|
Verongimorpha
Verongimorpha is the name of a subclass of sea sponges within the phylum Porifera Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile .... It was first authenticated and described by Erpenbeck et al. in 2012. References Taxa described in 2012 Sponge subclasses Taxa named by John Hooper (marine biologist) Taxa named by Gert Wörheide Taxa named by Rob van Soest {{Demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrillida
Chondrosiida is an order of sea sponges within the subclass Verongimorpha Verongimorpha is the name of a subclass of sea sponges within the phylum Porifera Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and .... References Verongimorpha Sponge orders {{Poriferan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysina Archeri
''Aplysina archeri'', also known as a stove-pipe sponge because of its shape, is a species of tube sponge that has long tube-like structures of cylindrical shape. Although they can grow in a single tube, they often grow in large groups of up to 22 tubes. A single tube can grow up to high and thick. These sponges mostly live in the Western Atlantic Ocean: the Caribbean, The Bahamas, Florida, and Bonaire. Like most sponges, they are filter feeders; they eat food such as plankton or suspended detritus as it passes them. Very little is known about their behavioral patterns except for their feeding ecology and reproductive biology. Tubes occur in varying colors including lavender, pink, gray, and brown. They reproduce both by Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual reproduction, sexual reproduction. These sponges take hundreds of years to grow and never stop growing until they die. Snails are among their natural predators. The population density of these sponges is decreasing becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verongiida
Verongiida (also known as Verongida) is an order of sea sponges within the phylum Porifera. The "skeleton" in these sponges is made up of spongin, rather than of spicules. They live in marine environments. The name was proposed by Patricia Bergquist Dame Patricia Rose Bergquist (née Smyth, 10 March 1933 – 9 September 2009) was a New Zealand zoologist who specialised in anatomy and taxonomy. At the time of her death, she was professor emerita of zoology and honorary professor of anatomy ... in 1978. References Sponge orders Verongimorpha Taxa named by Patricia Bergquist {{Demosponge-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rob Van Soest
Robertus Wilhelmus Maria van Soest, born in 1946, is a Dutch marine biologist. He works at the Naturalis Biodiversity Center and is also affiliated with the University of Amsterdam. He co-authored with John Hooper (marine biologist), John N. A. Hooper ''Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges'', a standard reference for sponge classification. He was editor in chief of the World Porifera Database (WPD) from 2004 to 2021, and is currently (March 2022) one of its taxonomic editors. He has contributed to the systematics, the phylogeny and the taxonomy of sponges, to their chemistry and biological properties (and the pharmacological use thereof) His zoological abbreviation is van Soest. Taxa A search on his name (March 2022) in the World Register of Marine Species, WoRMS database gives 691 taxa names authored by van Soest. See also :Taxa named by Rob van Soest, taxa named by Rob van Soest. Publications He has authored (co-authored) over at least 170 peer r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hooper (marine Biologist)
John N.A. Hooper is an Australian marine biologist and writer on science. He is the current Head of Biodiversity & Geosciences Programs at the Queensland Museum. His research has included studying the possible medical benefits of marine sponges, including beta blockers for heart disease, and for compounds to combat illnesses like gastro-intestinal disease and cancer. In 2007 he was a member of the Discussion Panel On Marine Genetic Resources for the eighth annual United Nations Informal Consultative Process for Oceans and the Law of the Sea (UNICPOLOS). Notable works Together with Rob van Soest, Hooper co-edited the influential book ''Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges''. In addition, the Web of Science lists over 90 articles in peer-reviewed journals that have been cited over 1650 times, with an h-index of 24.Web of Science The Web of Science (WoS; previously known as Web of Knowledge) is a paid-access platform that provides (typically via the interne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gert Wörheide
Gert Wörheide is a German marine biologist who works mainly on marine invertebrates. He earned his doctorate in geobiology from Georg-August-Universität, following this with a post-doctorate at Queensland Museum (1998-2002), where he worked with John Hooper on sponges, a collaboration which continues. Following his postdoctorate in Queensland, Wörheide returned to Germany to become a junior professor in molecular geobiology at Georg-August-Universität (2002-2008), and in October 2008 was appointed Chair of Geobiology & Paleontology at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich, LMU or LMU Munich; ) is a public university, public research university in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Originally established as the University of Ingolstadt in 1472 by Duke ... (University of Munich) (his current position), where he continues to work on evolution and genomics, and all things pertaining to marine invertebrates. His m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclass (biology)
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, class () is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are Domain (biology), domain, Kingdom (biology), kingdom, phylum, Order (biology), order, Family (biology), family, genus, and species, with class ranking between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name – and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'' – was first introduced by France, French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in the classification of plants that appeared in his ''Eléments de botanique'' of 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
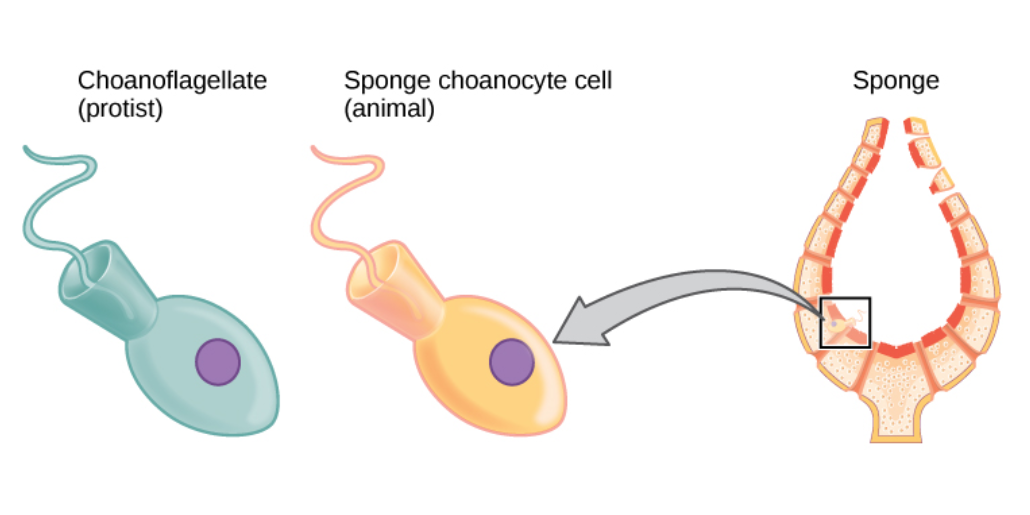
Sea Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar cells". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about eight phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |