|
Venezuela Province
The Venezuela Province (or Province of Caracas) was a province of the Spanish Empire (from 1527), of Gran Colombia (1824–1830) and later of Venezuela (from 1830), apart from an interlude (1528–1546) when it was contracted as a concession by the King of Spain to the German Welser banking family, as Klein-Venedig. Colonial history It has its origins with the 1527 foundation of Santa Ana de Coro by Juan de Ampíes, the province's first governor. Coro was the province's capital until 1546, followed by El Tocuyo (1546-1577). The capital was moved to Caracas in 1577 by Juan de Pimentel. At one time (founded 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klein-Venedig
( German for 'Little Venice') or Welserland () was the most significant territory of the German colonization of the Americas, from 1528 to 1546, in which the Welser banking and patrician family of the Free Imperial Cities of Augsburg and Nuremberg obtained colonial rights in the Province of Venezuela in return for debts owed by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, who was also King of Spain. In 1528, Charles V issued a charter by which the House of Welser possessed the rights to explore, rule and colonize the area, also with the motivation of searching for the legendary golden city of El Dorado. The venture was led at first by Ambrosius Ehinger, who founded Maracaibo in 1529. After the deaths of Ehinger (1533) and then his successor Georg von Speyer (1540), Philipp von Hutten continued exploration in the interior, and in his absence from the capital of the province, the crown of Spain claimed the right to appoint the governor. On Hutten's return to the capital, Santa Ana de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarch
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the Sovereign state, state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually, a monarch either personally inheritance, inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the Crown, the crown'') or is elective monarchy, selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may self-proclaimed monarchy, proclaim oneself monarch, which may be backed and Legitimacy (political), legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guayana Province
Guayana Province (1585−1864) was a province of Spanish Colonial Venezuela and independent Venezuela, located in the The Guianas, Guyana region of northeastern South America. The province was part of the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonial New Andalusia Province and Captaincy General of Venezuela from 1585 to 1821, and of independent Venezuela from 1821 to 1864. History Guayana Province covered a territory roughly equal to the present day country of Guyana and the Venezuelan Guayana Region from 1591 to 1739, when the province's territory was merged into the Spanish Trinidad-Guayana Province, along with Trinidad Province (present day Trinidad and Tobago). Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas is named after the Amazon River, and was formerly part of the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru, a region called Spanish Guyana. It was settled by the Portuguese in the early 18th century and incorporated into the Portuguese empire after the Treaty of Madrid (13 January 1750), Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Andalusia Province
New Andalusia Province or Province of Cumaná (1537–1864) was a province of the Spanish Empire, and later of Gran Colombia and Venezuela. It included the territory of present-day Venezuelan states Sucre, Anzoátegui and Monagas. Its most important cities were the Capital City Cumaná and New Barcelona. Spanish Empire Its provincial capital, Cumaná, was refounded in 1569 by explorer Diego Hernández de Serpa. The Province originally comprised what is now eastern Venezuela, western Guyana, and far northern Brazil. In the following centuries, its jurisdiction was reduced to Cumaná and Barcelona and was synonymous with Cumaná Province. Early in its history, the conquistador Joan Orpí founded a new Province, of ''Nueva Cataluña'' (New Catalonia), also known as ''New Barcelona'' after its capital, Barcelona, partly from territory belonging to New Andalusia. This lasted from 1637 to 1654, when it was incorporated into New Andalusia. Guayana Province (created 1585) provided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
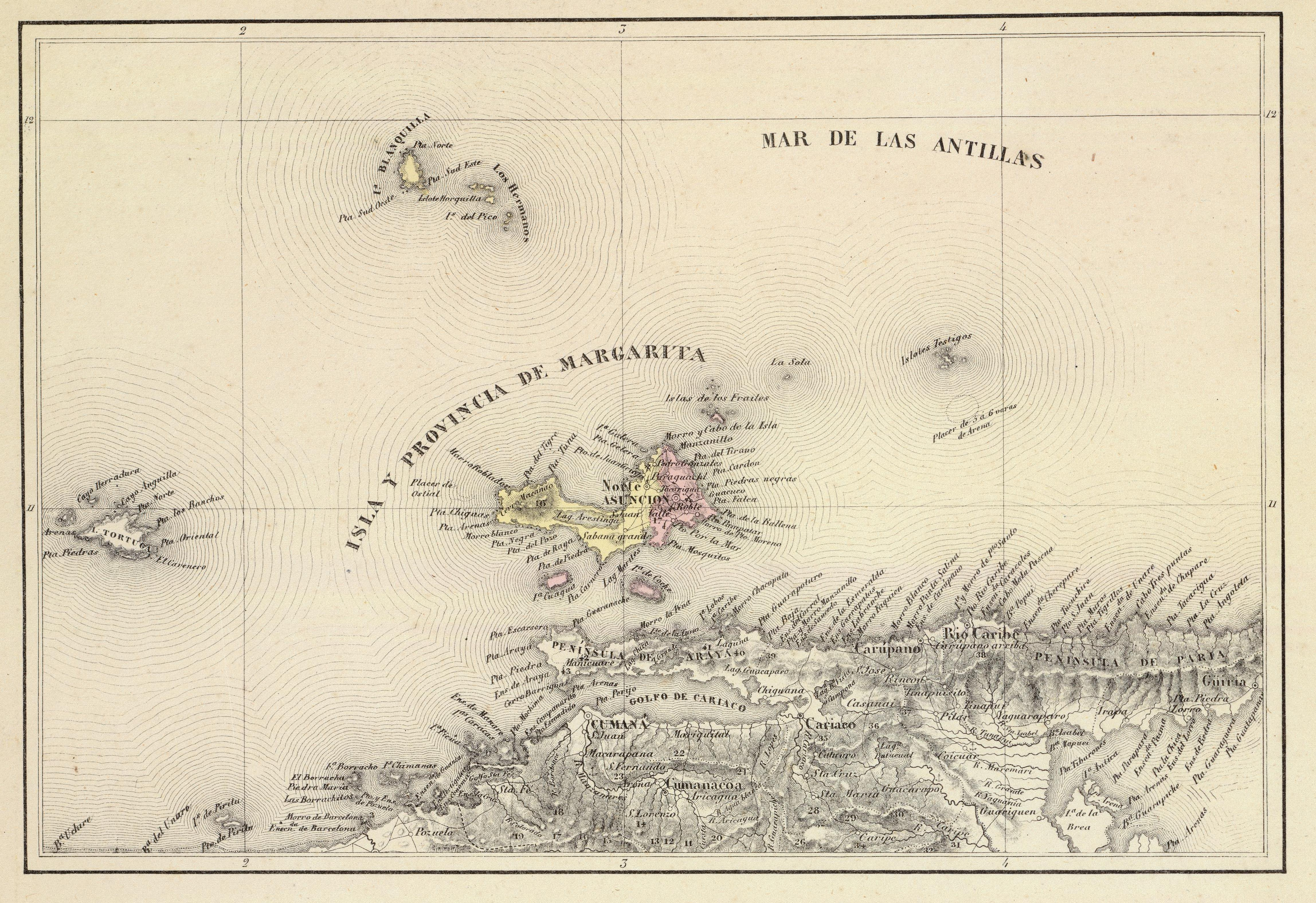
Isla Margarita
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the north west coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador who killed the governor Juan Villadrando. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and morality. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margarita Province
Margarita Province (1525 - 1864) was one of the provinces of the Spanish Empire, then one of the provinces of Gran Colombia, and later one of the Provinces of Venezuela. In Gran Colombia it belonged to the Orinoco Department which was created in 1824. With the creation of the States of Venezuela in 1864 it became Nueva Esparta. Divisions The Province was named for its most important part, Isla Margarita. Capital: Asunción Asunción (, ) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay. The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay of Asunción in the north .... Cantons: * Asunción Canton * Norte Canton (seat: Santa Ana del Norte). Governors A partial list of governors: References Citations Sources * * * * * * * * Provinces of Gran Colombia Provinces of Venezuela Provinces of the Spanish Empire Colonial Venezuela 1525 establishments in New Spain [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabozo
Calabozo, officially Villa de Todos los Santos de Calabozo, is a city in Venezuela located in Guárico state, capital of the Francisco de Miranda Municipality and former capital of the state. It has a population of 168,605, according to the National Institute of Statistics (INE) in 2020. It is located in the center-west of Guárico state, and is one of the main rice producers in the country. In addition, it has the largest irrigation system in Venezuela. Calabozo, is a mostly colonial city and is linked to its modern urban areas, being the largest colonial center in the country, and is located at 105 m a.s.l. n. m., at the margin of the Guárico River in the high central plain. Its location is on the banks of the Generoso Campilongo Dam, an important work both in its time and today, being the largest in Venezuela and one of the largest in Latin America. It is also the seat of the Roman Catholic archdiocese of Calabozo. Toponymy The toponymy of the city of Calabozo, in Guári ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Pimentel
Juan de Pimentel was an early governor of Venezuela Province, the Venezuela Province being one of the Spanish Empire. Under his governorship (1576 - 1583) the capital of the Province was moved from El Tocuyo to Caracas. He was a Knight of the Order of Santiago The Order of Santiago (; ) is a religious and military order founded in the 12th century. It owes its name to the patron saint of Spain, ''Santiago'' ( St. James the Greater). Its initial objective was to protect the pilgrims on the Way of S .... {{DEFAULTSORT:Pimentel, Juan de Knights of Santiago Royal governors of Venezuela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Ampíes
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of ''John''. The name is of Hebrew origin and has the meaning "God has been gracious." It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking countries around the world and in the Philippines, and also in the Isle of Man (pronounced differently). The name is becoming popular around the world and can be pronounced differently according that region. In Spanish, the diminutive form (equivalent to ''Johnny'') is , with feminine form (comparable to ''Jane'', ''Joan'', or ''Joanna'') , and feminine diminutive (equivalent to ''Janet'', ''Janey'', ''Joanie'', etc.). Chinese terms * ( or 娟, 隽) 'beautiful, graceful' is a common given name for Chinese women. * () The Chinese character 卷, which in Mandarin is almost homophonic with the characters for the female name, is a division of a traditional Chinese manuscript or book and can be translated as 'fascicle', 'scroll', 'chapter', or 'volume'. Notable people * Juan (fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), also known as Greater Colombia and officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and parts of Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador (i.e. excluding the Galápagos Islands), Panama, and Venezuela, along with the Caribbean coasts of Nicaragua and Costa Rica, parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil, and Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute, claimed the Essequibo region. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiography, historiographically to distinguish it from the current Colombia, Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state. However, Diplomatic recognition, international recognition of the legitimacy of the Gran Colombian state ran afoul of European opposition to the independence of states in the Americas. Austrian Empire, Austria, Bourb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of States of Venezuela, 23 states, the Venezuelan Capital District, Capital District and Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. The territory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Colonial Real
The silver real () was the currency of the Spanish colonies in America and the Philippines. In the seventeenth century the silver real was established at two billon reales (''reales de vellón'') or sixty-eight '' maravedíes''. Gold '' escudos'' (worth 16 reales) were also issued. The coins circulated throughout Spain's colonies and beyond, with the eight-real piece, known in English as the Spanish dollar, becoming an international standard and spawning, among other currencies, the United States dollar. A reform in 1737 set the silver real at two and half billon reales (reales de vellón) or eighty-five maravedís. This coin, called the ''real de plata fuerte'', became the new standard, issued as coins until the early 19th century. The gold escudo was worth 16 ''reales de plata fuerte''. History Coins were produced at mints in Bogotá, Caracas, Guatemala City, Lima, Mexico City, Popayán, Potosí, Santo Domingo and Santiago. For details, see the: * Colombian reales * Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |