|
Versamat
Versamat is a Kodak trade name for their automated film processing units, for both with versions for black and white as well as color-capable. First and foremost, Versamats were designed for short roll/single photo developing. Many places, however, have used it for long roll film; it can handle film up to approx. 12 inches wide. With long rolls, however, there are a lot of problems because the film passes over many rollers. Most long roll film processors, on the other hand, use one roller at the top and bottom of each tank, which means that the film contacts only a few of them for the entire run. The Versamat has multiple uses and possible processing styles. For instance, the Versamat 1140 has 7 tanks, each with a full rack in it. The film goes in the supply side, and follows the racks up and down through the tanks to be processed. Most Versamats use developer, followed by a stop bath, fix Fix or FIX may refer to: People with the name * Fix (surname) Arts, entertainment, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processing
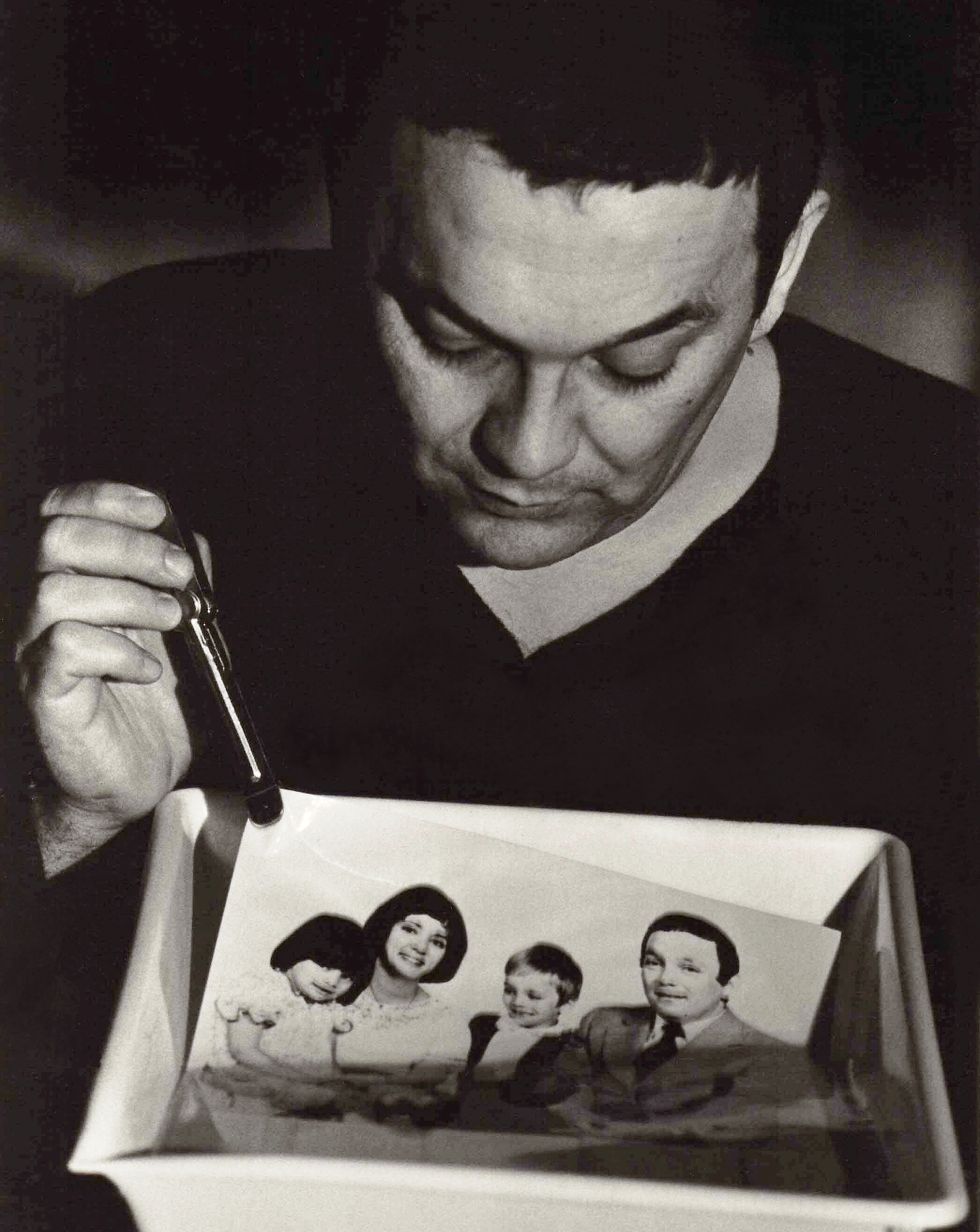
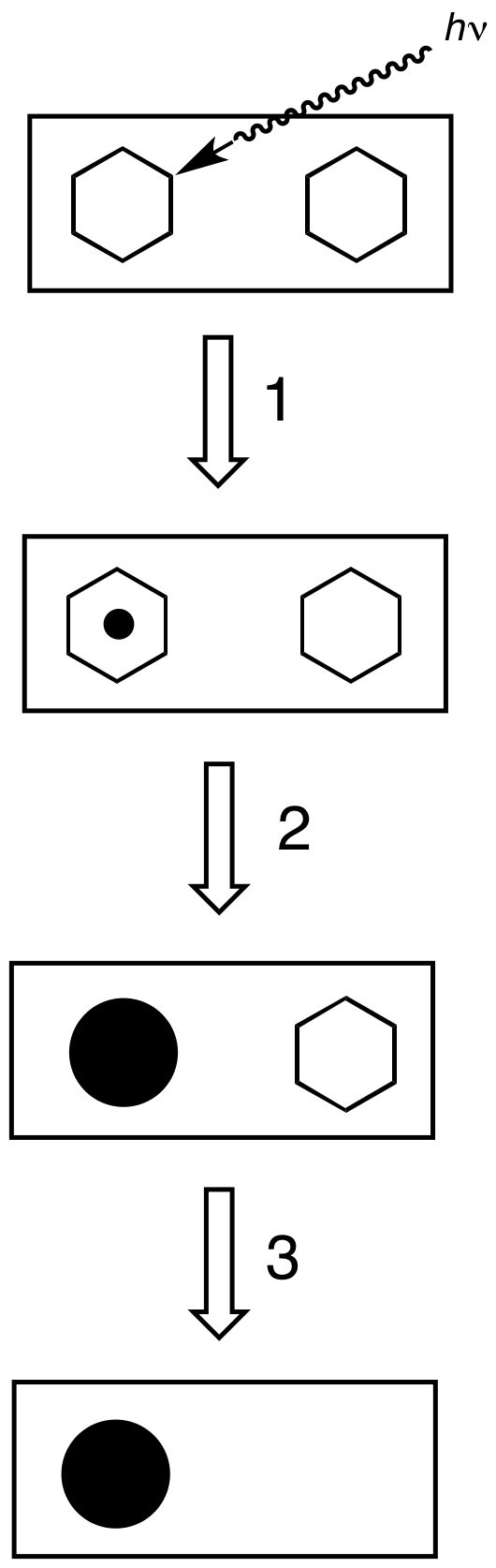
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Developer
In the Photographic processing, processing of photographic films, plates or papers, the photographic developer (or just developer) is one or more chemicals that convert the latent image to a visible image. Developing agents achieve this conversion by Redox, reducing the silver halides, which are pale-colored, into silver metal, which is black when in the form of fine particles.Karlheinz Keller et al. ''Photography'' in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . The conversion occurs within the gelatine matrix. The special feature of photography is that the developer acts more quickly on those particles of silver halide that have been exposed to light. When left in developer, all the silver halides will eventually be reduced and turn black. Generally, the longer a developer is allowed to work, the darker the image. Chemical composition of developers The developer typically consists of a mixture of chemical compounds prepared as an aqueous solut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stop Bath
A stop bath is an acidic solution used for processing black-and-white photographic film, plates, and paper. It is used to neutralize the alkaline developer, thus halting development. A stop bath is commonly a 2% dilution of acetic acid in water, though a 2.5% solution of potassium Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ... or sodium metabisulfite works just as well. Because organic developers only work in alkaline solutions, stop baths halt the development process almost immediately and provides precise control of development time. Neutralizing the alkalinity of basic developers also helps to preserve the strength of the fixer, making it last longer. Stop baths account for the vinegar-like odor of the darkroom. In its concentrated form it can cause chemical burns, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Fixer
Photographic fixer is a mixture of chemicals used in the final step in the photographic processing of film or paper. The fixer stabilises the image, removing the unexposed silver halide remaining on the photographic film or photographic paper, leaving behind the reduced metallic silver that forms the image. By fixation, the film or paper is insensitive to further action by light. Without fixing, the remaining silver halide would darken and cause fogging of the image. Chemistry Fixation is commonly achieved by treating the film or paper with a solution of thiosulfate salt. Popular salts are sodium thiosulfate—commonly called hypo—and ammonium thiosulfate—commonly used in modern rapid fixer formulae. Fixation by thiosulfate involves these chemical reactions (X = halide, typically Br−):Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . :AgX + 2 S2O32− → g(S2O3)2sup>3− + X− :AgX + 3 S2O32− → ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |