|
Vallis Vale
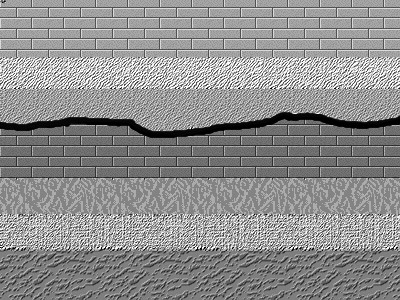
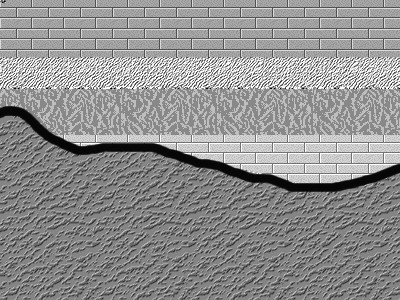
Vallis Vale () is a 23.9 hectare biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest near Great Elm in Somerset, notified in 1952. Vallis Vale is an ancient woodland site and supports an Ash-Wych Elm stand type with a restricted distribution in Britain. Vallis Vale exposes some of Britain's most classic rock outcrops, exhibiting several of the most easily demonstrated examples of angular unconformity available. A nationally important research and educational locality, of great renown for the part it has played in the historical development of geological Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth s ... science. Sources English Nature citation sheet for the site(accessed 10 August 2006) External links English Nature website(SSSI information) Sites of Special Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), that is, square metres (), and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about and one hectare contains about . In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the ''are'' was defined as 100 square metres, or one square decametre, and the hectare (" hecto-" + "are") was thus 100 ''ares'' or km2 ( square metres). When the metric system was further rationalised in 1960, resulting in the International System of Units (), the ''are'' was not included as a recognised unit. The hectare, however, remains as a non-SI unit accepted for use with the SI and whose use is "expected to continue indefinitely". Though the dekare/decare daa () and are (100 m2) are not officially "accepted for use", they are still used in some contexts. Description The hectare (), although not a unit of SI, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Site Of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain, or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland, is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man. SSSI/ASSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation legislation and most other legal nature/geological conservation designations in the United Kingdom are based upon them, including national nature reserve (United Kingdom), national nature reserves, Ramsar Convention, Ramsar sites, Special Protection Areas, and Special Area of Conservation, Special Areas of Conservation. The acronym "SSSI" is often pronounced "triple-S I". Selection and conservation Sites notified for their Biology, biological interest are known as Biological SSSIs (or ASSIs), and those notified for geological or Physical geography, physiographic interest are Geological SSSIs (or ASSIs). Sites may be divided into management units, with some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Elm
Great Elm is a village and civil parish between Mells and Frome in Somerset, England. The parish includes the hamlet of Hapsford. In 2011 the parish had a population of 171. History The name Great Elm was recorded as ''Telma'' in the Domesday Book of 1086, and then as ''Teames'' in 1236 which is a contraction of ''aet elm'' ''at the elm tree''. Little Elm developed into the village of Chantry. At Tedbury Camp southwest of the village a pot of Roman coins was dug up in 1961. After the Norman Conquest the manor was held by the Giffards and later by the Hidges family and then the Stracheys. The parish was part of the hundred of Frome. For many years in the 18th and 19th centuries Great Elm was the site of water powered mills owned by James Fussell IV. The Stracheys owned Rock House for a period early in the 20th century. Hapsford House on Hapsford Hill is a 19th-century country house. The Jackdaws Music Education Trust has been based in the village since 1993. Governan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somerset
Somerset ( , ), Archaism, archaically Somersetshire ( , , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. The largest settlement is the city of Bath, Somerset, Bath, and the county town is Taunton. Somerset is a predominantly rural county, especially to the south and west, with an area of and a population of 965,424. After Bath (101,557), the largest settlements are Weston-super-Mare (82,418), Taunton (60,479), and Yeovil (49,698). Wells, Somerset, Wells (12,000) is a city, the second-smallest by population in England. For Local government in England, local government purposes the county comprises three Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas: Bath and North East Somerset, North Somerset, and Somerset Council, Somerset. Bath and North East Somerset Council is a member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSSI Notification
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain, or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland, is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man. SSSI/ASSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation legislation and most other legal nature/geological conservation designations in the United Kingdom are based upon them, including national nature reserves, Ramsar sites, Special Protection Areas, and Special Areas of Conservation. The acronym "SSSI" is often pronounced "triple-S I". Selection and conservation Sites notified for their biological interest are known as Biological SSSIs (or ASSIs), and those notified for geological or physiographic interest are Geological SSSIs (or ASSIs). Sites may be divided into management units, with some areas including units that are noted for both biological and geological interest. Biological Biological SSSI/ASSIs ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Woodland
In the United Kingdom, ancient woodland is that which has existed continuously since 1600 in England, Wales and Northern Ireland (or 1750 in Scotland). The practice of planting woodland was uncommon before those dates, so a wood present in 1600 is likely to have developed naturally. In most ancient woods, the trees and shrubs have been felled periodically as part of the management cycle. Providing that the area has remained as woodland, the stand is still considered ancient. Since it may have been cut over many times in the past, ancient woodland does not necessarily contain trees that are particularly old. For many animal and plant species, ancient woodland sites provide the sole habitat. Furthermore, for many others, the conditions prevailing on these sites are much more suitable than those on other sites. Ancient woodland in the UK, like rainforest in the tropics, serves as a refuge for rare and endangered species. Consequently, ancient woodlands are frequently described as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in Berwickshire in 1788, both in Scotland. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology. It is integrated with Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface and the processes that have shaped that structure. Geologists study the mineralogical composition of rocks in order to get insight into their history of formation. Geology determines the relative ages of rocks found at a given location; geochemistry (a branch of geology) determines their Geochronology, absolute ages. By combining various petrological, crystallographic, and paleontological tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole. One aspect is to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides evidence for plate tectonics, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sites Of Special Scientific Interest In Somerset
__NOTOC__ This is a list of the Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs) in Somerset, England, United Kingdom. In England the body responsible for designating SSSIs is Natural England, which chooses a site because of its fauna, flora, geological or physiographical features. There are 127 sites designated in this Area of Search, of which 83 have been designated due to their biological interest, 35 due to their geological interest, and 9 for both. Natural England took over the role of designating and managing SSSIs from English Nature in October 2006 when it was formed from the amalgamation of English Nature, parts of the Countryside Agency and the Rural Development Service. Natural England, like its predecessor, uses the 1974–1996 county system, and as such the same approach is followed here, therefore some sites you may expect to find in this list could be in the Avon list. The data in the table is taken from English Nature in the form of citation sheets for each SSSI.''En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sites Of Special Scientific Interest Notified In 1952
Site most often refers to: * Archaeological site * Campsite, a place used for overnight stay in an outdoor area * Construction site * Location, a point or an area on the Earth's surface or elsewhere * Website, a set of related web pages, typically with a common domain name It may also refer to: * Site, a National Register of Historic Places property types, National Register of Historic Places property type * SITE (originally known as ''Sculpture in the Environment''), an American architecture and design firm * Site (mathematics), a category C together with a Grothendieck topology on C * ''The Site'', a 1990s TV series that aired on MSNBC * SITE Intelligence Group, a for-profit organization tracking jihadist and white supremacist organizations * SITE Institute, a terrorism-tracking organization, precursor to the SITE Intelligence Group * Sindh Industrial and Trading Estate, a company in Sindh, Pakistan * SITE Centers, American commercial real estate company * SITE Town, a densely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconformities
An unconformity is a buried erosion surface, erosional or non-depositional surface separating two Rock (geology), rock masses or Stratum, strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the Sedimentary rocks, sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in Berwickshire in 1788, both in Scotland. The rocks above an unconformity Law of superposition, are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents Geologic time, time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |