|
Verrier Elwin
Harry Verrier Holman Elwin (29 August 1902 – 22 February 1964) was a British-born Indian anthropologist, ethnologist and tribal activist. He is best known for his early work with the Baigas and Gonds of Orissa and Madhya Pradesh in central India. He later also worked on the tribals of several North East Indian states especially North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA). Elwin served as the deputy director of the Anthropological Survey of India upon its formation in 1945. Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru later appointed Elwin as an adviser on tribal affairs for north-eastern India, and went on to become the Anthropological Adviser to the Government of NEFA. He was awarded the third highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan. Elwin was a prolific researcher and writer. His autobiography, ''The Tribal World of Verrier Elwin,'' posthumously won him the 1965 Sahitya Akademi Award in English Language. Early life and education Harry Verrier Holman Elwin was born on 29 August 1902 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dover
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Great Britain, Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many English Channel migrant crossings (2018-present), illegal migrant crossings. The Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central India
Central India refers to a geographical region of India that generally includes the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh. The Central Zonal Council, established by the Government of India, includes these states as well as Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand to the north. The inclusion of Uttarakhand extends the region to the Himalayan border with Tibet/China. Other definitions Another approach, historically more usual, is to base "Central India" on a north-south axis, making it the part of India that is south of North India and north of South India; the definition of North India also varies hugely, but that of South India is generally agreed. This definition includes either some or all of the Deccan, in particular Maharashtra, and may or may not include some of the Indo-Gangetic Plain to the north. If Maharashtra is included "Central India" includes a good part of the western coast, including Mumbai, but the eastern coast is never included, as Odisha stretches down to me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Church Of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, tradition, with foundational doctrines being contained in the ''Thirty-nine Articles'' and ''The Books of Homilies''. The Church traces its history to the Christian hierarchy recorded as existing in the Roman Britain, Roman province of Britain by the 3rd century and to the 6th-century Gregorian mission to Kingdom of Kent, Kent led by Augustine of Canterbury. Its members are called ''Anglicans''. In 1534, the Church of England renounced the authority of the Papacy under the direction of Henry VIII, beginning the English Reformation. The guiding theologian that shaped Anglican doctrine was the Reformer Thomas Cranmer, who developed the Church of England's liturgical text, the ''Book of Common Prayer''. Papal authority was Second Statute of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxford Inter-Collegiate Christian Union
The Oxford Inter-Collegiate Christian Union, usually known as OICCU ( ), is the world's second oldest university Christian Union and is the University of Oxford's most prominent student Christian organisation. It was formed in 1879. Due to the strength of the Oxford Movement and later the Oxford Groups (alternative Christian movements), evangelical Christians in Oxford have generally faced a more pluriform environment than in Cambridge, and OICCU has tended to follow the general lead of its Cambridge counterpart, the Cambridge Inter-Collegiate Christian Union (CICCU). OICCU admits postgraduate students as well as undergraduates, although postgraduates are eligible only for associate membership, and their needs may be better served by the Oxford Graduate Christian Forum. Aims and purpose The OICCU vision is: ''Giving every student in Oxford University the chance to hear and respond to the Gospel of Jesus Christ'' The three aims of OICCU are: * ''Presenting the claims of Jesu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Master Of Arts (Oxbridge)
In the universities of Oxford, Cambridge, and Dublin, Bachelors of Arts (BAs) are promoted to the rank of Master of Arts (MA), typically upon application after three or four years after graduation. No further examination or study is required for this promotion, which is a mark of seniority rather than an additional postgraduate qualification. According to the formula of '' ad eundem gradum'', the graduates of the Universities of Oxford, Cambridge, and Dublin are eligible to apply to incorporate and be granted equivalent academic degrees at any of the other two universities, provided that they wish to register for such a degree or are members of the academic staff; they also pay a required fee. The example of the " Steamboat ladies" (roughly 720 women graduates of both Oxford and Cambridge who received Dublin academic degrees) is one of the most popular incidents of incorporation. While not an earned degree, both the original degree(s) and the incorporated ''ad eundem'' degree(s) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dean Close School
Dean Close School is a co-educational private boarding and day school (for pupils aged 3–18) in the public school tradition, located in Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, England. The school opened in 1886 and is divided into pre-prep, preparatory and senior schools located on separate but adjacent sites outside Cheltenham town centre, occupying the largest single private area of land within the town, at some 50 acres. Established in 1886 as an all-boys school, the school became co-educational in 1970. It takes day pupils, as well as boarders. Children as young as three join the pre-preparatory school, and the senior school teaches up to the age of eighteen. The headmaster of Dean Close School, Bradley Salisbury, is a member of the Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference. The headmaster of the Preparatory School, Paddy Moss, is a member of the IAPS and the Choir Schools' Association. Since 2015, the school has been led by a foundation, the Dean Close Foundation, inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and environments ranging from savannas to rainforests. As of the 2023 census, Sierra Leone has a population of 8,460,512. Freetown is its capital and largest city. Sierra Leone is a presidential republic, with a unicameral parliament and a directly elected president. It is a secular state. Its Constitution of Sierra Leone, constitution provides for the separation of state and religion and freedom of conscience. Muslims constitute three-quarters of the population, and there is a significant Christian minority. Notably, religious tolerance is very high. Sierra Leone's current territorial configuration was established in two phases: in 1808, the coastal Sierra Leone Colony and Protectorate, Sierra Leone Colony was founded as a place to resettle retu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anglicanism
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Most are members of national or regional Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, one of the largest Christian bodies in the world, and the world's third-largest Christian communion. When united and uniting churches, united churches in the Anglican Communion and the breakaway Continuing Anglican movement were not counted, there were an estimated 97.4 million Anglicans worldwide in 2020. Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The provinces within the Anglican ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edmund Henry Elwin
Edmund Henry Elwin, DD (18 September 1871 – 10 November 1909) was an English Anglican missionary and Anglican Bishop of Sierra Leone. Biography Elwin was educated at Dover College and Merton College, Oxford, England, where he gained a third class degree in Theology. Later he studied at Wycliffe Hall in Oxford, a theological training college in the Evangelical tradition. After his curacy in Oxford, Edmund Elwin became a missionary in Sierra Leone and soon became Vice Principal of Fourah Bay College which was affiliated to Durham University. He eventually became Principal and Secretary of the Sierra Leone Mission. When the then Bishop of Sierra Leone became Chaplain General to the British Forces in November 1901, Elwin was appointed his successor. He was consecrated as Bishop by the Archbishop of Canterbury in Westminster Cathedral on 25 January 1902. In March 1902 he received the degree Doctor of Divinity ''(Honoris causa)'' from the University of Oxford, and was elected a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
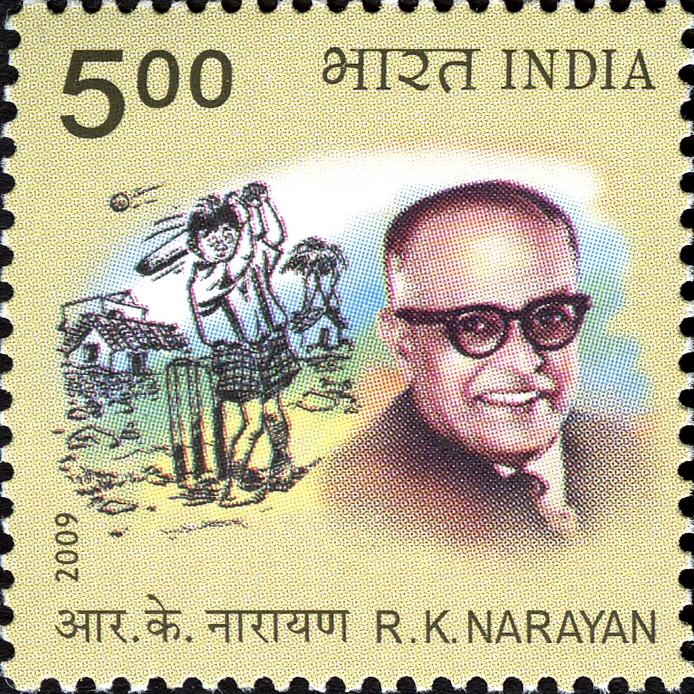
Sahitya Akademi Award To English Language Writers
The Sahitya Akademi Award is a literary honor in India awarded by the Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, which aims at "promoting Indian literature throughout the world". The Akademi annually confers on writers of "the most outstanding books of literary merit". The awards are given for works published in any of the 24 languages recognised by the akademi. Instituted in 1954, the award recognizes and promotes excellence in writing and acknowledge new trends. The annual process of selecting awardees runs for the preceding twelve months. , the award consists of an engraved copper-plaque, a shawl and a cash prize of . Recipients Further reading *Sahitya Akademi Award The Sahitya Akademi Award is a literary honour in India, which the Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, annually confers on writers of the most outstanding books of literary merit published in any of the 22 languages of the ... References {{Sahitya Akademi Award winn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sahitya Akademi Award
The Sahitya Akademi Award is a literary honour in India, which the Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, annually confers on writers of the most outstanding books of literary merit published in any of the 22 languages of the 8th Schedule to the Indian constitution as well as in English and Rajasthani language. Established in 1954, the award comprises a plaque and a cash prize of ₹ 1,00,000. The award's purpose is to recognise and promote excellence in Indian writing and also acknowledge new trends. The annual process of selecting awardees runs for the preceding twelve months. The plaque awarded by the Sahitya Akademi was designed by the Indian film-maker Satyajit Ray. Prior to this, the plaque occasionally was made of marble, but this practice was discontinued because of the excessive weight. During the Indo-Pakistan War of 1965, the plaque was substituted with national savings bonds. Recipients Other literary honors Sahitya Akademi Fellowships The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jawaharlal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru (14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat, and statesman who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20th century. Nehru was a principal leader of the Indian nationalist movement in the 1930s and 1940s. Upon India's independence in 1947, he served as the country's first prime minister for 16 years. Nehru promoted parliamentary democracy, secularism, and science and technology during the 1950s, powerfully influencing India's arc as a modern nation. In international affairs, he steered India clear of the two blocs of the Cold War. A well-regarded author, he wrote books such as '' Letters from a Father to His Daughter'' (1929), '' An Autobiography'' (1936) and '' The Discovery of India'' (1946), that have been read around the world. The son of Motilal Nehru, a prominent lawyer and Indian nationalist, Jawaharlal Nehru was educated in England—at Harrow School and T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |