|
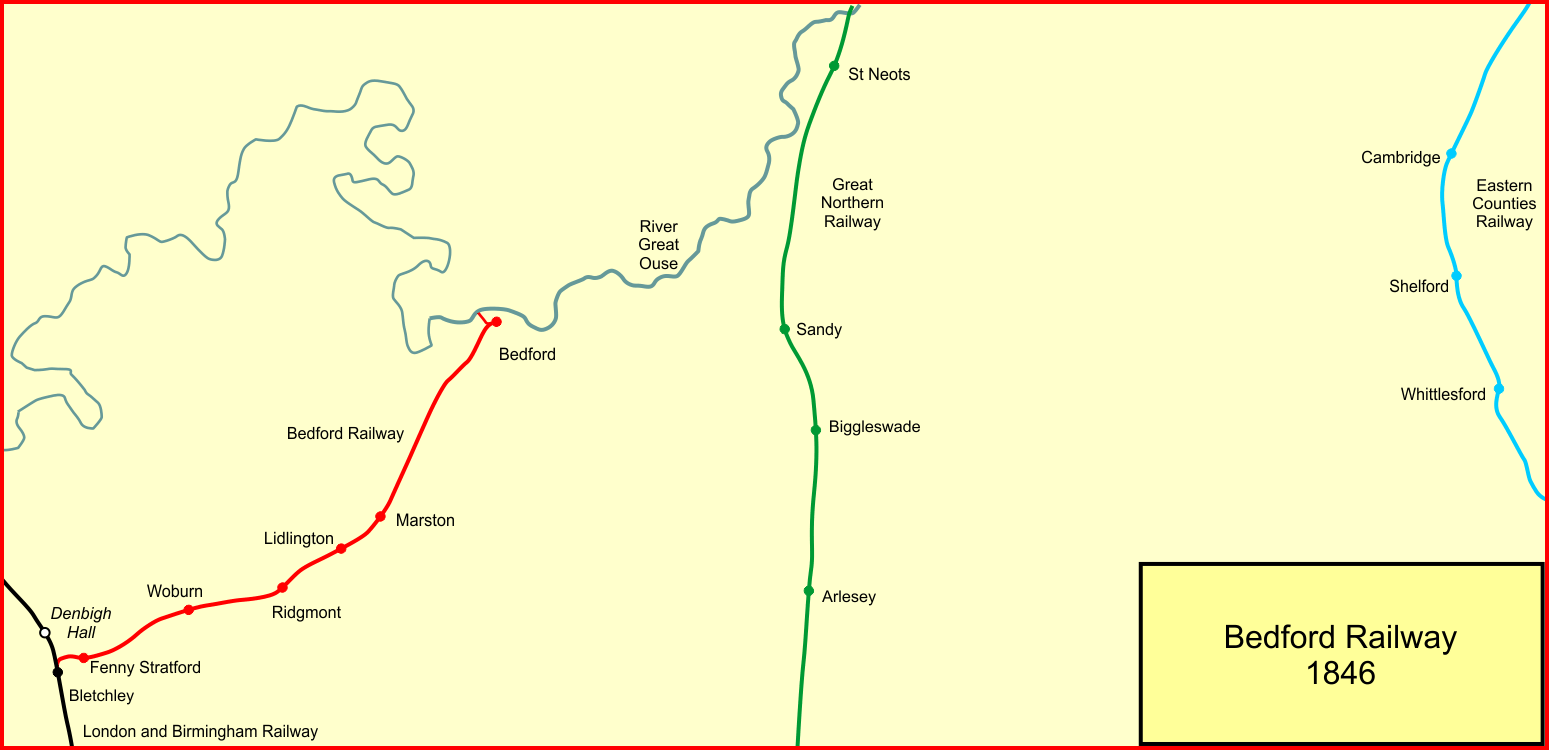
Varsity Line
The Varsity Line was the main railway line that linked the English university cities of Oxford and Cambridge, operated by the London and North Western Railway. In World War II, the line became a strategic route for freight avoiding London, and additional connections were made to nearby lines to improve it, but it was not greatly used for its intended purpose. After the war, the line was again scheduled to be developed as a strategic route, but that scheme was never fully implemented either. Passenger services were withdrawn from most of the line on 1 January 1968, and only the Bletchley–Bedford section remained open for passenger traffic. In 1987, the section between Oxford and Bicester was reopened, followed in 2015 by a connection to the Chiltern Main Line at Bicester, enabling Chiltern Railways to operate an Oxford to London passenger service. There are funded plans for the entire line to be re-established by the mid-2020s, partly on a new route and under a new name Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas: Rapid transit A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid acceleration. It uses passenger railcars operating singly or in multiple unit trains on fixed rails. It operates on separate right-of-way (transportation), rights-of-way from which all other vehicular and foot traffic are excluded (i.e. is fully grade separation, grade-separated from other traffic). The APTA definition also includes the use sophisticated railway signalling, signaling systems, and railway platform height, high platform loading. Originally, the term ''rapid transit'' was used in the 1800s to describe new forms of quick urban public transportation that had a right-of-way separated from street traffic. This set rapid transit apart from horsecars, trams, streetcars, bus, omnibuses, and other forms of public transport. A variant of the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Main Line
The Midland Main Line (MML), sometimes also spelt Midland Mainline, is a major Rail transport in Great Britain, railway line from London to Sheffield in Yorkshire via the East Midlands. It comprises the lines from London's St Pancras railway station, St Pancras station via , / and . Express passenger services on the line are operated by East Midlands Railway (EMR). The line is electrified between St Pancras and Wigston, south of Leicester railway station, Leicester, and the section south of Bedford forms a branch of the northern half of the Thameslink, Thameslink network, with a semi-fast service to Brighton railway station, Brighton and other suburban services. A northern part of the route, between Derby and Chesterfield, also forms part of the Cross Country Route operated by CrossCountry. Tracks from Nottingham to Leeds railway station, Leeds via Barnsley Interchange, Barnsley and Sheffield are shared with Northern Trains, Northern. East Midlands Railway also operates regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolverton Railway Station
Wolverton railway station serves Wolverton, a constituent town of Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, England. The station is on the West Coast Main Line, about 52 miles (84 km) from , between and . The station is one of the seven stations serving the Milton Keynes urban area. The station has four platforms, of which just two (3 and 4) are normally in use. The station serves the northern areas of Milton Keynes (including Wolverton itself, the nearby town of Stony Stratford and the village of New Bradwell) as well as the nearby villages in West Northamptonshire. Facilities There is a ticket office but it is only open on weekday mornings, subject to staff availability. Although categorised as "step-free access category B3", this station is not realistically accessible for passengers with mobility impairments because all but one of the platforms are only reachable by long stairways. History Station building The first station was built for the opening of the London and Bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolverton Railway Works
Wolverton railway works, known locally as Wolverton Works or just The Works, was established in Wolverton (Milton Keynes), Wolverton, Buckinghamshire#Ceremonial county, Buckinghamshire, by the London and Birmingham Railway Company in 1838 at the midpoint of the route from London to Birmingham. The line was developed by Robert Stephenson following the great success of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway line. The Victorian era new towns of Wolverton and New Bradwell were built to house the workers and service the works. The older towns of Stony Stratford and Newport Pagnell grew substantially too, being joined to it by the Wolverton and Stony Stratford Tramway and the Wolverton to Newport Pagnell Line (a branch line), respectively. The trams were also hauled by steam locomotives: the tram cars were certainly the largest ever in the UK and possibly the world. In modern times, Wolverton railway works remains notable as the home of the British Royal Train but otherwise is very mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria History Of The Counties Of England
The Victoria History of the Counties of England, commonly known as the Victoria County History (VCH), is an English history project which began in 1899 with the aim of creating an encyclopaedic history of each of the historic counties of England, and was dedicated to Queen Victoria. In 2012 the project was rededicated to Queen Elizabeth II in celebration of her Diamond Jubilee year. Since 1933 the project has been coordinated by the Institute of Historical Research in the University of London. History The history of the VCH falls into three main phases, defined by different funding regimes: an early phase, 1899–1914, when the project was conceived as a commercial enterprise, and progress was rapid; a second more desultory phase, 1914–1947, when relatively little progress was made; and the third phase beginning in 1947, when, under the auspices of the Institute of Historical Research, a high academic standard was set, and progress has been slow but reasonably steady. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England, running from Dover and London in the southeast, via St Albans to Wroxeter. The road crosses the River Thames at London and was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main Roman roads in Britannia (Roman-governed Great Britain during the Roman Empire). The line of the road was later the southwestern border of the Danelaw with Wessex and Mercia, and Watling Street was numbered as one of the major highways of medieval England. First used by the ancient Britons, mainly between the areas of modern Canterbury and using a natural ford near Westminster, the road was later paved by the Romans. It connected the ports of Dubris (Dover), Rutupiae ( Richborough Castle), Lemanis ( Lympne), and Regulbium (Reculver) in Kent to the Roman bridge over the Thames at Londinium (London). The route continued northwest through Verulamium (St&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stagecoach
A stagecoach (also: stage coach, stage, road coach, ) is a four-wheeled public transport coach used to carry paying passengers and light packages on journeys long enough to need a change of horses. It is strongly sprung and generally drawn by four horses although some versions are drawn by six horses. Commonly used before steam-powered rail transport was available, a stagecoach made long scheduled trips using stage stations or posts where the stagecoach's horses would be replaced by fresh horses. The business of running stagecoaches or the act of journeying in them was known as staging. Some familiar images of the stagecoach are that of a Royal Mail coach passing through a turnpike gate, a Dickensian passenger coach covered in snow pulling up at a coaching inn, a highwayman demanding a coach to "stand and deliver" and a Wells Fargo stagecoach arriving at or leaving an American frontier town. The yard of ale drinking glass is associated by legend with stagecoach driver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denbigh Hall Railway Station
Denbigh Hall railway station was a temporary terminus station on the London and Birmingham Railway in the Denbigh, Milton Keynes, Denbigh area of what is now Milton Keynes in Buckinghamshire, England. It was open for less than six months, between April and September 1838, and was situated near a point where the railway crossed Watling Street, about north of the current location of Bletchley railway station, though Bletchley did not open until after Denbigh Hall had closed. History The route of the London and Birmingham Railway was designed and engineered by Robert Stephenson. Two of the major civil engineering projects on the line were the six-span, high Wolverton railway station#Wolverton viaduct, Wolverton viaduct over the river Great Ouse, and the long Kilsby Tunnel near Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby. Work on this tunnel was prolonged, due to the builders unexpectedly encountering quicksand, and the route was not ready for the scheduled opening of the railway on 9 April 1838 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its Great Central Main Line, London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company was Railways Act 1921, grouped into the London and North Eastern Railway. History New name On assuming its new title, the Great Central Railway had a main line from Manchester London Road Station via , Sheffield Victoria railway station, Sheffield Victoria, and Grimsby Town railway station, Grimsby to . A second line left the line at Penistone and served , and Scunthorpe railway station, Scunthorpe, before rejoining the Grimsby line at . Other lines linked Sheffield to Barnsley (via ) and Doncaster (via Rotherham Central railway station, Rotherham) and also and Wrawby Junction. Branch lines in north Lincolnshire ran to Barton-upon-Humber and New Holland, North Lincolnshire, New Holland and served ironstone quarries in the Scunthorpe ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Counties Railway
The Eastern Counties Railway (ECR) was an English railway company incorporated in 1836 intended to link London with Ipswich via Colchester, and then extend to Norwich and Yarmouth. Construction began in 1837 on the first at the London end. Construction was beset by engineering and other problems, leading to severe financial difficulties. As a result, the project was truncated at Colchester in 1843 but through a series of acquisitions (including the Eastern Union Railway who completed the link between Colchester and Norwich) and opening of other lines, the ECR became the largest of the East Anglian railways. In 1862 ECR was merged with a number of other companies to form the Great Eastern Railway. Opening In 1835, a surveyor called Henry Sayer presented a plan for a new railway from London to York via Cambridge to London solicitors Dimes & Boyman. Together with John Clinton Robertson who was to become the first secretary of the ECR and engineers John Braithwaite it was concl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy, Bedfordshire
Sandy is a town and civil parish in Central Bedfordshire, England. It lies to the east of Bedford, to the south west of Cambridge and north of Central London. It had a population of 12,171 at the 2021 census. The town takes its name from a low range of sandy hills on the eastern side of the town, which form part of the Bedfordshire Greensand Ridge. The main part of the built-up area lies between the hills to the east and the River Ivel to the west. The A1 road skirts the western edge of the town. Sandy railway station is on the Great Northern route between London and Peterborough, with the railway running along the eastern edge of the built-up area. The parish also includes the hamlet of Beeston, which straddles the A1 to the south-west of the town. The headquarters of the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) is at The Lodge at Sandy Warren in the hills to the east of the town, where it has been based since 1961. History The Sandy area has a long histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway (Great Britain)
The Great Northern Railway (GNR) was a British railway company incorporated in 1846 with the object of building a line from London to York. It quickly saw that seizing control of territory was key to development, and it acquired, or took leases of, many local railways, whether actually built or not. In so doing, it overextended itself financially. Nevertheless, it succeeded in reaching into the coalfields of Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire, as well as establishing dominance in Lincolnshire and north London. Bringing coal south to London was dominant, but general agricultural business, and short- and long-distance passenger traffic, were important activities too. Its fast passenger express trains captured the public imagination, and its Chief Mechanical Engineer Nigel Gresley became a celebrity. Anglo-Scottish travel on the East Coast Main Line became commercially important; the GNR controlled the line from London to Doncaster and allied itself with the North Easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |