|
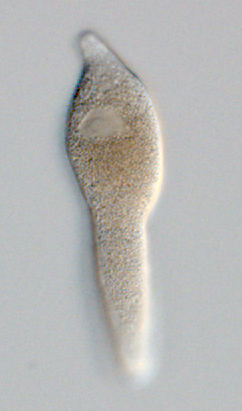
Veloxidium
''Veloxidium'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect marine invertebrates. Taxonomy This species was described in 2012 by Wakeman and Leander.Wakeman KC, Leander BS (2012) Molecular phylogeny of Pacific Archigregarines (Apicomplexa), including descriptions of ''Veloxidium leptosynaptae'' ''n. gen.'', ''n. sp.'', from the sea cucumber Leptosynapta clarki (Echinodermata), and two new species of ''Selenidium''. J Eukaryot Microbiol 59(3):232-45. There is one species in this genus - ''Veloxidium leptosynaptae''. Description This species infects the sea cucumber ''Leptosynapta clarki''. Life cycle The parasite infects the gastrointestinal tract and is presumably transmitted by the orofaecal route but the details of this mechanism are presently unknown. References Apicomplexa genera {{Apicomplexa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archigregarinorida
The ''Archigregarinorida'' are an order of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this order infect marine invertebrates — usually annelids, ascidians, hemichordates and sipunculids. Taxonomy This order was redefined by Levine in 1971. The order currently consists of 76 species in two families — ''Exoschizonidae'' and ''Selenidioididae''. The family ''Exoschizonidae'' contains one genus — ''Exoschizon'' — which has one species. The family ''Selenidioididae'' has six genera: ''Filipodium'' with 3 species, ''Merogregarina'' with one species, ''Meroselenidium'' with one species, '' Platyproteum'' with one species, ''Selenidioides'' with 11 species and ''Veloxidium'' with one species. Phylogenetics DNA studies suggest that the archigregarines are ancestral to the other gregarines. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that this group is paraphyletic and will need division. The Neogregarinorida appear to be derived from the Eugregarinorida. Assuming this is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. However, gregarines are closely related to both ''Toxoplasma'' and ''Plasmodium'', which cause toxoplasmosis and malaria, respectively. Both protists use protein complexes similar to those that are formed by the gregarines for gliding motility and invading target cells. This makes them excellent models for studying gliding motility with the goal of developing treatment options for toxoplasmosis and malaria. Thousands of different species of gregarines are expected to be found in insects, and 99% of these gregarines still need to be described. Each insect can be the host of multiple species. One of the most studied gregarines is ''Gregarina garnhami''. In general, gregarines are regarded as very successful parasites, as their hosts are spread over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenidioididae
The ''Selenidioididae'' are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this order infect marine invertebrates. Taxonomy The order Archigregarinorida was redefined by Levine in 1971Levine N D (1971) Taxonomy of the Archigregarinorida and Selenidiidae (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) J Euk Micro 18 (4) 704-717 DOI: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03401.x and divided into two families: Exoschizonidae The Exoschizonidae are a family in the phylum Apicomplexa. History This family was created by Levine in 1971.Levine ND (1971) Taxonomy of the Archigregarinorida and Selenidiidae (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) J Euk Microbiol 18 (4) 704–717 Taxonom ... and Selenidioididae. There are seven genera and 74 species recognised in this family. Description Species in this family undergo asexual schizogony. Life cycle The species in the family infect the gastrointestinal tract and are presumably transmitted by the orofaecal route but the details of this mechanism are prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:εὖ, εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and wikt:� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata ( Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. All species are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis ('' Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cryptosporidiosis ('' Cryptosporidium parvum'') * Cyclosporiasis ('' Cyclospora cayetanensis'') * Cystoisosporiasis ('' Cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conoidasida
Conoidasida is a class of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa. The class was defined in 1988 by Levine and contains two subclasses – the coccidia and the gregarines. All members of this class have a complete, hollow, truncated conoid. Gregarines tend to parasitize invertebrates with the mature gamonts being extracellular, the coccidia mostly infect vertebrates and have intracellular gamonts. Description A conoid is found in most species and when present forms complete but truncated cone. Sexual and asexual reproduction are present in life cycle of all species. Each zygote normally forms an oocyst wall within which it undergoes meiosis. This is sometimes followed by mitosis. This process of sporogony produces mobile vermiform infectious sporozoites. Multiple mitotic divisions (schizogony) also occur during merogony of the feeding stages (trophozoites) and during gametogony. Motility Microgametes of some species are flagellated. Locomotion of other gametes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships between phyla, which are contained in larger clades, like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |