|
Vancosamine Biosynth Part 1
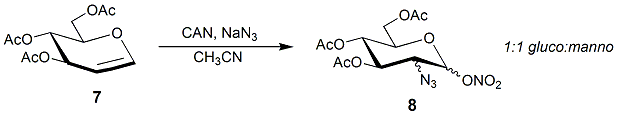
Vancosamines are aminosugars that are a part of vancomycin and other molecules within the vancomycin family of antibiotics. Vancosamine synthesis is encoded by the vancomycin (''vps'') biosynthetic cluster. Epivancosamine, a closely related aminosugar, is encoded by the chloroeremomycin (''cep'') biosynthetic cluster. History Vancosamine was first isolated by Lomakina ''et al'' in 1968. In 1972, Johnson ''et al'' were the first to identify and completely characterize vancosamine. Epivancosamine was subsequently isolated in 1988 by Hunt ''et al'' at Eli Lilly Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of vancosamine and epivancosamine are identical, except in the last step. The enzymes that catalyze the reactions have been designated EvaA-E. A molecule of TDP-D-glucose enters the pathway via conversion to molecule 1 by an oxidoreductase enzyme and then a dehydratase enzyme. In the next step, EvaA dehydrates molecule 1 by deprotonating at 3-C to form and enolate, which then eliminates 2-OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminosugars
In organic chemistry, an amino sugar is a sugar molecule in which a hydroxyl group has been replaced with an amine group. More than 60 amino sugars are known, with one of the most abundant being N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetyl--glucosamine (a 2-amino-2-deoxysugar), which is the main component of chitin. Derivatives of amine containing sugars, such as N-acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid, whose Nitrogen, nitrogens are part of more complex functional groups rather than formally being amines, are also considered amino sugars. Aminoglycosides are a class of antimicrobial compounds that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. These compounds are conjugates of amino sugars and aminocyclitols. Synthesis From glycals Glycals are cyclic enol ether derivatives of monosaccharides, having a double bond between carbon atoms 1 and 2 of the ring. ''N''-functionalized of glycals at the C2 position, combined with glycosidic bond formation at C1 is a common strategy for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancomycin
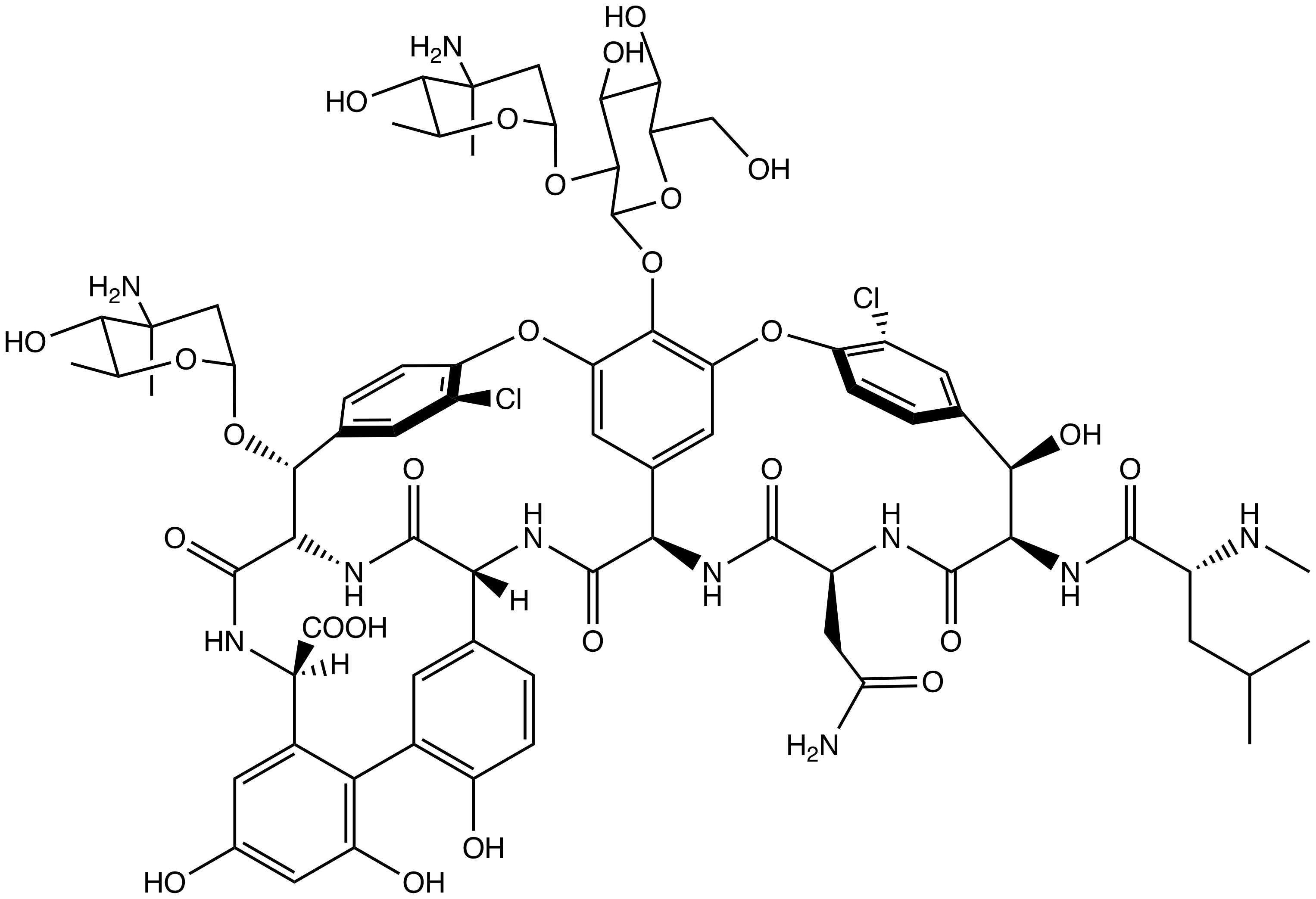
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat certain bacterial infections. It is administered intravenously ( injection into a vein) to treat complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose. Vancomycin is also taken orally (by mouth) to treat ''Clostridioides difficile'' infections. When taken orally, it is poorly absorbed. Common side effects include pain in the area of injection and allergic reactions. Occasionally, hearing loss, low blood pressure, or bone marrow suppression occur. Safety in pregnancy is not clear, but no evidence of harm has been found, and it is likely safe for use when breastfeeding. It is a type of glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall. Vancomycin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroeremomycin
Chloroeremomycin is a member of the glycopeptide family of antibiotics, such as vancomycin. The molecule is a non-ribosomal polypeptide that has been glycosylated. It is composed of seven amino acids and three saccharide units. Although chloroeremomycin has never been used in human medicine, oritavancin, a semi-synthetic derivative of chloroeremomycin, has full FDA approval. Chloroeremomycin is a type of glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall. Chloroeremomycin is naturally produced by ''Amycolatopsis orientalis''. History Chloroeremomycin was discovered by Eli Lilly in the 1980s. In the 1990s, researchers at Eli Lilly developed biphenyl-chloroeremomycin, now known as oritavancin, as a functionalized derivative of chloroeremomycin to combat rising antibacterial resistance to vancomycin. The chloroeremomycin gene cluster was sequenced by van Wageningen ''et al'' in 1998.van Wageningen, A. M. A., Kirkpatrick, P. N., Williams, D. H., Harris, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eli Lilly
Eli Lilly (July 8, 1838 – June 6, 1898) was a Union Army officer, pharmacist, chemist, and businessman who founded Eli Lilly and Company. Lilly enlisted in the Union Army during the American Civil War and recruited a company of men to serve with him in the 18th Independent Battery Indiana Light Artillery. He was later promoted to Major (United States), major and then colonel, and was given command of the 9th Indiana Infantry Regiment. Lilly was captured in September 1864 and held as a prisoner of war until January 1865. After the war, he attempted to run a plantations in the American South, plantation in Mississippi, but it failed and he returned to his pharmacy profession after the death of his first wife. Lilly remarried and worked with business partners in several pharmacies in Indiana and Illinois before opening his own business in 1876 in Indianapolis. Lilly's company manufactured drugs and marketed them on a wholesale basis to pharmacies. Lilly's pharmaceutical f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautomer
In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life. Care should be taken not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Tautomers are distinct chemical species that can be distinguished by their differing atomic connectivities, molecular geometries, and physicochemical and spectroscopic properties, whereas resonance forms are merely alternative Lewis structure (valence bond theory) depictions of a single chemical species, whose true structure is a quantum superposition, essentially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transamination
Transamination is a chemical reaction that transfers an amino group to a ketoacid to form new amino acids.This pathway is responsible for the deamination of most amino acids. This is one of the major degradation pathways which convert essential amino acids to non-essential amino acids (amino acids that can be synthesized de novo by the organism). Transamination in biochemistry is accomplished by enzymes called transaminases or aminotransferases. α-ketoglutarate acts as the predominant amino-group acceptor and produces glutamate as the new amino acid. :Amino acid, Aminoacid + α-ketoglutarate ↔ α-keto acid + Glutamic acid, glutamate Glutamate's amino group, in turn, is transferred to oxaloacetate in a second transamination reaction yielding aspartate. :Glutamic acid, Glutamate + oxaloacetate ↔ α-ketoglutarate + aspartate Mechanism of action Transamination catalyzed by aminotransferase occurs in two stages. In the first step, the α amino group of an amino acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in two optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancosamine Biosynth Part 1
Vancosamines are aminosugars that are a part of vancomycin and other molecules within the vancomycin family of antibiotics. Vancosamine synthesis is encoded by the vancomycin (''vps'') biosynthetic cluster. Epivancosamine, a closely related aminosugar, is encoded by the chloroeremomycin (''cep'') biosynthetic cluster. History Vancosamine was first isolated by Lomakina ''et al'' in 1968. In 1972, Johnson ''et al'' were the first to identify and completely characterize vancosamine. Epivancosamine was subsequently isolated in 1988 by Hunt ''et al'' at Eli Lilly Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of vancosamine and epivancosamine are identical, except in the last step. The enzymes that catalyze the reactions have been designated EvaA-E. A molecule of TDP-D-glucose enters the pathway via conversion to molecule 1 by an oxidoreductase enzyme and then a dehydratase enzyme. In the next step, EvaA dehydrates molecule 1 by deprotonating at 3-C to form and enolate, which then eliminates 2-OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-Adenosyl Methionine
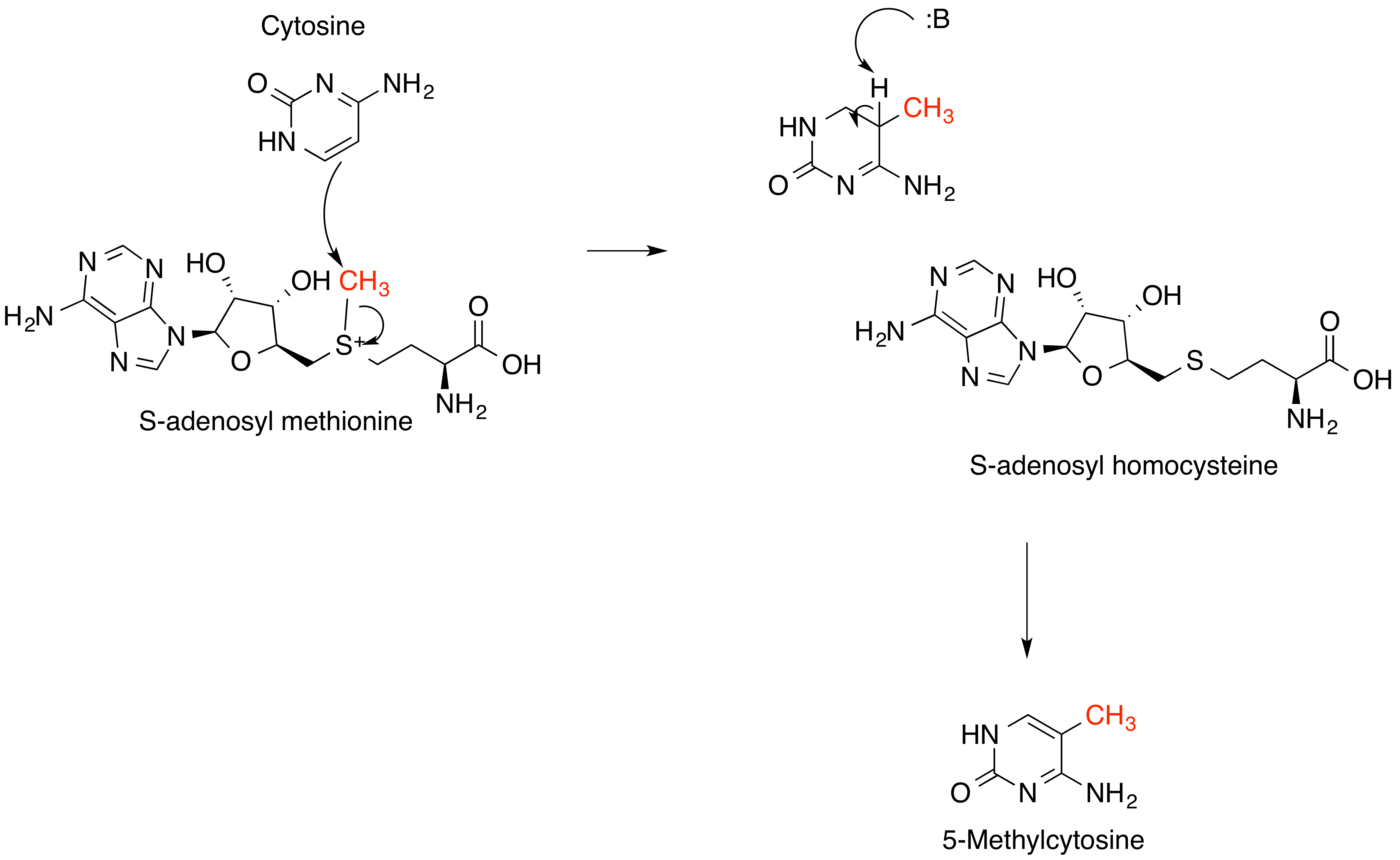
''S''-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952. In bacteria, SAM is bound by the SAM riboswitch, which regulates genes involved in methionine or cysteine biosynthesis. In eukaryotic cells, SAM serves as a regulator of a variety of processes including DNA, tRNA, and rRNA methylation; immune response; amino acid metabolism; transsulfuration; and more. In plants, SAM is crucial to the biosynthesis of ethylene, an important plant hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a Cofactor (biochemistry), coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cell (biology), cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an Redox, oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In cellular metabolism, NAD is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, so it is found in two forms: NAD is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced; with H+, this reaction forms NADH, which can be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate (biochemistry), substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the redox, reduced form, whereas NADP is the redox, oxidized form. NADP is used by all forms of cellular life. NADP is essential for life because it is needed for cellular respiration. NADP differs from NAD+, NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine Moiety (chemistry), moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+, NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancosamine Biosynthesis Part 2
Vancosamines are aminosugars that are a part of vancomycin and other molecules within the vancomycin family of antibiotics. Vancosamine synthesis is encoded by the vancomycin (''vps'') biosynthetic cluster. Epivancosamine, a closely related aminosugar, is encoded by the chloroeremomycin (''cep'') biosynthetic cluster. History Vancosamine was first isolated by Lomakina ''et al'' in 1968. In 1972, Johnson ''et al'' were the first to identify and completely characterize vancosamine. Epivancosamine was subsequently isolated in 1988 by Hunt ''et al'' at Eli Lilly Biosynthesis The biosynthesis of vancosamine and epivancosamine are identical, except in the last step. The enzymes that catalyze the reactions have been designated EvaA-E. A molecule of TDP-D-glucose enters the pathway via conversion to molecule 1 by an oxidoreductase enzyme and then a dehydratase enzyme. In the next step, EvaA dehydrates molecule 1 by deprotonating at 3-C to form and enolate, which then eliminates 2-OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |