|
Vatnaöldur
Vatnaöldur () is the name of a series of craters in the Southern Region (Iceland), Suðurland region of Iceland. They are located in the Highlands of Iceland, north–west of the Veiðivötn and north–east of Landmannalaugar, within the municipality of Rangárþing ytra. It is part of the Geological deformation of Iceland#Eastern volcanic zone, Eastern volcanic zone (EVZ). The craters were formed during a series of eruptions associated with a basaltic dyke intrusion from the volcanic system of Bárðarbunga around the year 877. These eruptions, like those of the neighbouring Veiðivötn, were from about (or ) long volcanic fissures within the area of a lake. The mainly explosive eruptions emitted of tholeiite basalt.G. Larsen, Thor Thordarson: Phreatomagmatism in the Eastern Volcanic Zone; 25 July 2010 There was an associated rhyolite eruption near Torfajökull triggered by the intrusion. The associated tephra layer is called the Settlement layer, and covers more than half of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanic Eruptions In Iceland
This is an incomplete list of volcanic eruptions in Iceland. Please see External links below for databases of Icelandic eruptions which include over 530 events. ''For latest information about the current/ongoing series of eruptions near Grindavik on the Reykjanes peninsula - See 2023–2025 Sundhnúkur eruptions'' Index map of eruptions, fissures, glaciers and notable sites Alphabetic index of eruptions, fissures and notable sites Rome wasn't built in a day, (''Under construction.'') There are about 32 volcanic systems in Iceland. Volcanic system means a volcano-tectonic fissure system and – very often a bigger volcano, a so-called central volcano which in most cases is a stratovolcano and may contain a caldera. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bárðarbunga
Bárðarbunga (, alternative name Veiðivötn), is an active and productive stratovolcano located under Vatnajökull in Vatnajökull National Park which is Iceland's most extensive glacier. The second highest mountain in Iceland, above sea level, Bárðarbunga is also part of the Bárðarbunga-Veiðivötn volcanic system that is approximately long and wide. Bárðarbunga erupted in late August 2014, the eruption style effusive, which is common in Iceland, but had not been seen for a few years. Lava covered the surrounding landscape northwest of the Vatnajökull glacier. Description Bárðarbunga is a subglacial stratovolcano and central volcano under the ice cap of Vatnajökull glacier in the Vatnajökull National Park in Iceland. It is one of the six volcanic systems under Vatnajökull. The central volcano has a rim that rises to about above sea level, making it the second highest mountain in Iceland, being lower than Hvannadalshnjúkur. The caldera is about , u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torfajökull
Torfajökull ( Icelandic for "Torfi's glacier"; ) is a rhyolitic stratovolcano, with a large caldera (central volcano) capped by a glacier of the same name and associated with a complex of subglacial volcanoes. Torfajökull last erupted in 1477 and consists of the largest area of silicic extrusive rocks in Iceland. This is now known to be due to a VEI 5 eruption 55,000 years ago. Geography The volcano is located north of Mýrdalsjökull and south of Þórisvatn Lake, Iceland. To its south-west is the volcano and glacier of Tindfjallajökull and almost directly to its west is the volcano of Hekla. Adjacent to the southern edge of its glacier of Torfajökull it has a peak of but the south-eastern caldera margin also extends to the glacier of Kaldaklofsjökull which is on the western slopes of a peak called Háskerðingur that is high. Laufafell dome at is at the north-western edge of the Torfajökull volcanic system and almost halfway between Hekla and the glacier of Torfajö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Volcanic Zone Of Iceland
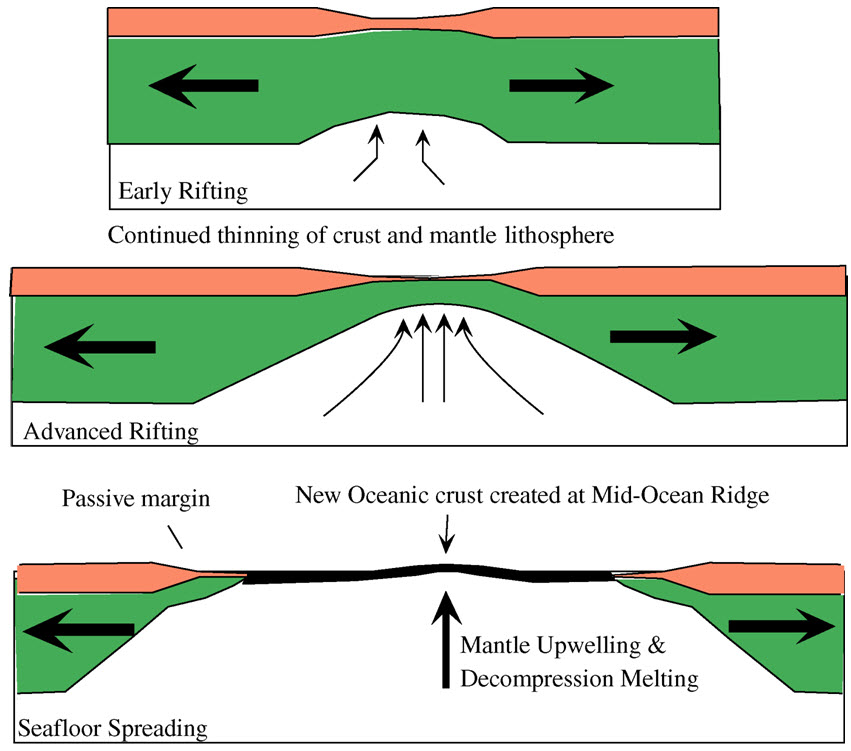
The geological deformation of Iceland is the way that the rocks of the island of Iceland are changing due to tectonic forces. The geological deformation help to explain the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, fissures, and the shape of the island. Iceland is the largest landmass () situated on an oceanic ridge. It is an elevated plateau of the sea floor, situated at the crossing of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Greenland-Iceland-Scotland ridge. It lies along an oceanic divergent plate boundary: the western part of Iceland sits on the North American Plate and the eastern part sits on the Eurasian Plate. The Reykjanes Ridge of the Mid-Atlantic ridge system in this region crosses the island from southwest and connects to the Kolbeinsey Ridge in the northeast. Iceland is geologically young: all rocks there were formed within the last 25 million years. It started forming in the Early Miocene sub-epoch, but the oldest rocks found at the surface of Iceland are from the Middle Miocene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Volcanoes Of Iceland
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri Lanka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haraldur Sigurðsson
Haraldur Sigurðsson or Haraldur Sigurdsson (born May 31, 1939) is an Icelandic volcanologist and geochemist. Education Sigurdsson was born in Stykkishólmur in western Iceland. He studied geology and geochemistry in the United Kingdom, where he obtained a Bachelor of Science (BSc) degree from Queen's University, Belfast, followed by a PhD under the supervision of George Malcolm Brown from Durham University in 1970. Career and research Sigurdsson worked on monitoring and research of the volcanoes of the Caribbean until 1974, when he was appointed professor at the Graduate School of Oceanography, University of Rhode Island. He is best known for his work on the reconstruction of major volcanic eruptions of the past, including the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD in Italy and the consequent destruction of the Roman cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. In 1991, Sigurdsson discovered tektite glass spherules at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K–T boundary) in Haiti, providing pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Iceland
There are too many presumed extinct or now inactive volcanic features to list all of these below, so most monogenetic volcanoes can not be mentioned individually. This list of volcanoes in Iceland only includes major active and dormant volcano, volcanic mountains, of which at least 18 vents have erupted since human settlement of Iceland began around 900 AD. Subsequent to the main list a list is presented that classifies the volcanoes into zones, systems and types. This is in the context that there are several classification systems and many of the volcanoes may have separate shallow magma chambers and a deeper common magma source. Where a major vent is part of a larger volcano this is indicated in the list comment. Since some of these vent eruptions have been very large, disruptive or been regarded in popular culture as a separate volcano they have been included in the list but where this is not the case it is not appropriate to duplicate or create entries. So for minor vent eru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Iceland
The geology of Iceland is unique and of particular interest to geologists. Iceland lies on the divergent boundary between the Eurasian plate and the North American plate. It also lies above a hotspot, the Iceland plume. The plume is believed to have caused the formation of Iceland itself, the island first appearing over the ocean surface about 16 to 18 million years ago. The result is an island characterized by repeated volcanism and geothermal phenomena such as geysers. The eruption of Laki in 1783 caused much devastation and loss of life, leading to a famine that killed about 25% of the island's population and resulted in a drop in global temperatures, as sulfur dioxide was spewed into the Northern Hemisphere. This caused crop failures in Europe and may have caused droughts in India. The eruption has been estimated to have killed over six million people globally. Between 1963 and 1967, the new island of Surtsey was created off the southwest coast by a volcanic eruption. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of Iceland
:''The volcano system in Iceland that started activity on August 17, 2014, and ended on February 27, 2015, is Bárðarbunga.'' :''The volcano in Iceland that erupted in May 2011 is Grímsvötn.'' Iceland experiences frequent volcanic activity, due to its location both on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary, and being over a hotspot. Nearly thirty volcanoes are known to have erupted in the Holocene epoch; these include Eldgjá, source of the largest lava eruption in human history. Some of the various eruptions of lava, gas and ash have been both destructive of property and deadly to life over the years, as well as disruptive to local and European air travel. Volcanic systems and volcanic zones of Iceland Holocene volcanism in Iceland is mostly to be found in the ''Neovolcanic Zone'', comprising the Reykjanes volcanic belt (RVB), the West volcanic zone (WVZ), the Mid-Iceland belt (MIB), the East volcanic zone (EVZ) and the North volcanic zone (NVZ). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism. Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, they remain as tephra unless hot enough to fuse into pyroclastic rock or tuff. When a volcano explodes, it releases a variety of tephra including ash, cinders, and blocks. These layers settle on the land and, over time, sedimentation occurs incorporating these tephra layers into the geologic record. Tephrochronology is a geochronological technique that uses discrete layers of tephra—volcanic ash from a single eruption—to create a chronological framework in which Paleoecology, paleoenvironmental or Archaeology, archaeological records can be placed. Often, when a volcano explodes, biological organisms are killed and their remains are buried within the tephra layer. These fossils are later dated by scientists to determine the age of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matrix (geology), groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent of granite. Its high silica content makes rhyolitic magma extremely viscosity, viscous. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been used extensively for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fissure Vent
A fissure vent, also known as a volcanic fissure, eruption fissure or simply a fissure, is a linear volcanic vent through which lava erupts, usually without any explosive activity. The vent is often a few metres wide and may be many kilometres long. Fissure vents can cause large flood basalts which run first in lava channels and later in lava tubes. After some time, the eruption tends to become focused at one or more spatter cones. Volcanic cones and their craters that are aligned along a fissure form a crater row. Small fissure vents may not be easily discernible from the air, but the crater rows (see Laki) or the canyons (see Eldgjá) built up by some of them are. The dikes that feed fissures reach the surface from depths of a few kilometers and connect them to deeper magma reservoirs, often under volcanic centers. Fissures are usually found in or along rifts and rift zones, such as Iceland and the East African Rift. Fissure vents are often part of the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |