman", e.g. the ''Roman Missal'', to distinguish them from the liturgical books for the other rites of the church. Classification These liturgical books have been classified as seven: the Missal, the Pontifical, the Liturgy of the Hours (in earlier editions called the Breviary), the Ritual, the Martyrology, the Gradual, and the Antiphonary. Another sevenfold list indicates, instead of the last two, the Cæremoniale Episcoporum, and the Memoriale Rituum. In reality, the number is not fixed. Some names, such as the Ritual and the Pontifical, refer not to a single volume but to a collection of books that fit within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymn
A hymn is a type of song, and partially synonymous with devotional song, specifically written for the purpose of adoration or prayer, and typically addressed to a deity or deities, or to a prominent figure or personification. The word ''hymn'' derives from Greek language, Greek (''hymnos''), which means "a song of praise". A writer of hymns is known as a hymnist. The singing or composition of hymns is called hymnody. Collections of hymns are known as hymnals or hymn books. Hymns may or may not include instrumental accompaniment. Polyhymnia is the Greco/Roman goddess of hymns. Although most familiar to speakers of English in the context of Christianity, hymns are also a fixture of other major religious groups, world religions, especially on the Indian subcontinent (''stotras''). Hymns also survive from antiquity, especially from Egyptian and Greek cultures. Some of the oldest surviving examples of notated music are hymns with Greek texts. Origins Ancient Eastern hymns include th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invitatory
The invitatory (Latin: invitatorium; also invitatory psalm) is the psalm used to start certain daily prayer offices in Catholic and Anglican traditions. Most often it is Psalm 94(95), also known as the Venite.Numbered 94 in the Greek Septuagint, 95 in the Hebrew Masoretic text: see Psalms > Numbering. The term derives from Medieval Latin ''invītātōrium'', derived from ''invītāre'', "to invite." Catholic The invitatory is used to start Nocturns in the Liturgy of the Hours, the Catholic Church's Divine Office. It is usually Psalm 94(95), which begins ''Venite exsultemus'' in Latin. After the reform of the Liturgy of the Hours following the Second Vatican Council, the Invitatory is said either before the Office of Readings or Lauds, whichever is said first in a liturgical day. In place of Psalm 94(95), Psalm 99(100), Psalm 66(67), or Psalm 23(24) may be used as circumstances may suggest. Verse 17 of Psalm 50(51) ''Domine, labia mea aperies'' is often used as the invitato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, temptation by Satan, according to the Gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark and Gospel of Luke, Luke, before beginning his Ministry of Jesus, public ministry. Lent is usually observed in the Catholic Church, Catholic, Lutheranism, Lutheran, Moravian Church, Moravian, Anglican Communion, Anglican, United and uniting churches, United Protestant and Eastern Orthodoxy, Orthodox Christian traditions, among others. A number of Anabaptism, Anabaptist, Baptists, Baptist, Methodism, Methodist, Calvinism, Reformed (including certain Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continental Reformed, Presbyterianism, Presbyterian and Congregational church, Congregationalist churches), and Nondenominational Christianity, nondenominational Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alleluia
''Hallelujah'' (; , Modern Hebrew, Modern ) is an interjection from the Hebrew language, used as an expression of gratitude to God. The term is used 24 times in the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh (in the book of Psalms), twice in deuterocanonical books, and four times in the Christian Book of Revelation. The phrase is used in Judaism as part of the Hallel prayers, and in Christianity, Christian prayer, where since the earliest timesScott Nash, "Hallelujah" in ''Mercer Dictionary of the Bible'' (Mercer University Press 1990 ), p. 355 it is used in various ways in liturgy, liturgies, especially those of the Catholic Church, the Lutheran Churches and the Eastern Orthodox Church, the three of which use the Latin form '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloria Patri
The ''Gloria Patri'', also known in English as the Glory Be to the Father or, colloquially, the Glory Be, is a doxology, a short hymn of praise to God in various Christian liturgies. It is also referred to as the Minor Doxology ''(Doxologia Minor)'' or Lesser Doxology, to distinguish it from the Greater Doxology, the Gloria in Excelsis Deo. The earliest Christian doxologies are addressed to the Father "through" (διὰ) the Son, or to the Father and the Holy Spirit with (μετά) the Son, or to the Son with (σύν) the Father and the Holy Spirit. The Trinitarian doxology addressed in parallel fashion to all three Divine Persons of the Trinity, joined by ''and'' (καί), as in the form of baptism, Matthew 28:19, became universal in Nicaean Christianity, which was established as the official faith of the Roman Empire with the Edict of Thessalonica in 380. Greek version The Greek wording is as follows: :, : :, : :Glory to the Father, and to the Son, and to the Holy Spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deus, In Adiutorium Meum Intende
"Deus, in adiutorium meum intende", with the response "Domine, ad adiuvandum me festina" (respectively, "O , come to my assistance" and "O , make haste to help me") are the first verse of Psalm 70 (Psalm 69 in the Vulgate): "Make haste, O , to deliver me; make haste to help me, O ." In this form they are a traditional Latin Christian prayer. These words form the introductory prayer to every Hour of the Roman, Ambrosian, and monastic Breviaries, except during the last three days of Holy Week, and in the Office of the Dead. While these are recited or sung, all present bless themselves with the sign of the cross. Since the liturgical revision of the Second Vatican Council all liturgical hours begin with these words (apart from the first recited each day where the verse is replaced by the Invitatory. Tradition says that Benedict of Nursia introduced this custom into the monastic Office, heavily influenced by the writings of Saint John Cassian. Saint Gregory the Great extended it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsory
A responsory or respond is a type of chant in western Christian liturgies. Definition The most general definition of a responsory is any psalm, canticle, or other sacred musical work sung responsorially, that is, with a cantor or small group singing verses while the whole choir or congregation respond with a refrain. However, this article focuses on those chants of the western Christian tradition that have traditionally been designated by the term responsory. In the Roman Rite and rites strongly influenced by it, such as the pre-reformation English rite and the monastic rite of the Rule of St. Benedict, these chants ordinarily follow readings at services of the Divine Office (also called the Liturgy of the Hours); however, they have also been used as processional chants. Structure and performance A responsory has two parts: a respond (or refrain), and a verse. Methods of performance vary, but typically the respond will be begun by the cantor then taken up by the entire choir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite () is the most common ritual family for performing the ecclesiastical services of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. The Roman Rite governs Rite (Christianity), rites such as the Roman Mass and the Liturgy of the Hours as well as the manner in which Sacraments of the Catholic Church, sacraments and Blessing in the Catholic Church, blessings are performed. The Roman Rite developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–1563 (see ''Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites which had survived into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |