|
Vasily Mishin
Vasily Pavlovich Mishin (; 18 January 1917 – 10 October 2001) was a Russian engineer in the former Soviet Union, and a prominent rocket pioneer, best remembered for the failures in the Soviet space program that took place under his management. Biography Mishin was born in Byvalino in the Bogorodsky Uyezd, and studied mathematics at the Moscow Aviation Institute. Mishin was one of the first Soviet specialists to see Nazi Germany's V-2 facilities at the end of World War II, along with others such as Sergei Korolev, who preceded him as the OKB-1 design bureau head, and Valentin Glushko, who succeeded him. Mishin worked with Korolev as his deputy in the Experimental Design Bureau working on projects such as the development of the first Soviet ICBM as well in the Sputnik and Vostok programs. He became head of Korolev's OKB-1 design bureau and was the Chief Designer after Korolev's death in 1966, during surgery to remove a tumor from Korolev's colon. He inherited the N1 rocket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavlovo-Posadsky District
Pavlovo-Posadsky District () is an administrativeLaw #11/2013-OZ and municipalLaw #41/2005-OZ district (raion), one of the thirty-six in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It is located in the east of the oblast. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town A town is a type of a human settlement, generally larger than a village but smaller than a city. The criteria for distinguishing a town vary globally, often depending on factors such as population size, economic character, administrative stat ... of Pavlovsky Posad. Population: 83,520 ( 2010 Census); The population of Pavlovsky Posad accounts for 76.3% of the district's total population. References Notes Sources * * * {{Use mdy dates, date=March 2013 Districts of Moscow Oblast __NOTOC__ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentin Glushko
Valentin Petrovich Glushko (; ; born 2 September 1908 – 10 January 1989) was a Soviet engineer who was program manager of the Soviet space program from 1974 until 1989. Glushko served as a main designer of rocket engines in the Soviet program during the heights of the Space Race between United States and the Soviet Union, and was the proponent of cybernetics within the space program. Biography Valentin Glushko was born on 2 September 1908 (21 August according to the old calendar) in Odesa to a Ukrainian cossack father and a Russian peasant mother. At the age of fourteen he became interested in aeronautics after reading novels by Jules Verne. He is known to have written a letter to Konstantin Tsiolkovsky in 1923. He studied at an Odessa trade school, where he learned to be a sheet metal worker. After graduation he apprenticed at a hydraulics fitting plant. He was first trained as a fitter, then moved to lathe operator. During his time in Odessa, Glushko performed experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 1
Soyuz 1 (, ''Union 1'') was a crewed spaceflight of the Soviet space program. Launched into orbit on 23 April 1967 carrying cosmonaut colonel Vladimir Komarov, Soyuz 1 was the first crewed flight of the Soyuz spacecraft. The flight was plagued with technical issues, and Komarov was killed when the descent module crashed into the ground due to a parachute failure. This was the first in-flight fatality in the history of spaceflight. The original mission plan was complex, involving a rendezvous with Soyuz 2 and an exchange of crew members before returning to Earth. However, the launch of Soyuz 2 was called off due to thunderstorms. Crew Backup crew Mission parameters * Mass: * Perigee: * Apogee: * Inclination: 50.8° * Period: 88.7 minutes Background Soyuz 1 was the first crewed flight of the first-generation Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft and Soyuz rocket, designed as part of the Soviet lunar program. It was the first Soviet crewed spaceflight in over two years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Kamanin
Nikolai Petrovich Kamanin (; 18 October 1908 – 11 March 1982) was a Soviet Air Force general and a program manager in the Soviet space program. A career aviator, he was awarded the title of Hero of the Soviet Union in 1934 for the rescue of SS ''Chelyuskin'' crew from an improvised airfield on the frozen surface of the Chukchi Sea near Kolyuchin Island. In World War II he successfully commanded an air brigade, air division, and air corps, reaching the rank of Airforce Colonel General and Air Army commander after the war. It was at this time that his son, Arkady Kamanin, became a fighter pilot at the age of 14, the youngest military pilot in world history. From 1960 to 1971, General Kamanin was the program manager of the cosmonaut training in the Soviet space program. He recruited and trained the first generation of cosmonauts, including Yuri Gagarin, Valentina Tereshkova, Gherman Titov and Alexei Leonov. Kamanin was the Soviet Air Force representative to the space program, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
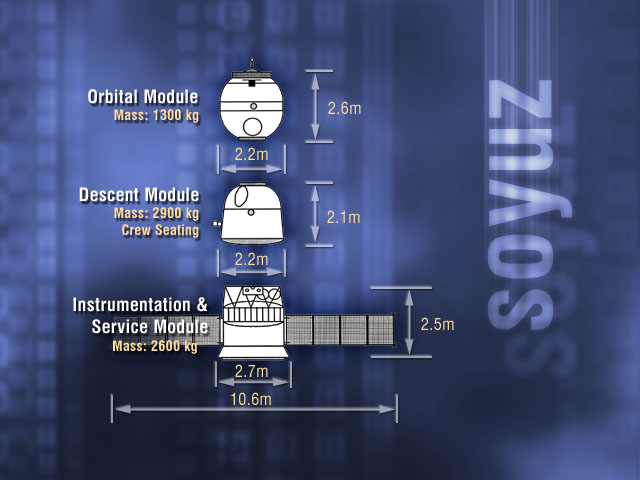
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia (corporation), Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched atop the similarly named Soyuz (rocket family), Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Following the Soviet Union's dissolution, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, continued to develop and utilize the Soyuz. Between the Space Shuttle retirement, Space Shuttle's 2011 retirement and the SpaceX Crew Dragon's 2020 debut, Soyuz was the sole means of crewed transportation to and from the International Space Station, a role it continues to fulfill. The Soyuz design has also influenced other spacecraft, including China's Shenzhou (spacecraft), Shenzhou and Russia's Progress (spacecraft), Progress cargo vehicle. The Soyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexei Leonov
Alexei Arkhipovich Leonov. (30 May 1934 – 11 October 2019) was a Soviet and Russian cosmonaut and aviator, Soviet Air Forces, Air Force major general, writer, and artist. On 18 March 1965, he became the first person to conduct a Extravehicular activity, spacewalk, exiting the Space capsule, capsule during the Voskhod 2 mission for 12 minutes and 9 seconds. He was also selected to be the first Soviet person to Soviet crewed lunar programs, land on the Moon although the project was cancelled. In July 1975, Leonov commanded the Soyuz program, Soyuz capsule in the Apollo–Soyuz mission, which docked in space for two days with an American Apollo command and service module, Apollo capsule. Leonov was twice Hero of the Soviet Union (1965, 1975), a Major General of Aviation (1975), laureate of the USSR State Prize (1981), and a member of the Supreme Council of the United Russia party (2002–2019). Early life and military service Leonov was born on 30 May 1934 in Tisulsky Dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed spaceflight, became the first person to journey into outer space. Travelling on Vostok 1, Gagarin completed one orbit of Earth on 12 April 1961, with his flight taking 108 minutes. By achieving this major milestone for the Soviet Union amidst the Space Race, he became an international celebrity and was awarded many medals and titles, including his country's highest distinction: Hero of the Soviet Union. Hailing from the village of Klushino in the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, Gagarin was a foundryman at a steel plant in Lyubertsy in his youth. He later joined the Soviet Air Forces as a pilot and was stationed at the Luostari/Pechenga (air base), Luostari Air Base, near the Norway–Russia border, Norway–Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chairman of the Council of Ministers (premier) from 1958 to 1964. During his tenure, he stunned the communist world with his denunciation of his predecessor Joseph Stalin and embarked on a campaign of de-Stalinization with his key ally Anastas Mikoyan. Khrushchev sponsored the early Soviet space program and presided over various domestic reforms. After some false starts, and a Cuban Missile Crisis, narrowly avoided nuclear war over Cuba, he conducted successful negotiations with the United States to reduce Cold War tensions. In 1964, the Kremlin circle Nikita Khrushchev#Removal, stripped him of power, replacing him with Leonid Brezhnev as the First Secretary and Alexei Kosygin as the Premier. Khrushchev was born in a village in western Russia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernier Thruster
A vernier thruster is a rocket engine used on a spacecraft or launch vehicle for fine adjustments to the attitude or velocity. Depending on the design of a craft's maneuvering and stability systems, it may simply be a smaller thruster complementing the main propulsion system, or it may complement larger attitude control thrusters, or may be a part of the reaction control system. The name is derived from vernier calipers (named after Pierre Vernier) which have a primary scale for gross measurements, and a secondary scale for fine measurements. Vernier thrusters are used when a heavy spacecraft requires a wide range of different thrust levels for attitude or velocity control, as for maneuvering during docking with other spacecraft. On space vehicles with two sizes of attitude control thrusters, the main ACS (Attitude Control System) thrusters are used for larger movements, while the verniers are reserved for smaller adjustments. Due to their weight and the extra plumbing requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Attitude Control
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle or satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on the current attitude and specification of a desired attitude. Before and during attitude control can be performed, spacecraft attitude determination must be performed, which requires sensors for absolute or relative measurement. The broader integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called ''guidance, navigation and control'', which also involves non-attitude concepts, such as position determination and navigation. Motivation A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Engine Test Facility
A rocket engine test facility is a location where rocket engines may be tested on the ground, under controlled conditions. A ground test program is generally required before the engine is certified for flight. Ground testing is very inexpensive in comparison to the cost of risking an entire mission or the lives of a flight crew. The test conditions available are usually described as ''sea level ambient'' or ''altitude''. Sea level testing is useful for evaluations of start characteristics for rockets launched from the ground. However, sea level testing does not provide a true simulation of the majority of the operating environment of the rocket. Better simulations are provided by altitude test facilities. Sea level tests The facility must restrain the rocket and direct the rocket exhaust safely toward the open atmosphere. Structural integrity, system operations, and sea level thrust can be measured and verified. However, rockets are primarily intended for operations in very thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N1 (rocket)
The N1 (from , "Carrier Rocket"; Cyrillic: Н1) was a super heavy-lift launch vehicle intended to deliver payloads beyond low Earth orbit. The N1 was the Soviet counterpart to the US Saturn V and was intended to enable crewed travel to the Moon and beyond, with studies beginning as early as 1959. Its first stage, Block A, was the most powerful rocket stage ever flown for over 50 years, with the record standing until Starship's first integrated flight test. However, each of the four attempts to launch an N1 failed in flight, with the second attempt resulting in the vehicle crashing back onto its launch pad shortly after liftoff. Adverse characteristics of the large cluster of thirty engines and its complex fuel and oxidizer feeder systems were not revealed earlier in development because static test firings had not been conducted. The N1-L3 version was designed to compete with the United States Apollo program to land a person on the Moon, using a similar lunar orbit rendezvou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |