|
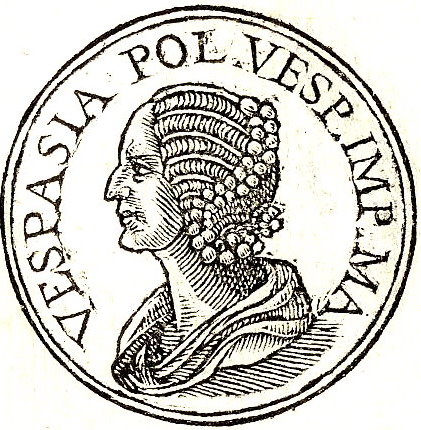
Vespasia Polla
Vespasia Polla (also known as Vespasia Pollia, born c. 15 BC, fl 1st century AD) was the mother of the Roman emperor Vespasian, and grandmother to the emperors Titus and Domitian. Polla came from an equestrian family at Nursia. Suetonius identifies her father as the Vespasius Pollio who was a three-time military tribune and a '' praefectus castrorum''. Her brother rose as high as the praetorship. The Vespasii were regarded as an old family of great renown, and Suetonius notes a site called ''Vespasiae'' where many of their monuments had been built. This site was located on a mountaintop near the sixth milestone on the road between Nursia and Spoletum (present-day Spoleto).Suetonius, ''Life of Vespasian'', 1.2-3. Vespasia married a tax collector Titus Flavius Sabinus, and survived him. Their daughter Flavia Vespasia died in her infancy. One son, also named Titus Flavius Sabinus, served as consul Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Castrorum
The ''praefectus castrorum'' ("camp prefect") was, in the Roman army of the early Empire, the third most senior staff officer of the Roman legion after the legate ('' legatus'') and the senior military tribune (''tribunus laticlavius''), both of whom were from the senatorial class. The ''praefectus castrorum'' was a quartermaster responsible for military logistics and requisition (training, equipment procurement and maintenance, and construction of the camp, etc.) but could command the legion whenever the senior commanders were absent. The post was usually held by a soldier promoted from the centurionate, having already served as a chief centurion (''primus pilus'') of a legion, and was therefore open to ordinary, plebeian citizens. Prefects of this rank, for example Sextus Vibius Gallus,'' SEG'' 57 1293 were awarded prizes (''dona'') to mark their achievements. See also * Military logistics * Praefectus ''Praefectus'', often with a further qualification, was the formal ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Footman
A footman is a male domestic worker employed mainly to wait at table or attend a coach or carriage. Etymology Originally in the 14th century a footman denoted a soldier or any pedestrian, later it indicated a foot servant. A running footman delivered messages.The Concise Oxford Dictionary, He might run beside or behind the carriages of aristocrats, running alongside the coach to make sure it was not overturned by such obstacles as ditches or tree roots. A footman might also run ahead to the destination to prepare for his lord's arrival. Roles The name was applied to a household domestic worker, servant who waited at table and attended, rode on his employer's coach or carriage in case of untoward incidents. In many cases, a footman was expected to serve as an armed bodyguard. Many were skilled with pistols to defend their employer's coach against Highwayman, highwaymen. The ''first footman'' was the designation given to the highest-ranking servant of this class in a given hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the Roman censor, censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding ''fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its Roman provinces, provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former King of Rome, kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Flavius Sabinus (consul AD 52)
Titus Flavius T. f. T. n. Sabinus (d. December 20, AD 69) was a Roman politician and soldier. A native of Reate, he was the elder son of Titus Flavius Sabinus and Vespasia Polla, and brother of the Emperor Vespasian. Career Sabinus is first mentioned in the reign of Claudius, in AD 45, when he served as a legate under Aulus Plautius in Britain, along with his brother, Vespasian. He afterwards governed Moesia for seven years. Sabinus was consul ''suffectus'' with Gnaeus Hosidius Geta in AD 47, and was ''praefectus urbi'' for the last eleven years of Nero's reign. Upon the ascension of Galba in the year 68, he was replaced as urban prefect by Aulus Ducenius Geminus. However, with the death of Galba, and ascension of Otho in January of 69, Sabinus was reinstated. Sabinus may have been part of the Pisonian conspiracy against Nero, but if so he was never arrested.Maier, pp. 393–414. Sabinus was an important supporter of his brother; when Vespasian found himself in financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Flavius Sabinus (father Of Vespasian)
Titus Flavius T. f. Sabinus was a Roman eques and the father of the emperor Vespasian. Sabinus came from Reate in the Sabine region of Italy, the son of Titus Flavius Petro and his wife, Tertulla. He served as a customs official and then as a banker in the province of Asia, where he was honoured with statues dedicated "To an Honest Tax-gatherer", and later as a banker at Aventicum among the Helvetii in Gaul, where he died. Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus, '' De Vita Caesarum'', ''Vespasian'' 1. With his wife Vespasia Polla Vespasia Polla (also known as Vespasia Pollia, born c. 15 BC, fl 1st century AD) was the mother of the Roman emperor Vespasian, and grandmother to the emperors Titus and Domitian. Polla came from an equestrian family at Nursia. Suetonius i ... he had at least two sons, the consul Titus Flavius Sabinus, and Titus Flavius Vespasianus, the future emperor Vespasian; and also a daughter who died in infancy, Flavia Vespasia. Family tree Sources {{DEF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoleto
Spoleto (, also , , ; ) is an ancient city in the Italian province of Perugia in east-central Umbria on a foothill of the Apennines. It is south of Trevi, north of Terni, southeast of Perugia; southeast of Florence; and north of Rome. History Spoleto was situated on the eastern branch of the Via Flaminia, which forked into two roads at Narni and rejoined at , near Foligno. An ancient road also ran hence to Norcia, Nursia. The of the 1st century BC still exists. The forum lies under today's marketplace. Located at the head of a large, broad valley, surrounded by mountains, Spoleto has long occupied a strategic geographical position. It appears to have been an important town to the original Umbri tribes, who built walls around their settlement in the 5th century BC, some of which are visible today. The first historical mention of is the notice of the foundation of a colony there in 241 BC; and it was still, according to Cicero "": a Latin colony in 95 BC. After the Bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Milestone
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetor
''Praetor'' ( , ), also ''pretor'', was the title granted by the government of ancient Rome to a man acting in one of two official capacities: (i) the commander of an army, and (ii) as an elected ''magistratus'' (magistrate), assigned to discharge various duties. The functions of the magistracy, the ''praetura'' (praetorship), are described by the adjective itself: the ''praetoria potestas'' (praetorian power), the ''praetorium imperium'' (praetorian authority), and the ''praetorium ius'' (praetorian law), the legal precedents established by the ''praetores'' (praetors). ''Praetorium'', as a substantive, denoted the location from which the praetor exercised his authority, either the headquarters of his ''castra'', the courthouse (tribunal) of his judiciary, or the city hall of his provincial governorship. The minimum age for holding the praetorship was 39 during the Roman Republic, but it was later changed to 30 in the early Empire. History of the title The status of the ''pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Tribune
A military tribune () was an officer of the Roman army who ranked below the legate and above the centurion. Young men of Equestrian rank often served as military tribunes as a stepping stone to the Senate. The should not be confused with the elected political office of tribune of the people () nor with that of . Early Rome The word ''tribunus'' derives from '' tribus'', "tribe". In Rome's earliest history, each of the three tribes (Ramnes, Luceres, and Tities) sent one commander when an army was mustered, since there was no standing army. The tribunes were commanders of the original legion of 3,000. By the time of the Greek historian Polybius (d. 118 BC), the tribunes numbered six, and they were appointed by the consuls. However, the process by which tribunes were chosen and assigned is complex and varies at different times. Republican period In the Republican period, there were six appointed to each legion. Authority was given to two at a time, and command rotated amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' ( ; usually abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for 'flourished') denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are Will (law), wills Attestation clause, attested by John Jones in 1204 and 1229, as well as a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)", even though Jones was born before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire. His most important surviving work is ''De vita Caesarum'', commonly known in English as '' The Twelve Caesars'', a set of biographies of 12 successive Roman rulers from Julius Caesar to Domitian. Other works by Suetonius concerned the daily life of Rome, politics, oratory, and the lives of famous writers, including poets, historians, and grammarians. A few of these books have partially survived, but many have been lost. Life Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus was probably born about AD 69, a date deduced from his remarks describing himself as a "young man" 20 years after Nero's death. His place of birth is disputed, but most scholars place it in Hippo Regius, a small north African town in Numidia, in modern-day Algeria. It is certain that Suetonius came from a family of moderate social position, that his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |