|
Varli Language
Varli or Warli is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Warli people. The language is usually classified as Marathi, but sometimes as Konkani or Bhil Bhil or Bheel refer to the various Indigenous peoples, indigenous groups inhabiting western India, including parts of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh and are also found in distant places such as Bengal and Tripura. Though they now speak the Bhili .... References Further reading * * External links Varli Phonology and Grammar Sketches (archive.org) Southern Indo-Aryan languages [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the northwest. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India, the third most populous country subdivision in South Asia and the fourth-most populous in the world. The state is divided into 6 divisions and 36 districts. Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra due to its historical significance as a major trading port and its status as India's financial hub, housing key institutions and a diverse economy. Additionally, Mumbai's well-developed infrastructure and cultural diversity make it a suitable administrative center for the state, and the most populous urban are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories of India by area, fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the List of states and union territories of India by population, ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million in 2011. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujarati people, Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state List of Indus Valley civilisation sites#List of Indus Valley sites discovered, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warli
The Warli or ''Varli'' are an indigenous tribe (Adivasi) of western India, living in mountainous as well as coastal areas along the Maharashtra-Gujarat border and surrounding areas. They have their own animistic beliefs, life, customs and traditions, and as a result of acculturation they have adopted many Hindu beliefs. The Warli speak the unwritten Varli language which belongs to the southern zone of the Indo-Aryan languages. Demographics Warlis are found in Jawhar, Vikramgad, Mokhada, Dahanu and Talasari talukas of the northern Palghar district, parts of Nashik and Dhule as well as Navapur taluka of Nandurbar of Maharashtra, Valsad, Dangs, Navsari and Surat districts of Gujarat, and the union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. Waralis have sub castes such as ''Murde varli'' and ''Davar varali''. Warli painting In the book ''The Painted World of the Warlis'' Yashodhara Dalmia claimed that the Warli carry on a tradition stretching back to 2500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranian Languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also known as Indo-Iranic languages or collectively the Aryan languages) constitute the largest branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.7 billion speakers worldwide, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia. Indo-Iranian languages are divided into three major branches: Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and Nuristani languages. The Badeshi language remains unclassified within the Indo-Iranian branch. The largest Indo-Iranian language is the Hindustani language (Hindi-Urdu)."Hindi" L1: 322 million (2011 Indian census), including perhaps 150 million speakers of other languages that reported their language as "Hindi" on the census. L2: 274 million (2016, source unknown). Urdu L1: 67 million (2011 & 2017 censuses), L2: 102 million (1999 Pakistan, source unknown, and 2001 Indian census): ''Ethnologue'' 21. . . The areas with Indo-Iranian languages stretch from Europe ( Romani) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Bangladesh, Northern India, Eastern Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of First language, first-speakers are Hindustani language, Hindi–Urdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Bangladesh, Northern India, Eastern Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of first-speakers are Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi first language: 260.3 million (2001), as second language: 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
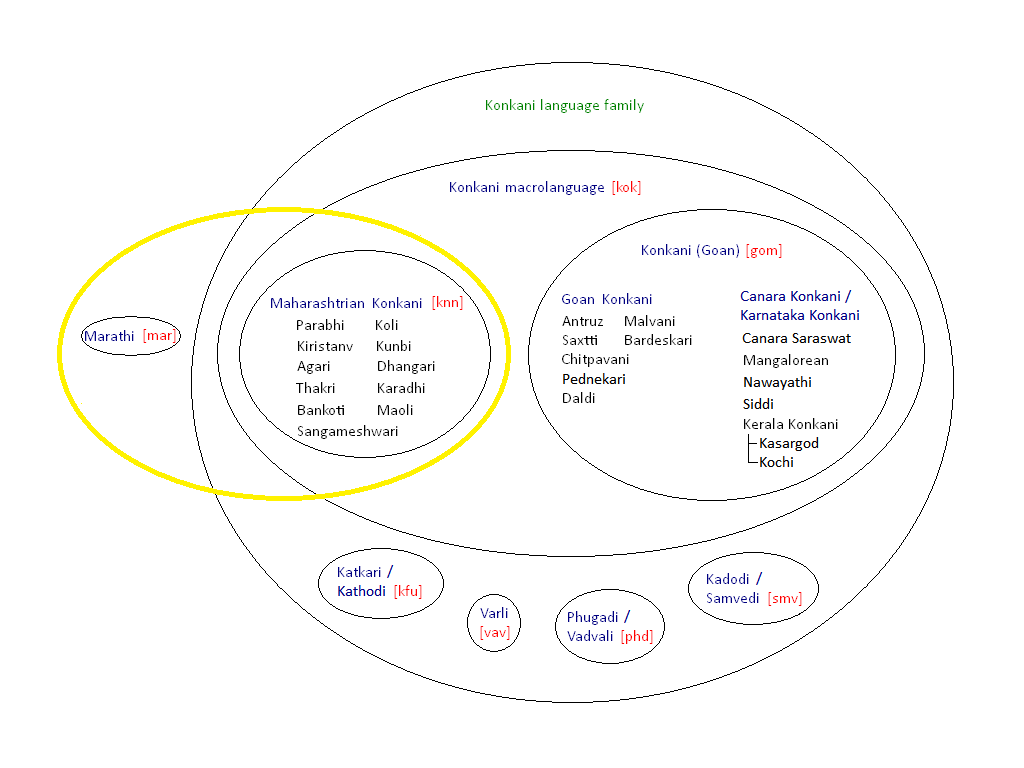
Marathi–Konkani Languages
The Marathi—Konkani languages are the mainland Southern Indo-Aryan languages, spoken in Maharashtra and the Konkan region of India. The other branch of Southern Indo-Aryan languages is called Insular Indic languages, which are spoken in Insular South Asia (predominantly the island countries, Sri Lanka and Maldives). Languages The languages are: Marathi, Konkani, Phudagi, Kadodi (Samavedi), Katkari, Varli and Andh. Several of the Marathi-Konkani languages have been variously claimed to be dialects of both Marathi and Konkani. Maharashtrian Konkani A collection of dialects of Marathi-Konkani languages spoken in the Konkan region is referred to as Maharashtrian Konkani. It is often mistakenly extended to cover Goan Konkani which is an independent language. George Abraham Grierson has referred to this dialect as the ''Konkan Standard of Marathi'' in order to differentiate it from Konkani language. The sub dialects of Konkani gradually merge from standard Marathi into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brāhmī'' script. It is one of the official scripts of India, official scripts of India and Nepal. It was developed in, and was in regular use by, the 8th century CE. It had achieved its modern form by 1000 CE. The Devanāgarī script, composed of 48 primary characters, including 14 vowels and 34 consonants, is the fourth most widely List of writing systems by adoption, adopted writing system in the world, being used for over 120 languages, the most popular of which is Hindi (). The orthography of this script reflects the pronunciation of the language. Unlike the Latin alphabet, the script has no concept of letter case, meaning the script is a unicase, unicameral alphabet. It is written from left to right, has a strong preference for symmetri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Alphabet
The Gujarati script (, transliterated: ) is an abugida for the Gujarati language, Kutchi language, and various other languages. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. It is a variant of the Devanagari script differentiated by the loss of the S''hirorekhā'', the characteristic horizontal line running above the letters and by a number of modifications to some characters. Gujarati numerical digits are also different from their Devanagari counterparts. Origin The Gujarati script () was adapted from the Nagari script to write the Gujarati language. The Gujarati language and script developed in three distinct phases — 10th to 15th century, 15th to 17th century and 17th to 19th century. The first phase is marked by use of Prakrit, Apabramsa and its variants such as Paisaci, Shauraseni, Magadhi and Maharashtri. In second phase, Old Gujarati script was in wide use. The earliest known document in the Old Gujarati script is a handwritten manuscript ''Adi Parv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Language
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Bangladesh, Northern India, Eastern Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and Nepal. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of first-speakers are Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi first language: 260.3 million (2001), as second language: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathi-Konkani Languages
The Marathi—Konkani languages are the mainland Southern Indo-Aryan languages, spoken in Maharashtra and the Konkan region of India. The other branch of Southern Indo-Aryan languages is called Insular Indic languages, which are spoken in Insular South Asia (predominantly the island countries, Sri Lanka and Maldives). Languages The languages are: Marathi, Konkani, Phudagi, Kadodi (Samavedi), Katkari, Varli and Andh. Several of the Marathi-Konkani languages have been variously claimed to be dialects of both Marathi and Konkani. Maharashtrian Konkani A collection of dialects of Marathi-Konkani languages spoken in the Konkan region is referred to as Maharashtrian Konkani. It is often mistakenly extended to cover Goan Konkani which is an independent language. George Abraham Grierson has referred to this dialect as the ''Konkan Standard of Marathi'' in order to differentiate it from Konkani language. The sub dialects of Konkani gradually merge from standard Marathi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |