|
Valve Events
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin ''valva'', the moving part of a door, in turn from ''volvere'', to turn, roll. The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which swings down to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed up by the flow itself when the flow is moving in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. Modern control valves may regulate pressure or flow downstream and operate on sophisticated automation systems. Valves have many uses, including controlling water for irrigation, ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Valves With Spigots
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dishwasher
A dishwasher is a machine that is used to clean dishware, cookware, and cutlery automatically. Unlike dishwashing, manual dishwashing, which relies on physical scrubbing to remove soiling, the mechanical dishwasher cleans by spraying hot water, typically between , at the dishes, with lower temperatures of water used for delicate items. A mix of water and dishwasher detergent is pumped to one or more rotating sprayers, cleaning the dishes with the cleaning mixture. The mixture is recirculated to save water and energy. Often there is a pre-rinse, which may or may not include detergent, and the water is then drained. This is followed by the main wash with fresh water and detergent. Once the wash is finished, the water is drained; more hot water enters the tub by means of an electromechanical solenoid valve, and the rinse cycle(s) begin. After the rinse process finishes, the water is drained again and the dishes are dried using one of several drying methods. Typically a rinse aid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actuator
An actuator is a machine element, component of a machine that produces force, torque, or Displacement (geometry), displacement, when an electrical, Pneumatics, pneumatic or Hydraulic fluid, hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an actuating system). The effect is usually produced in a controlled way. An actuator translates such an input signal into the required form of mechanical energy. It is a type of transducer. In simple terms, it is a "mover". An actuator requires a control device (which provides control signal) and a source of energy. The control signal is relatively low in energy and may be voltage, electric current, Compressed air, pneumatic, or hydraulic fluid pressure, or even human power. In the electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic sense, it is a form of automation, automation or automatic control. The displacement achieved is commonly linear or rotational, as exemplified by linear motors and rotary motors, respectively. Rotary motion is more natural for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Valve
A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk. Safety valves were first developed for use on steam boilers during the Industrial Revolution. Early boilers operating without them were prone to explosion unless carefully operated. Vacuum safety valves (or combined pressure/vacuum safety valves) are used to prevent a tank from collapsing while it is being emptied, or when cold rinse water is used after hot CIP (clean-in-place) or SIP (sterilization-in-place) procedures. When sizing a vacuum safety valve, the calculation method is not defined in any norm, particularly in the hot CIP / cold water scenario, but some ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering Porting (engine)#Two-stroke porting, ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion piston engine, internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (mechanical Device)
In mechanics, a diaphragm is a sheet of a semi-flexible material anchored at its periphery and most often round in shape. It serves either as a barrier between two chambers, moving slightly up into one chamber or down into the other depending on differences in pressure, or as a device that vibrates when certain frequencies are applied to it. A diaphragm pump uses a diaphragm to pump a fluid. A typical design is to have air on one side constantly vary in pressure, with fluid on the other side. The increase and decrease in volume caused by the action of the diaphragm alternately forces fluid out the chamber and draws more fluid in from its source. The action of the diaphragm is very similar to the action of a plunger with the exception that a diaphragm responds to changes in pressure rather than the mechanical force of the shaft. A diaphragm pressure tank is a tank which has pressurant sealed inside on one side of the diaphragm. It is favored in certain applications due to its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
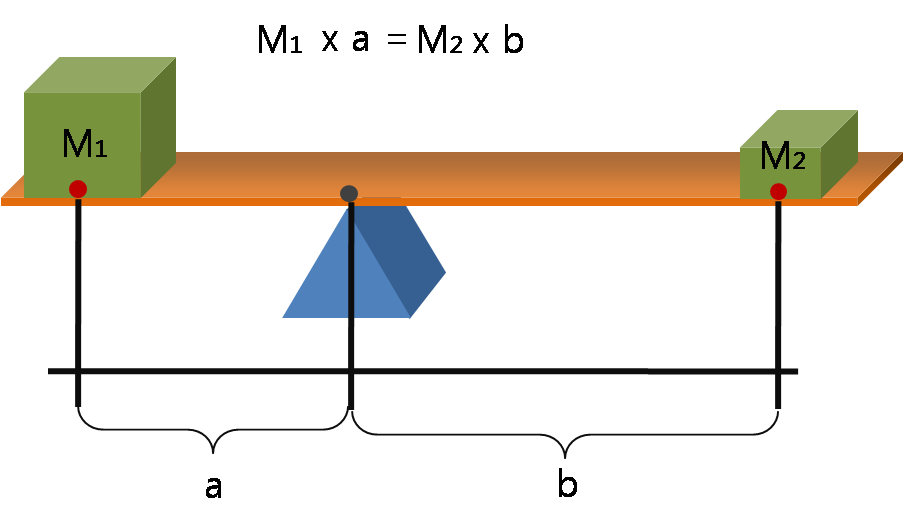
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam (structure), beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '':wikt:fulcrum, fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load, and effort, the lever is divided into Lever#Types of levers, three types. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage, which is mechanical advantage gained in the system, equal to the ratio of the output force to the input force. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English language, English around 1300 from . This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to , itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The word's primary origin is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy. Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of applications such as Water well pump, pumping water from wells, aquarium filtering, pond filtering and Water aeration, aeration, in the car industry for Water cooling, water-cooling and fuel injection, in the energy industry for Pumping (oil well), pumping oil and natural gas or for operating cooling towers and other components of heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. In the medical industry, pumps are used for biochemical processes in developing and manufacturing medicine, and as artificial replacements for body parts, in particular the artificial heart and Penile implant, penile prosthesis. When a pump contains two or more pump mechanisms with fluid being directed to flow through them in series, it is called a ''multi-stage pump''. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chambers Of The Heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |