|
Validly Published Name
In botanical nomenclature, a validly published name is a name that meets the requirements in the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (''ICN'') for valid publication. Valid publication of a name represents the minimum requirements for a botanical name to exist: terms that appear to be names but have not been validly published are referred to in the ''ICN'' as "designations". A validly published name may not satisfy all the requirements to be '' legitimate''. It is also not necessarily the correct name for a particular taxon and rank. Names that are not valid by ICN standards (''nomen invalidum'', ''nom. inval.'') are sometimes in use. This may occur when a taxonomist finds and recognises a taxon and thinks of a name, but delays publishing it in an adequate manner. A common reason to delay valid publication is that a taxonomist intends to write a ''magnum opus'' that provides an overview of the group, rather than a series of small papers. Another re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Available Name
In zoological nomenclature, an available name is a Binomial nomenclature, scientific name for a taxon of animals that has been published after 1757 and conforming to all the mandatory provisions of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature for the establishment of a zoological name. In contrast, an unavailable name is a name that does not conform to the rules of that code and that therefore is not available for use as a valid name for a taxon. Such a name does not fulfil the requirements in Articles 10 through 20 of the Code, or is excluded under Article 1.3. Requirements For a name to be available, in addition to meeting certain criteria for publication, there are a number of general requirements it must fulfill: it must include a description or definition of the taxon, must use only the Latin alphabet, must be formulated within the binomial nomenclature framework, must be newly-proposed (not a redescription under the same name of a taxon previously made available) and orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
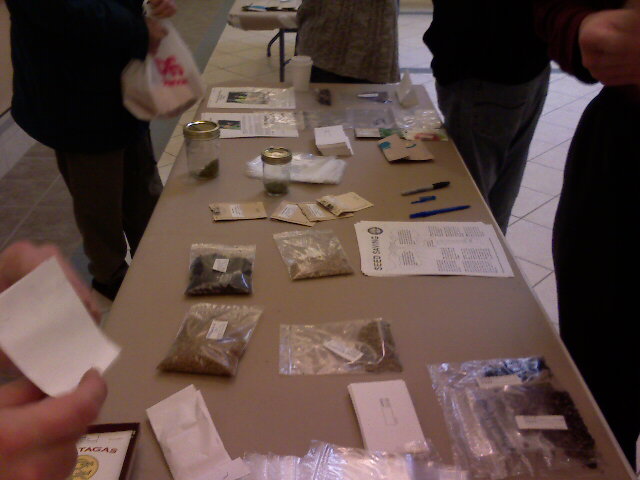
Seed-exchange
Seed swaps are events where gardeners meet to exchange seeds. Swapping can be arranged online or by mail, especially when participants are spread out geographically. Swap meet events, where growers meet and exchange their excess seeds in person, are also growing in popularity. In part this is due to increased interest in organic gardening and heritage or heirloom plant varietals. This reflects gardeners' interest in "unusual or particular varieties of flowers and vegetables", according to Kathy Jentz of ''Washington Gardener Magazine'' (Maryland). Seed swaps also help consumers who, due to increases in the cost of living or cut down on expenditures, wish to grow their own food. Some events are organized as part of an educational effort, where visitors are taught gardening and growing skills and how to preserve an area's cultural heritage and biodiversity. In the United States, the last Saturday of January is "National Seed Swap Day". Cultural and culinary significance Swapping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomen Nudum
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, a ''nomen nudum'' ('naked name'; plural ''nomina nuda'') is a designation which looks exactly like a scientific name of an organism, and may have originally been intended to be one, but it has not been published with an adequate description. This makes it a "bare" or "naked" name, which cannot be accepted as it stands. A largely equivalent but much less frequently used term is ''nomen tantum'' ("name only"). Sometimes, "''nomina nuda''" is erroneously considered a synonym for the term "unavailable names". However, not all unavailable names are ''nomina nuda'' which applies to published names, ''i.e.'' any published name that does not fulfill the requirements of Article 12 (if published before 1931) or Article 13 (if published after 1930). In zoology According to the rules of zoological nomenclature a ''nomen nudum'' is unavailable name, unavailable; the glossary of the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' gives this definition: And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Scientific Naming
This is a list of terms and symbols used in scientific names for organisms, and in describing the names. For proper parts of the names themselves, see List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. Many of the abbreviations are used with or without a full stop, stop. Naming standards and taxonomic organizations and their codes and taxonomies * ICTV – International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses * ICSP – International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes ** formerly the ICSB – International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology ** publishes the ICNP – International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes *** formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) * ICZN – International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature ** publishes ''ICZN'' – the ''International Code of Zoological Nomenclature'' or "ICZN Code" * IBC – International Botanical Congress ** publishes ''ICN'' – the ''International Code of Nome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correct Name (botany)
In botany, the correct name according to the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) is the one and only botanical name that is to be used for a particular taxon, when that taxon has a particular circumscription, position and rank. Determining whether a name is correct is a complex procedure. The name must be validly published, a process which is defined in no less than 16 Articles of the ICN. It must also be " legitimate", which imposes some further requirements. If there are two or more legitimate names for the same taxon (with the same circumscription, position and rank), then the correct name is the one which has priority, i.e. it was published earliest, although names may be conserved if they have been very widely used. Validly published names other than the correct name are called synonyms. Since taxonomists may disagree as to the circumscription, position or rank of a taxon, there can be more than one correct name for a particular plant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homonym (biology)
In biology, a homonym is a name for a taxon that is identical in spelling to another such name, that belongs to a different taxon. The rule in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature is that the first such name to be published is the senior homonym and is to be used (it is "valid name (zoology), valid"); any others are junior homonyms and must be replaced with new names. It is, however, possible that if a senior homonym is archaic, and not in "prevailing usage," it may be declared a ''nomen oblitum'' and rendered unavailable, while the junior homonym is preserved as a ''nomen protectum''. :For example: :*Georges Cuvier, Cuvier proposed the genus ''Echidna'' in 1797 for the echidna, spiny anteater. :*However, Johann Reinhold Forster, Forster had already published the name ''Echidna'' in 1777 for a genus of moray eels. :*Forster's use thus has Priority (biology), priority, with Cuvier's being a junior homonym. :*Johann Karl Wilhelm Illiger, Illiger published the replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Strain
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) or Prokaryotic Code, formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC), governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short history of the Bacteriological CodURL It denotes the rules for naming taxa of bacteria, according to their relative rank. As such it is one of the nomenclature codes of biology. Originally the ''International Code of Botanical Nomenclature'' dealt with bacteria, and this kept references to bacteria until these were eliminated at the 1975 International Botanical Congress. An early Code for the nomenclature of bacteria was approved at the 4th International Congress for Microbiology in 1947, but was later discarded. The latest version to be printed in book form is the 1990 Revision, but the book does not represent the current rules. The 2008 and 2022 Revisions have been published in the '' International Journal of Systematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassobius Gelatinovorus
''Thalassobius'' is a genus of bacteria in the family Rhodobacteraceae.See the NCBI The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is loca ...br>webpage on Thalassobius Data extracted from the References Further reading * Bacteria genera Rhodobacteraceae {{Rhodobacterales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Journal Of Systematic Bacteriology
The ''International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in the field of microbial systematics that was established in 1951. Its scope covers the taxonomy, nomenclature, identification, characterisation, culture preservation, phylogeny, evolution, and biodiversity of all microorganisms, including prokaryotes, yeasts and yeast-like organisms, protozoa and algae. The journal is currently published monthly by the Microbiology Society. An official publication of the International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes (ICSP) and International Union of Microbiological Societies (Bacteriology and Applied Microbiology Division), the journal is the single official international forum for the publication of new species names for prokaryotes. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Code Of Nomenclature Of Prokaryotes
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) or Prokaryotic Code, formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC), governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short history of the Bacteriological CodURL It denotes the rules for naming taxa of bacteria, according to their relative rank. As such it is one of the nomenclature codes of biology. Originally the '' International Code of Botanical Nomenclature'' dealt with bacteria, and this kept references to bacteria until these were eliminated at the 1975 International Botanical Congress. An early Code for the nomenclature of bacteria was approved at the 4th International Congress for Microbiology in 1947, but was later discarded. The latest version to be printed in book form is the 1990 Revision, but the book does not represent the current rules. The 2008 and 2022 Revisions have been published in the '' International Journal of Systemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the HTTP, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Web was invented by English computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee while at CERN in 1989 and opened to the public in 1993. It was conceived as a "universal linked information system". Documents and other media content are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |