|
Venkatasuchus
''Venkatasuchus'' is an extinct genus of aetosaur from the Late Triassic Dharmaram Formation of India. It was described in 2023 on the basis of a series of associated osteoderms that formed the paramedian and lateral armour. Based on the osteoderms the carapace of ''Venkatasuchus'' was disc-shaped and very wide, with curved, horn-like elements along its sides. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that ''Venkatasuchus'' belonged to the subfamily Typothoracinae and more specifically the clade Paratypothoracini. ''Venkatasuchus'' is among the few aetosaurs recovered from the region that would later become Gondwana and lends credence to the idea that late Triassic India represented a connective hub between Laurasian and Gondwanan fauna. The genus is monotypic, meaning it only includes a single species, ''Venkatasuchus armatum''. History and naming ''Venkatasuchus'' is known from a series of osteoderms that have been recovered from the Late Triassic Lower Dharmaram Formation of India, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuttysuchus
''Kuttysuchus'' is an extinct group of Typothoracinae, typothoracine aetosaur from the Late Triassic Lower Dharmaram Formation, Dharmaram Formation of India. It was described in 2025 on the basis of multiple isolated osteoderms that were nonetheless distinct in their appearance from not only the contemporary ''Venkatasuchus'' but also from other aetosaur taxa. The specific combination of characters suggests that ''Kuttysuchus'' was a member of the clade Paratypothoracini, with phylogenetic analysis indicating it to have been a basal member of the group. The genus is monotypic, only containing a single species. ''Kuttysuchus minori''. History and naming ''Kuttysuchus'' was described in early 2025 on the basis of a series of isolated paramedian osteoderms, with one almost complete bone serving as the holotype. All fossils stem from the sandstone-dominated lower unit of the Dharmaram Formation, located in the Pranhita–Godavari Basin of eastern India and thought to date from the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
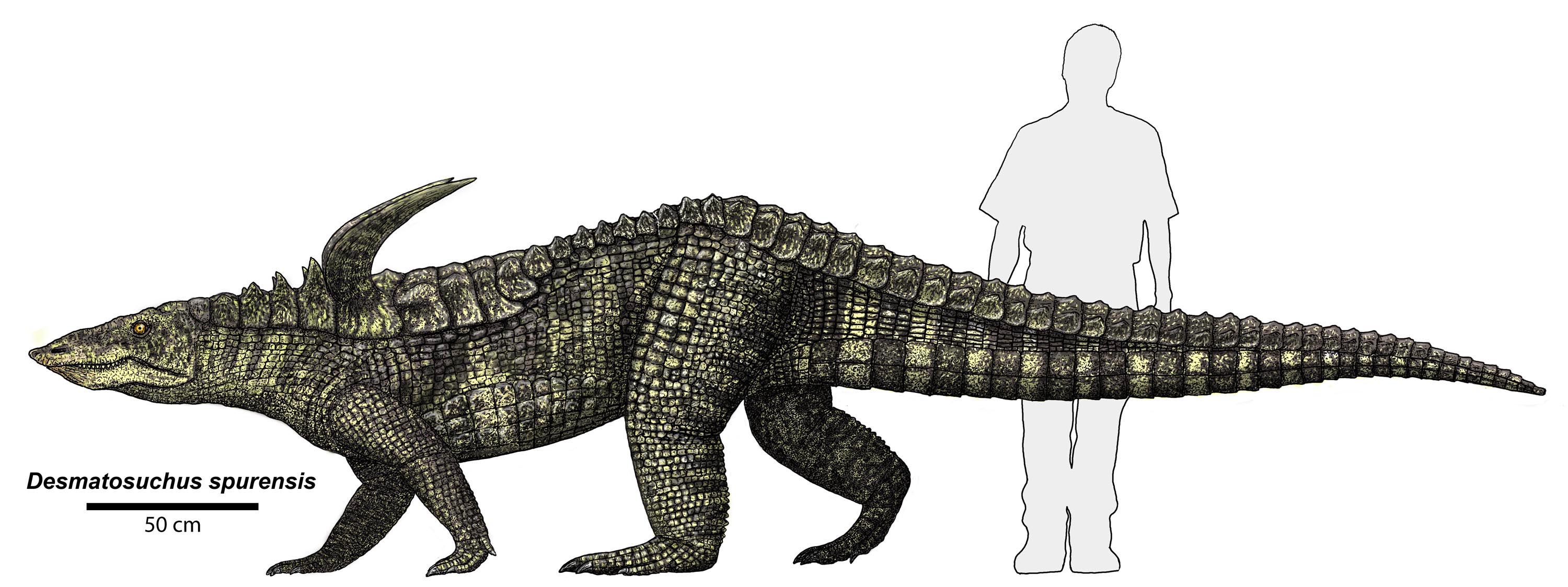
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order (biology), order Aetosauria (; from Ancient Greek, Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized Omnivore, omnivorous or Herbivore, herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North America, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their Stratigraphy, stratigraphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stagonolepidoidea
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria (; from Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Dharmaram Formation
The Lower Dharmaram Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in Telangana, India. It is one of the formations of the Pranhita–Godavari Basin. It is of latest Norian and Rhaetian ages (Upper Triassic), and is notable for its fossils of early dinosaurs. Vertebrate fauna cf. '' Paratypothorax'', cf. ''Nicrosaurus'', fragmentary remains of sauropodomorphs ( ISI R279, 280, 281) and neotheropods (ISI R283) have also been recovered from it.Novas et al., 2011, p.345 Saurischians Pseudosuchians Correlations The formation has been correlated with the Lower Elliot Formation (Karoo Basin) and Forest Sandstone of Africa, the Caturrita Formation of the Paraná Basin in Brazil, the Laguna Colorada and Los Colorados Formations (Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin) of Argentina, the Chinle Formation of North America, the Trossingen Formation of the Keuper of Germany, and the Nam Phong Formation of Thailand.Novas et al., 2011, p.343 See also * List of dinosaur-bearing r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typothoracinae
Aetosaurinae is one of the two main clades of aetosaurs, the other being Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to ''Aetosaurus'' than ''Desmatosuchus''. Aetosaurinae currently comprises ''Aetosaurus,'' similar forms such as ''Coahomasuchus'' and ''Stenomyti'', and the widespread and successful aetosaur clade Typothoracinae. Previous usage Aetosaurinae was originally named in 2000, as a subfamily solely including ''Aetosaurus'', which was assumed to be the earliest-diverging aetosaur. In 2007, it was extended to include the subfamily Typothoracinae as well as various Basal (phylogenetics), basal aetosaurs which were not clearly within Desmatosuchinae. These proposed non-typothoracine aetosaurines included ''Coahomasuchus'', ''Neoaetosauroides'', ''Aetosauroides'', ''Stagonolepis, Stagonolepis robertsoni,'' and ''"Stagonolepis"'' (''Calyptosuchus'') ''wellesi''. As a subfamily containing practically all non-desmatosuchine aetosaurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaurinae
Aetosaurinae is one of the two main clades of aetosaurs, the other being Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to '' Aetosaurus'' than ''Desmatosuchus''. Aetosaurinae currently comprises ''Aetosaurus,'' similar forms such as '' Coahomasuchus'' and '' Stenomyti'', and the widespread and successful aetosaur clade Typothoracinae. Previous usage Aetosaurinae was originally named in 2000, as a subfamily solely including ''Aetosaurus'', which was assumed to be the earliest-diverging aetosaur. In 2007, it was extended to include the subfamily Typothoracinae as well as various basal aetosaurs which were not clearly within Desmatosuchinae. These proposed non-typothoracine aetosaurines included ''Coahomasuchus'', '' Neoaetosauroides'', '' Aetosauroides'', '' Stagonolepis robertsoni,'' and ''"Stagonolepis"'' (''Calyptosuchus'') ''wellesi''. As a subfamily containing practically all non-desmatosuchine aetosaurs, Aetosaurinae was poorly sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paratypothoracini
Aetosaurinae is one of the two main clades of aetosaurs, the other being Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to ''Aetosaurus'' than ''Desmatosuchus''. Aetosaurinae currently comprises ''Aetosaurus,'' similar forms such as '' Coahomasuchus'' and '' Stenomyti'', and the widespread and successful aetosaur clade Typothoracinae. Previous usage Aetosaurinae was originally named in 2000, as a subfamily solely including ''Aetosaurus'', which was assumed to be the earliest-diverging aetosaur. In 2007, it was extended to include the subfamily Typothoracinae as well as various basal aetosaurs which were not clearly within Desmatosuchinae. These proposed non-typothoracine aetosaurines included ''Coahomasuchus'', '' Neoaetosauroides'', ''Aetosauroides'', '' Stagonolepis robertsoni,'' and ''"Stagonolepis"'' (''Calyptosuchus'') ''wellesi''. As a subfamily containing practically all non-desmatosuchine aetosaurs, Aetosaurinae was poorly support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kocurypelta
''Kocurypelta'' is an extinct genus of paratypothoracin aetosaur from the Late Triassic (Norian)-aged Lissauer Breccia of southern Poland. Only the type species is known, which is ''K. silvestris'', described by Czepiński ''et al.'' in 2021. Discovery and naming The holotype (ZPAL V.66/4), which consists of part of the maxilla, and referred material (three dorsal paramedial plates and a ventral plate fragment), was found in a layer of the Lissauer Breccia, of which the location was believed to have been lost after the formation was studied by Friedrich von Huene while describing ''Velocipes'' in 1932,Huene, F. von. (1932). ''Die fossile Reptil-Ordnung Saurischia, ihre Entwicklung und Geschichte''. ''Monogr. Geol. Pal''. 4 (1) pts. 1 and 2, viii + 361 pp. near Kocury, during excavations that began in 2012, that re-discovered and re-explored the formation. The remains were described as the new species ''Kocurypelta silvestris'' in 2021. Description According to Czepiński ''et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue ( mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor. In fracture healing, endochondral osteogenesis is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long bones treated by plaster of Paris, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation with metal plates, screws, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis. Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification is often confused with ossification. Calcificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rioarribasuchus
''Rioarribasuchus'' is a genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Chinle Formation in Arizona and New Mexico that date back to the upper Late Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. History ''"Desmatosuchus" chamaensis'' was named in 2003 and found from the Petrified Forest Member of the Chinle Formation in New Mexico. It was suggested to be more closely related to '' Paratypothorax'', and so Parker gave it the name ''Heliocanthus''. However, this new generic name was first proposed in an unpublished thesis, and thus did not meet ICZN regulations for the naming of a new taxon. Later published papers reasserted the genetic separation of ''"D". chamaensis'' from ''Desmatosuchus'', but the name ''Heliocanthus'' remained a ''nomen nudum'' until 2007, where it was thoroughly rediscribed in a paper published by the ''Journal of Systematic Palaeontology''. However, a paper previously published in late 2006 assigned ''"D". chamaensis'' to the new genus ''Rioarribasuchus''. As a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', ''Herrerasaurus'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |