|
Verinopolis
Verinopolis or Berinopolis () was a city and bishopric in ancient Galatia, central Anatolia (modern Turkey). History The city is known only from its bishopric and as an administrative unit, from the 7th to the late 13th centuries. Its location is unknown, and its traditional identification (e.g. by William Mitchell Ramsay or Raymond Janin) with the late antique waystation of Aegonne or Euagina, localized near the modern settlement of Büyük Köhne (today Sorgun), is most probably incorrect. The city is not known before the 7th century, but obviously existed earlier, since it was named or renamed from a previous, unknown name, in honour of Verina, wife of the Emperor Zeno. The city belonged to the Roman province of Galatia Prima, and later to the Bucellarian Theme, until Emperor Leo VI the Wise () detached it (along with the neighbouring ''banda'' of Stavros or Stavropolis and Myriokephalon) to form the new ''tourma'' of Saniana in the theme of Charsianon. In the ''Not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolis Of Ancyra
The Metropolis of Ancyra () was a Christian (Eastern Orthodox after the East–West Schism) bishopric in Ancyra (modern Ankara, Turkey) and metropolitan see of Galatia Prima. The see survived the Seljuk Turkish conquest at the end of the 11th century, and remained active until the end of the Ottoman Empire and the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923. History Early Christianity The city of Ancyra had been the political centre of the Roman province of Galatia since its establishment in 25 BC. The arrival of Christianity in Ancyra is probably to be dated to the time of the Apostles in the mid-1st century AD but is attested in the sources only much later. Modern historians suggest that Apostles Peter and Andrew in person preached in the city, and founded the local Church, with a certain Cresces, a disciple of the Paul the Apostle, who lived between 56 and 117 AD, as the city's first bishop.. The existence of a Christian church in Ancyra is not attested until arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
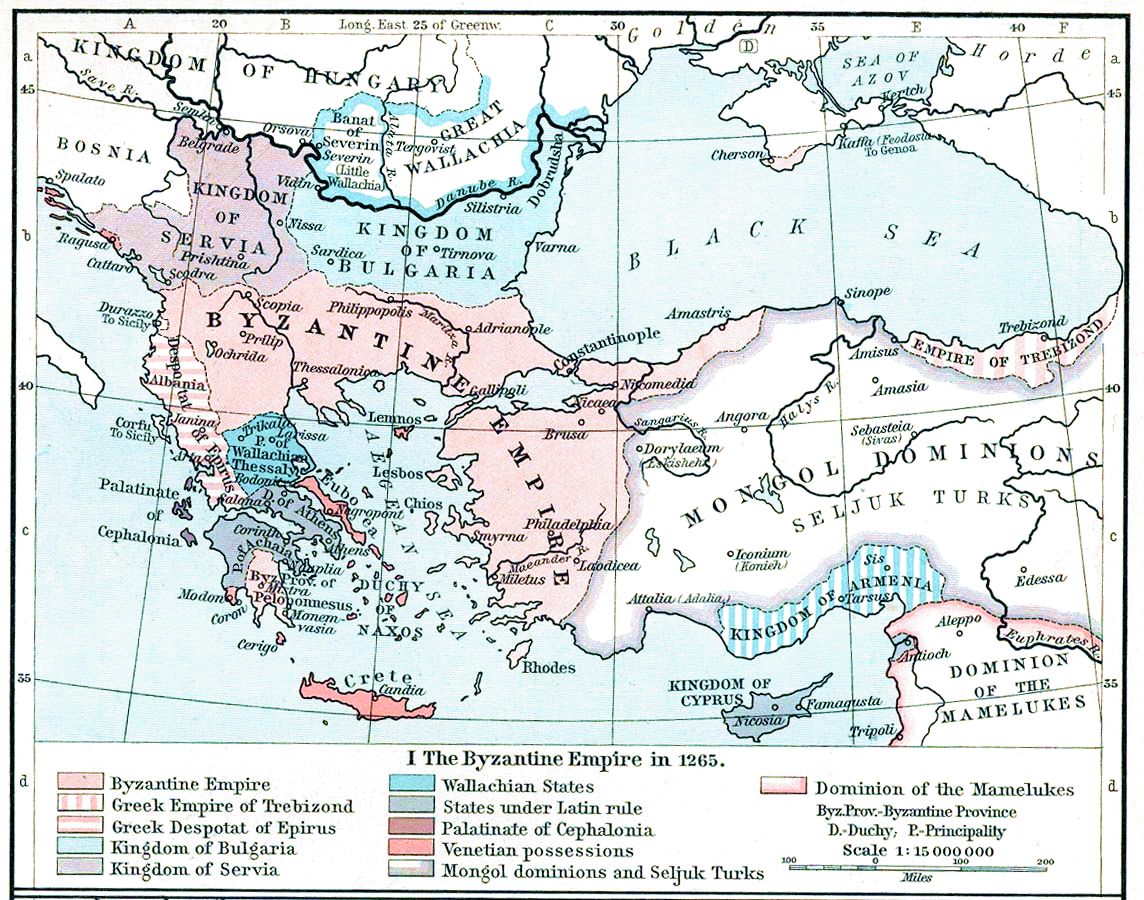
Ancient Galatia
Galatia (; , ''Galatía'') was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East. Geography Galatia was bounded to the north by Bithynia and Paphlagonia, to the east by Pontus and Cappadocia, to the south by Cilicia and Lycaonia, and to the west by Phrygia. Its capital was Ancyra (i.e. Ankara, today the capital of modern Turkey). Celtic Galatia The terms "Galatians" came to be used by the Greeks for the three Celtic peoples of Anatolia: the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii. By the 1st century BC, the Celts had become so Hellenized that some Greek writers called them ''Hellenogalatai'' (Ἑλληνογαλάται). The Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Council Of Constantinople (Eastern Orthodox)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was held in 879–880. It confirmed the reinstatement of Photius I as patriarch of Constantinople. The result of this council is accepted by the Eastern Orthodox as having the authority of an ecumenical council. Eastern Orthodox sometimes call it the eighth ecumenical council. Background The Council settled the dispute that had broken out after the deposition of Ignatius as Patriarch of Constantinople in 858. Ignatius, himself appointed to his office in an uncanonical manner, opposed Caesar Bardas, who had deposed the regent Theodora. In response, Bardas' nephew, the youthful Emperor Michael III engineered Ignatius's deposition and confinement on the charge of treason. The patriarchal throne was filled with Photius, a renowned scholar and kinsman of Bardas. The deposition of Ignatius without a formal ecclesiastical trial and the sudden promotion of Photius caused scandal in the church. Pope Nicholas I and the western bishops took up the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Council Of Constantinople (Roman Catholic)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was the eighth ecumenical council of the Catholic Church held in Constantinople from 5 October 869, to 28 February 870. It was poorly attended, the first session by only 12 bishops and the number of bishops later never exceeded 103. In contrast, the pro-Photian council of 879–80 was attended by 383 bishops. The Council met in ten sessions from October 869 to February 870 and issued 27 canons. The council was called by Emperor Basil I the Macedonian, with the support of Pope Hadrian II."Photius", in Cross, F. L., ed. ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church''. New York: Oxford University Press. 2005 It deposed and anathematized Photius, a layman who had been appointed as Patriarch of Constantinople, and reinstated his predecessor Ignatius. The Council also reaffirmed the decisions of the Second Council of Nicaea in support of icons and holy images and required the image of Christ to have veneration equal with that of the gospel bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Council Of Nicaea
The Second Council of Nicaea is recognized as the last of the first seven ecumenical councils by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. In addition, it is also recognized as such by Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics and others. Protestantism, Protestant opinions on it are varied. The Council assembled in 787 AD in Nicaea (site of the First Council of Nicaea; present-day İznik, Bursa Province, Bursa, in Turkey), to restore the use and veneration of icons (or holy images),Gibbon, p. 1693. which had been suppressed by emperor, imperial edict inside the Byzantine Empire during the reign of Leo III the Isaurian, Leo III (717–741). His son, Constantine V (741–775), had held the Council of Hieria to make the suppression official. The Council determined that the honorary veneration (''timētikē proskynēsis'') of icons was permitted, and that the true adoration (''alēthinē latreia'') was reserved for God alone. It further stated that the honor paid to the icon e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinisext Council
The Quinisext Council (; , literally meaning, ''Fifth-Sixth Meeting''), i.e., the Fifth-Sixth Council, often called the Council ''in Trullo'', Trullan Council, or the Penthekte Synod, was a church council held in 692 at Constantinople under Justinian II. The synod is known as the "Council ''in Trullo''" because, like the Sixth Ecumenical Council, it was held in a domed hall in the Imperial Palace ( [], meaning a cup or dome). Both the Second Council of Constantinople, Fifth and the Third Council of Constantinople, Sixth Ecumenical Councils had omitted to draw up disciplinary canon law, canons, and as this council was intended to complete both in this respect, it took the name of Quinisext. Decisions Many of the council's Canon (canon law), canons were reiterations. It endorsed not only the six ecumenical councils already held (canon 1), but also: * the 85 Apostolic Canons, * the Synod of Ancyra * the Synod of Neocaesarea, * the Synod of Gangra, * the Synod of Antioch i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Council Of Constantinople
The Third Council of Constantinople, counted as the Sixth Ecumenical Council by the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches, and by certain other Western Churches, met in 680–681 and condemned monoenergism and monothelitism as heretical and defined Jesus Christ as having two energies and two wills (divine and human). George Ostrogorsky, ''History of the Byzantine State'' (Rutgers University Press, 1995), 127. Background The council settled a set of theological controversies that went back to the sixth century but had intensified under the emperors Heraclius () and Constans II (). Heraclius had set out to recover much of the part of his empire lost to the Persians and had attempted to bridge the controversy with monophysitism, which was particularly strong in Syria and Egypt, by proposing a moderate theological position that had as good support in the tradition as any other. The result was first monoenergism, i.e., that Christ, though existing in two natures (divine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocephalous
Autocephaly (; ) is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches. The status has been compared with that of the churches (provinces) within the Anglican Communion. Overview of autocephaly In the first centuries of the history of the Christian church, the autocephalous status of a local church was promulgated by canons of the ecumenical councils. There developed the pentarchy, i.e., a model of ecclesiastical organization where the universal Church was governed by the primates (patriarchs) of the five major episcopal sees of the Roman Empire: Rome, Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, and Jerusalem. The independent (autocephalous) position of the Church of Cyprus by ancient custom was recognized against the claims of the Patriarch of Antioch, at the Council of Ephesus (431); it is unclear whether the Church of Cyprus had always been inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologos, Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He Reconquest of Constantinople, recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and Byzantine navy, navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffragan See
A suffragan diocese is one of the dioceses other than the metropolitan archdiocese that constitute an ecclesiastical province. It exists in some Christian denominations, in particular the Catholic Church, the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, and the Romanian Orthodox Church. In the Catholic Church, although such a diocese is governed by its own bishop or ordinary, who is the suffragan bishop, the metropolitan archbishop has in its regard certain rights and duties of oversight. He has no power of governance within a suffragan diocese, but has some limited rights and duties to intervene in cases of neglect by the authorities of the diocese itself. See also * Suffragan bishop * Suffragan Bishop in Europe (a title in the Church of England) * List of Roman Catholic archdioceses (by country and continent) * List of Roman Catholic dioceses (alphabetical) This is a growing list of territorial dioceses and ordinariates in communion with the Holy See. There are approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarchate Of Constantinople
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople (, ; ; , "Roman Orthodox Patriarchate, Ecumenical Patriarchate of Istanbul") is one of the fifteen to seventeen autocephalous churches that together compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. It is headed by the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople. Because of its historical location as the capital of the former Eastern Roman Empire and its role as the mother church of most modern Eastern Orthodox churches, Constantinople holds a special place of honor within Eastern Orthodox Christianity and serves as the seat for the Ecumenical Patriarch, who enjoys the status of ''primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the world's Eastern Orthodox prelates and is regarded as the representative and spiritual leader of Eastern Orthodox Christians. Phanar (Turkish: '' Fener''), the name of the neighbourhood where ecumenical patriarch resides, is often used as a metaphor or shorthand for the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. The Ecumeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |