|
Vaishnav
Vaishnavism () ), also called Vishnuism, is one of the major Hindu traditions, that considers Vishnu as the sole supreme being leading all other Hindu deities, that is, ''Mahavishnu''. It is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. Its followers are called Vaishnavites or ''Vaishnava''s (), and it includes sub-sects like Krishnaism and Ramanandi Sampradaya, Ramaism, which consider Krishna and Rama as the supreme beings respectively. According to a 2020 estimate by The World Religion Database (WRD), hosted at Boston University’s Institute on Culture, Religion and World Affairs (CURA), Vaishnavism is the largest Hindu sect, constituting about 399 million Hindus. The ancient emergence of Vaishnavism is unclear, and broadly hypothesized as a History of Hinduism, fusion of various regional non-Vedic religions with worship of Vishnu. It is considered a merger of several popular non-Vedic theistic traditions, particularly the Bhagavata cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishnaism
Krishnaism is a term used in scholarly circles to describe large group of independent Hinduism, Hindu traditions—sampradayas related to Vaishnavism—that center on the devotion to Krishna as ''Svayam Bhagavan'', ''Ishvara'', ''Para Brahman'', who is the source of all reality, not simply an avatar of Vishnu. This is its difference from such Vaishnavite groupings as Sri Vaishnavism, Sadh Vaishnavism, Ramanandi, Ramaism, Radha Vallabh Sampradaya, Radhaism, Sitaism etc. There is also a personal Krishnaism, that is devotion to Krishna outside of any tradition and community, as in the case of the saint-poet Meera Bai. Leading scholars do not define Krishnaism as a suborder or offshoot of Vaishnavism, considering it at least a parallel and no less ancient current of Hinduism. The teachings of the ''Bhagavad Gita'' can be considered as the first Krishnaite system of theology. Krishnaism originated in the late centuries BCE from the followers of the heroic Vāsudeva Krishna, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
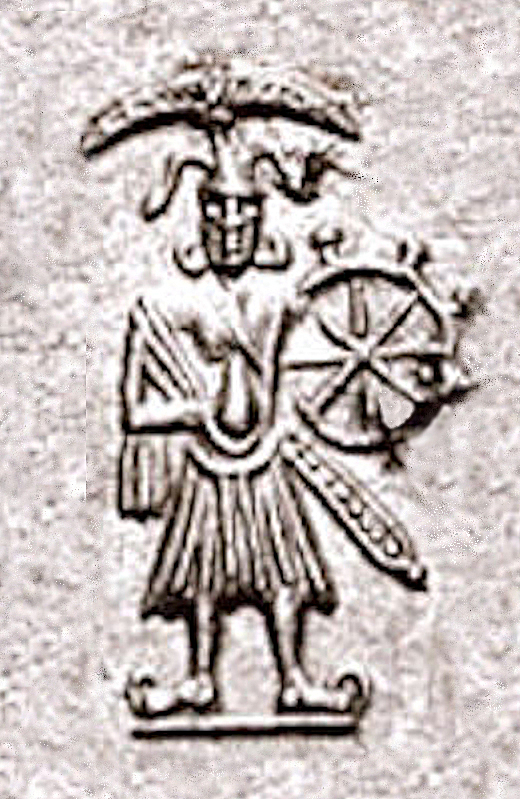
Jagannath
Jagannath (; formerly ) is a Hindu deity worshipped in regional Hindu traditions in India as part of a triad along with (Krishna's) brother Balabhadra, and sister, Subhadra. Jagannath, within Odia Hinduism, is the supreme god, '' Purushottama'', and the '' Para Brahman''. To most Vaishnava Hindus, particularly the Krishnaites, Jagannath is a form of Krishna, sometimes as the avatar of Vishnu. To some Shaiva and Shakta Hindus, he is a symmetry-filled tantric form of Bhairava, a fierce manifestation of Shiva associated with annihilation. Jagannathism ( Odia Vaishnavism) — the particular sector of Jagannath as a major deity — emerged in the Early Middle Ages and later became an independent state regional temple-centered tradition of Krishnaism/Vaishnavism. The idol of Jagannath is a carved and decorated wooden stump with large round eyes and a symmetric face, and the idol has a conspicuous absence of hands or legs. The worship procedures, sacraments and rituals asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is widely revered among Hindu divinities. Krishna's birthday is celebrated every year by Hindus on Krishna Janmashtami according to the lunisolar calendar, lunisolar Hindu calendar, which falls in late August or early September of the Gregorian calendar. The anecdotes and narratives of Krishna's life are generally titled as ''Krishna Līlā''. He is a central figure in the ''Mahabharata'', the ''Bhagavata Purana'', the ''Brahma Vaivarta Purana,'' and the ''Bhagavad Gita'', and is mentioned in many Hindu philosophy, Hindu philosophical, Hindu theology, theological, and Hindu mythology, mythological texts. They portray him in various perspectives: as a god-child, a prankster, a model lover, a divine hero, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu With An Adorer
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation (sattva). Vishnu is known as ''The Preserver'' within the Trimurti, the triple deity of Para Brahman, supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva.Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' () (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme Lord who creates, protects, and transforms the Hindu cosmology, universe. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power (Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the supreme being is with qualities (Saguna Brahman, Saguna), and has definite form, but is limitless, transcendent and unchanging absolute Brahman, and the primal Atma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Denominations
Hindu denominations, ''sampradayas'', traditions, movements, and sects are traditions and sub-traditions within Hinduism centered on one or more gods or goddesses, such as Vishnu, Shiva, Shakti and so on. The term ''sampradaya'' is used for branches with a particular founder-guru with a particular philosophy. Hinduism has no central doctrinal authority and many practising Hindus do not claim to belong to any particular denomination or tradition. Four major traditions are, however, used in scholarly studies: ''Vaishnavism'', ''Shaivism'', ''Shaktism'' and ''Smartism''.Lance Nelson (2007), An Introductory Dictionary of Theology and Religious Studies (Editors: Orlando O. Espín, James B. Nickoloff), Liturgical Press, , pages 562–563 These are sometimes referred to as the denominations of Hinduism, and they differ in the primary deity at the centre of each tradition.SS Kumar (2010), Bhakti — the Yoga of Love, LIT Verlag Münster, , pp. 35–36. A notable feature of Hindu denom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
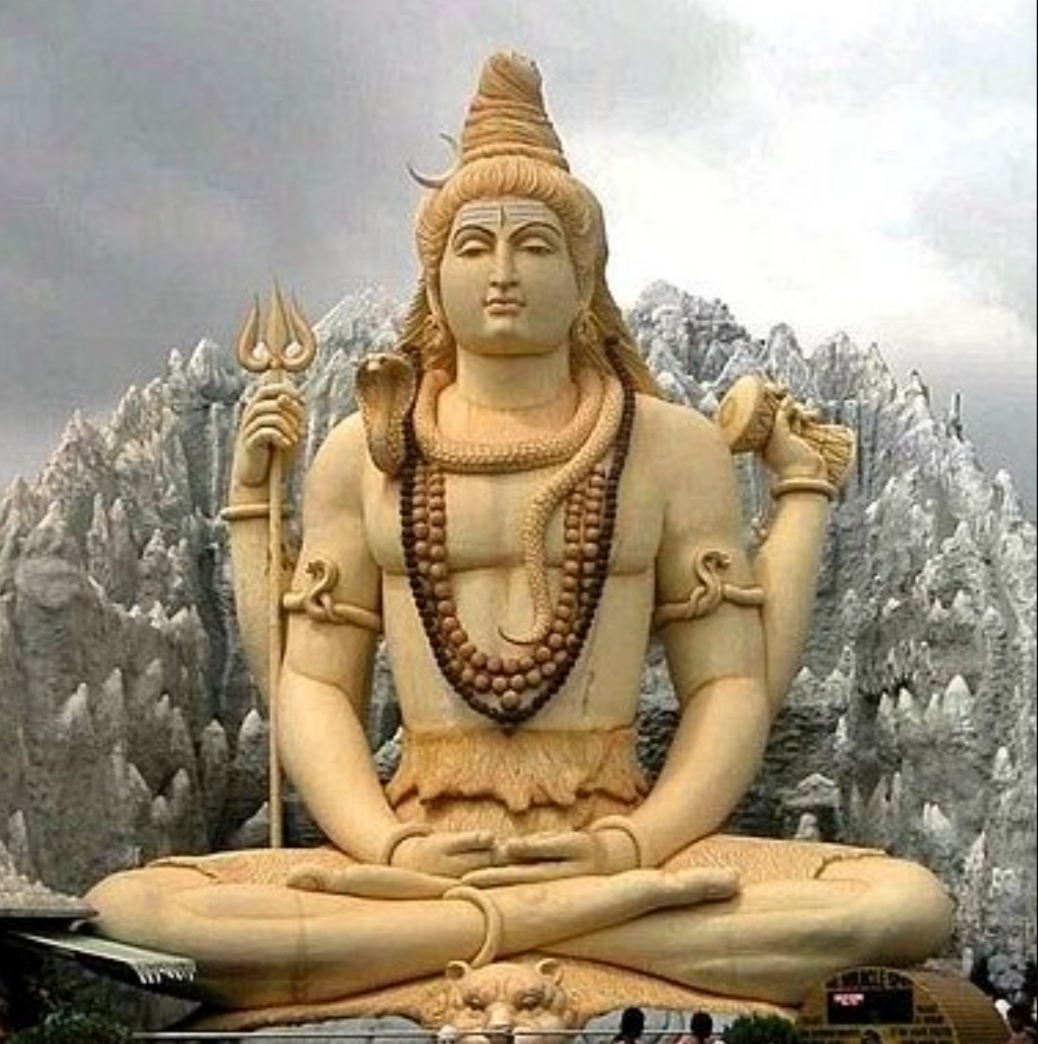
Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in South India, Southern India), Sri Lanka, and Nepal.Keay, p.xxvii. The followers of Shaivism are called Shaivas or Shaivites. According to Chakravarti, Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Aryan religions and traditions, Vedic Rudra, and post-Vedic traditions, accommodating local traditions and Yoga, puja and bhakti. According to Bisschop, early shaivism is rooted in the worship of vedic deity Rudra. The earliest evidence for sectarian Rudra-Shiva worship appears with the Pasupata (early CE), possibly owing to the Origins of Hinduism, Hindu synthesis, when many local traditions were aligned with the Brahmanism, Vedic-Brahmanical fold. The Pāśupata movement rapidly expanded through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramanandi Sampradaya
The Ramanandi (), also known as Ramavats (), is one of the largest sects of Vaishnavas. Out of 52 sub-branches of Vaishnavism, divided into four Vaishnava '' sampradayas'', 36 are held by the Ramanandi. The sect mainly emphasizes the worship of Rama, Sita, Hanuman, and the avatars of Vishnu. They consider Rama and Sita as the Supreme Absolute who are not different from each other. It is considered to have been founded by Ramananda, a 14th-century Vaishnava saint.Schomer and McLeod (1987), The Sants: Studies in a Devotional Tradition of India, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 4-6Selva Raj and William Harman (2007), Dealing with Deities: The Ritual Vow in South Asia, State University of New York Press, , pages 165-166James G Lochtefeld (2002), The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: N-Z, Rosen Publishing, , pages 553-554 History The Ramanandi Sampradaya originates from Rama, who initiated Sita with his six-letter mantra. Sita later initiated her beloved disciple Hanuman wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hinduism
The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its traditions tracing back to prehistoric religions such as those of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation. Hinduism has been called the "oldest religion" in the world, but scholars regard Hinduism as a relatively recent synthesis of various Indian cultures and traditions, with diverse roots and no single founder, which emerged around the beginning of the Common Era. The history of Hinduism is often divided into periods of development. The first period is the pre-Vedic period, which includes the Indus Valley Civilization and local pre-historic religions. Northern India had the Vedic period with the introduction of the historical Vedic religion by the Indo-Aryan migrations, starting somewhere between 1900 BCE and 1400 BCE. The subsequent period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaktism
Shaktism () is a major Hindu denomination in which the God in Hinduism, deity or metaphysics, metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically to be a woman. Shaktism involves a galaxy of goddesses, all regarded as different aspects, manifestations, or personifications of the divine feminine energy called ''Shakti''. It includes various modes of worship, ranging from those focused on the most worshipped Durga, to gracious Parvati, and the fierce Kali. After the decline of Buddhism in India, various Hindu and Buddhist goddesses were combined to form the Mahavidya, a Pantheon (religion), pantheon of ten goddesses. The most common forms of the Mahadevi worshipped in Shaktism include: Durga, Kali, Saraswati, Lakshmi, Parvati, and Tripura Sundari. Also worshipped are the various Gramadevatas across the Indian villages. Shaktism also encompasses various Tantra#Śaiva and Śākta tantra, tantric sub-traditions, including Vidyapitha and Kulamārga. Shaktism emphasizes that intense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origins Of Hinduism
The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its traditions tracing back to prehistoric religions such as those of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilisation. Hinduism has been called the "oldest religion" in the world, but scholars regard Hinduism as a relatively recent synthesis of various Indian cultures and traditions, with diverse roots and no single founder, which emerged around the beginning of the Common Era. The history of Hinduism is often divided into periods of development. The first period is the pre-Vedic period, which includes the Indus Valley Civilization and local pre-historic religions. Northern India had the Vedic period with the introduction of the historical Vedic religion by the Indo-Aryan migrations, starting somewhere between 1900 BCE and 1400 BCE. The subsequent period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vithoba
Vithoba (IAST: ''Viṭhobā''), also known as Vitthala (IAST: ''Viṭṭhala''), and Panduranga (IAST: ''Pāṇḍuraṅga''), is a Hindu deity predominantly worshipped in the Indian states of Maharashtra and Karnataka. He is a form of the Hindu deity Vishnu in his avatar: Krishna. Vithoba is often depicted as a dark young boy, standing arms akimbo on a brick, sometimes accompanied by his consort Rakhumai. Vithoba is the focus of an essentially monotheistic, non-ritualistic bhakti-driven Varkari faith in Maharashtra and the Haridasa sect established in Dvaita Vedanta in Karnataka. Vithoba Temple, Pandharpur is his main temple. Vithoba legends revolve around his devotee Pundalik who is credited for bringing the deity to Pandharpur, and around Vithoba's role as a saviour to the poet-saints of the Varkari faith. The Varkari poet-saints are known for their unique genre of devotional lyric, the abhang, dedicated to Vithoba and composed in Marathi. Other devotional literature dedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |